Exchange-correlation energy 48 54Ч55 157 158
Exchange-correlation potential 154 159 180 189 194 226Ч227 228 229 252
Extremal area of Fermi surface 9 10 28Ч29 38 138 143 394
Extremal effective mass 26
Fast Fourier transforms 497Ч502
FE 196 227Ч231 233 234 236 237 241Ч243 248
Fe in Pd(Fe) 476Ч477
Fe in Rh-Fe 474Ч476
Fe, 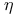 oscillations in 259Ч265 oscillations in 259Ч265
Fe,  oscillations in 259Ч264 oscillations in 259Ч264
Fe, as trace impurity in Cu 508
Fe, band structure of 152 251Ч253
Fe, Fermi surface 251Ч269
Fe, magnetic (spin-flip) excitations in 265Ч269 271Ч277
Fee structures, alkaline earth metals 214Ч215
Fee structures, Brillouin zones 150
Fee structures, transition metals 152 153 167Ч173 193 196 199 204Ч210 252 370Ч371
Fermi energy 5 21 346
Fermi energy in pseudopotential models 295 296 298 338 339Ч340
Fermi energy in rigid-band model 338
Fermi energy of alloys 332Ч333 337Ч338 339Ч340 346
Fermi energy of transition metals 179 181
Fermi liquid theory 57Ч58 83Ч101
Fermi liquid theory, basic formulation 88Ч92
Fermi liquid theory, equilibrium properties 84Ч94
Fermi liquid theory, parameters 89 92Ч94 449 451
Fermi liquid theory, transport properties 94Ч101
Fermi sea, volume of 99 100Ч101
Fermi surface 4Ч7 see "Under "Stress "Angular "Dilation" "Hydrostatic "Pressure" "Tetragonal "Uniaxial
Fermi surface and band structure 197Ч222
Fermi surface and band structure, for alkaline earth metals 214Ч215
Fermi surface and band structure, for bcc metals 210Ч214
Fermi surface and band structure, for fcc metals 204Ч210
Fermi surface and band structure, for Fe 251Ч265
Fermi surface and band structure, for hcp metals 216Ч222
Fermi surface and band structure, for Ni 251Ч254
Fermi surface and band structure, for noble metals 199Ч204
Fermi surface and displaced analogue, interaction with 32-34
Fermi surface and ferromagnetism 225Ч277
Fermi surface of alloys 321Ч326
Fermi surface of alloys, (for strong scattering) 325Ч326
Fermi surface of alloys, definition of 322
Fermi surface of alloys, scattering rate variation over 381Ч386 388Ч391
Fermi surface of alloys, sharpness of 323Ч325
Fermi surface of alloys, size of 321 352Ч353
Fermi surface, chord quantization of 30Ч31
Fermi surface, closed 11Ч13
Fermi surface, effective zones on 23Ч30
Fermi surface, effective zones on, topological changes in 24 36Ч39
Fermi surface, electron sheets on 13Ч14
Fermi surface, extremal areas of 9 10 28Ч29 38 138 143 394
Fermi surface, from many-body point of view 99Ч101
Fermi surface, hole 13Ч14 257 349 353 450 475
Fermi surface, hot spots on 18Ч19
Fermi surface, majority and minority spin sheets of 235-237
Fermi surface, measurement of 101
Fermi surface, open 11Ч19
Fermi surface, plane sections of 7Ч20
Fermi surface, plane sections of and magnetic field direction 34Ч35
Fermi surface, scattering rate variation over for Au 380Ч381
Fermi surface, scattering rate variation over for Cu and Cu alloys 380Ч386
Fermi surface, scattering rate variation over for K and K alloys 388Ч391
Fermi surface, shape of 206 207 211 218 220 234 254Ч258 263 302 304Ч305 310Ч316
Fermi surface, shape of and magnetic anisotropy 34Ч35 237Ч239
Fermi surface, shape of and phase transition 22 29Ч30
Fermi surface, shape of, determination of 8Ч10 12Ч14 50 150Ч151 233Ч234
Fermi surface, sharpness of 88 99Ч100 323Ч325
Fermi surface, size of 10 238 352Ч353
Fermi surface, temperature dependence of area of 243Ч251 265Ч271
Fermi surface, volume of 99Ч101 234
Fermi surface, volume of, for 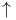 and and 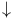 236Ч237 238 236Ч237 238
Fermi surface, volume of, relation to area 292 313
Fermi velocity 292 370
Fermi velocity, for 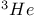 87 87
Fermi wave vector, for 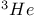 87 87
fermions 4
ferromagnetism see also "Magnetic excitations"
Ferromagnetism and the dHvA effect 231Ч251
Ferromagnetism in 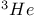 93Ч94 93Ч94
Ferromagnetism in 3d transition metals 225Ч231
Ferromagnetism in dilute alloys 207 473 476Ч477
Ferromagnetism, band structures and Fermi surfaces of Fe and Ni 251Ч265
Field modulation technique 135 395 400Ч401
First sound 97Ч99
Fluid helium hydrostatic pressure technique 279 305
Fluomagnets 276
Forgetting distance 10
Fourier analysis see "Waveshapes in the dHvA effect"
Fourier series inversion 370Ч372 380Ч381
Free-electron gas 34
Free-electron gas, exchange in 52Ч55
Free-electron scaling 292 307
Freeze-out of spin-flip scattering 398 471 472 478
Frequency dependence of first and zero sound 97Ч99
Frequency of dHvA oscillations 9 233
Frequency of dHvA oscillations, high-precision measurements of 479Ч508
Friedel phase shifts 347Ч354 374Ч375 384Ч386
Friedel phase shifts, for noble metal alloys 354 386
Friedel sum 352Ч353 354 356
Friedel sum rule 348 349 353 374
Friedel Ч Anderson model 458 471
Frozen potentials 188 191
g-factors in magnetic impurity systems 405Ч408 414 457Ч458
g-factors in pure metals 438Ч455
g-factors, effective 405Ч407
g-factors, measurement of 136Ч137 396Ч399 403Ч405 439Ч446
g-factors, measurement of, results and interpretation 201 207 446Ч455
g-factors, tensor nature of 438 455
Galvanomagnetic effects 12Ч20 43Ч44 150Ч152 213 221 233
Galvanomagnetic effects,  oscillations in Fe 264 265 oscillations in Fe 264 265
Gaspar potential 158
Gaussian data window 499Ч501
Gaussian distribution of mosaic structure 426Ч431
Gaussian scattering from lattice dis-locations 433Ч434
GD 153 221Ч222
Gd as solute in Au alloy 471 473Ч474
Geometric concepts in the electron theory of metals 3Ч45
Geometric resonance 29
Geometrical scale factor 434Ч435
Giant moments 477
Giant oscillations 43Ч44 142Ч144
Graphical techniques for determining phase 493Ч497
graphite 143 358
Ground state 4 5 47 75 155 226
Gruneisen coefficient 318
H, as interstitial impurity in Cu 356
Hall effect 12 14 27 28 489
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations see also "Relative harmonic amplitudes"
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations and g-factor measurements 136Ч137 397
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations and magnetic impurity effects 459Ч462
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations and magnetic interaction 124 136Ч137 396Ч399 412Ч420 444 460Ч468 506
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations and spin-spiitting zeros 396 397 412 471 473
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations, enhancement by field modulation technique 395 400Ч401
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations, field dependence of 368 506
Harmonic amplitudes of dHvA oscillations, third harmonic 412Ч420 443Ч445 462Ч469 473
Harrison model 20Ч22
Hartree potential 52 95
Hartree Ч Fock approximation 51Ч52 58 229
Hcp structures, Brillouin zones 150
Hcp structures, transition metals 167Ч170 186 193 196Ч197 216Ч222
Helicon 27 135
Hg, 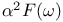 plots 78Ч79 plots 78Ч79
Hg, dHvA amplitude, field dependence 367Ч368
Hg, dHvA amplitude, temperature dependence 83
Ho 471 473 474
Hole Fermi surfaces 13Ч14 257 349 353 450 475
Hole-particle pairs 228Ч229
Hot spots 18Ч19
Hot-electron effects 121
Hybridization, effect on band structure 167 170Ч173 190 199Ч200 210 216Ч217
| Hydrodynamic sound 86Ч87 97
Hydrostatic pressure, Fermi surface dependence on 201 207 278 279 297 299Ч302
Hydrostatic pressure, Fermi surface dependence on, direct experiments 284Ч286
Hydrostatic pressure, lattice strain produced by 280
Hyper-Hartree Ч Fock method 159
Hyperbolic points 36Ч37 39
Hysteresis 129 140 489 490 503
Impurity scattering 39 109 292 328Ч356 362Ч365 368Ч392
Impurity scattering, magnetic 359 397Ч399 405Ч412 456Ч478
Impurity-impurity interactions 471Ч473
IN 121 287 301
In, alloys of 339 359
In, electron-phonon coupling constant 71
In, g-factor 449Ч450
Incoherent states in dilute alloys 332 348
Inelastic scattering 104 106 107 109 111 232 272
Interatomic exchange interactions 477
Interband absorption energy, for noble metals 203 204
Interband transitions 39Ч40
Intercept technique 375Ч378
Interelectronic distance 62 64Ч65 452
Interference and dHvA dephasing effect 420Ч422
Interference of magnetic field in scattering processes 18Ч19
Interference, between electron waves and magnetic breakdown 44
Interference, due to side-lobes from square data-windows 498Ч499
Intraband transitions 39Ч40
Intrinsic band masses 177 182Ч183
inversion 368Ч375
Inversion, basic inversion equations 369Ч370
Inversion, Fourier series inversion 370Ч372
Inversion, Kubic harmonic inversion 372Ч373
Inversion, phase shift inversion 374Ч375
Ion core 67 180
Ionicity scale 181
Ions 50Ч51 55 92
Ir, electronic structure of 204Ч210
Iterative analysis of harmonic content 414Ч415 460
Itinerant-electron ferromagnets 225Ч277 477
Jack surface 211 264
JDOS 198 213
Joint-density of states (JDOS) 198 213
jumps 15 38
Jumps, between hot spots 19
Jumps, due to specular reflection 11
Jungle-gym surface 211 212
K 99 see
K, alloys, conduction electron scattering in 387Ч392
K, alloys, conduction electron scattering in, K(Na) 355 360 387 388 390Ч391
K, alloys, conduction electron scattering in, K(Rb) 355 360 387 388 390Ч391
K, g-factor 136 447 454
K, spin-susceptibility 447 449
Khaikin oscillations 31
Khar'kov style 8
kinetic energy 47 53 54 157Ч187
Kinetic theory of gases 110
KKR method 150 165Ч166 291Ч292 294Ч295 341Ч342 346
Kohn Ч Korringa Ч Rostocker (KKR), method 150 165Ч166 291Ч292 294Ч295 341Ч342 346
Kohn Ч Sham Ч Gaspar potential 58 252 253 255
Kondo effect 457Ч458 471 474 476 478
Kubic Harmonics 345Ч372 372Ч373 387Ч388 390
Kubo Ч Greenwood theory 103 120
L-gap 200 202 203 204
la 209
Landau function 5 6
Landau levels and magnetic impurities 397Ч398 407 408
Landau levels in alloys 323 325 333Ч337 363
Landau levels, spin-splitting of 396 398
Landau theory of a Fermi liquid 5Ч6 88Ч94 95Ч96
Lattice 20Ч21
Lattice, dislocations in 422 423 431Ч435
Lattice, distortion by impurities 323Ч324 333 339 349 352Ч355 387 390
Lattice, strain characterization 279Ч285
LCAO Method 173 241
LD method 158 181 187 188 202 204 207 215 217 218 223
LD-ASA method 179 180 182 189Ч190 191Ч192
LD-KKR method 191
Lens surfaces 211 258 261 266
Lifetimes of quasi-particles 79Ч83 107 323 362Ч392
Lifshitz Ч Kosevich (LK) theory see "LK theory"
Line-shape of NMR resonance 490
Linear recursion technique 504Ч505
LK theory 8Ч10 126Ч127 137 233Ч235 333Ч334 368 393Ч394
LK theory and harmonic content 395 415Ч420
LK theory and harmonic content and g-factor measurement 439Ч441 443Ч445 446 447 448 450
Local density (LD) approximation see "LD" "LD-ASA" "LD-KKR"
Local exchange energy 52Ч54
Local magnetic moments 405Ч407 470Ч473
Local spin density (LDO) approximation see "LSD" "LSD-ASA" "SDF-LSD"
Lomer model 152
Longitudinal sound waves 283 288Ч289 291 318
Lorentz force 16Ч17
LSD theory 194Ч196 222 223 252 255
LSD-ASA theory 194
lu 221
Magnetic breakdown 39Ч44 143 361 396
Magnetic breakdown in ferromagnets 237 263Ч264
Magnetic breakdown in transition metals 211Ч212 217 219
Magnetic excitations in itinerant electron ferromagnets 225 229 232 243Ч251
Magnetic excitations in itinerant electron ferromagnets, spin-flip excitations 265Ч277
Magnetic excitations in itinerant electron ferromagnets, temperature dependence of dHvA phase 250
Magnetic excitations in itinerant electron ferromagnets, temperature dependence of Fermi surface area 248Ч249
Magnetic excitations in itinerant electron ferromagnets, thermodynamic properties at low temperatures 243Ч248
Magnetic field, "interference" of in scattering processes 18Ч19
Magnetic field, high-precision measurements of 489Ч492 503Ч504
Magnetic field, inhomogeneity of 420 436Ч437 486Ч489 507
Magnetic field, relation to, dHvA amplitude 427Ч430 506 see
Magnetic field, relation to, Fermi surface 34Ч35 237Ч239
Magnetic field, relation to, freeze-out of spin-flip scattering 471Ч473
Magnetic field, relation to, g-values 455
Magnetic field, relation to, relative phase shifts (mosaic structure) 427Ч430
Magnetic field, relation to, specific resistance 12Ч13
Magnetic field, requirements of, for high-precision dHvA measurements 482 486Ч492
Magnetic field, stability of 489
Magnetic Gibbs function 128Ч129 132 140
Magnetic impurity scattering 359 397Ч399 405Ч412 456Ч478
Magnetic induction and magnetic interaction 124Ч126 290 396 412
Magnetic induction, orientation of, and Fermi surface in ferromagnets 237Ч239
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) 124Ч145
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and acoustic attenuation 142Ч143
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and domains 128 130Ч135 290
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and g-factor measurement 136Ч137 396Ч397 398Ч399 439Ч441 443 444Ч446
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and magnetoresistance 143Ч145
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and magnetostriction 142
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and magnetothermal oscillations 140Ч141
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and phase instabilities 126Ч131
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and phase measurement 493 494 497 505 506
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect) and waveshape analysis 124 136Ч137 396Ч399 412Ч420 444 460Ч468 506
Magnetic interaction (Shoenberg effect), explanation of 124Ч126
Magnetic interferometer 506
Magnetic pairs 399 471Ч473
Magnetic torque 287 288
Magnetoacoustics 219
Magneton number 252Ч253 255
Magnetoplasma wave 27Ч28 99
Magnetoresistance and magnetic interaction 143Ч145
Magnetoresistance of Au 150
Magnetoresistance of Be 43Ч44 143Ч145
Magnetoresistance of Zr 217
Magnetoresistance, anomalous in dilute alloys 471
Magnetostriction 142 287Ч290 310
Magnetothermal oscillations 140Ч141 358
Magnons 4 93 229 243Ч247
Majority spin 227 235Ч237 252Ч259 269 270 477
Many-body effects 46Ч101
Many-body effects and the interpretation of g-factor results 451Ч452
Mass see "Effective cyclotron mass" "Effective "Electron-photon
Mean free path see "Vector mean free path"
MG 301
Mg, alloys of 339 360
Mg, magnetic breakdown and dHvA effect in 42 43
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



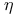 oscillations in
oscillations in  oscillations in
oscillations in  and
and 
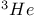
 oscillations in Fe
oscillations in Fe 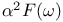 plots
plots