Spin density function see "SDF" "SDF-LSD" "SDF-
Spin polarization 237 241 242 245Ч246 266Ч276
Spin-density fluctuations 93 208 229 230 232 245 474Ч478
Spin-dependent scattering (SDS) due to magnetic impurities 397Ч398 408Ч412 458Ч469 471
Spin-flip excitations 228Ч229 245Ч246 265Ч277
Spin-flip scattering 331 398 471 478
Spin-orbit coupling 159
Spin-orbit coupling and band structure 171 184Ч186 208 209 216
Spin-orbit coupling and constant energy surfaces 153 205Ч206 211 217
Spin-orbit coupling and Fermi surfaces 215 221Ч222 236 253 257 263Ч264
Spin-orbit coupling and Fermi surfaces for alloys 339 340
Spin-orbit coupling and Fermi surfaces in Strain-response models 297Ч300
Spin-orbit coupling and Fermi surfaces, and magnetic anisotropy 237Ч238
Spin-orbit coupling and g-shifts 438 449 452Ч454
Spin-orbit coupling, parameter values 184Ч185 263 264
Spin-splitting 136 221 396 403
Spin-splitting and local magnetic moments 397Ч399 406Ч407 477
Spin-splitting zeros 207 396 397 412 460 464 467 471 473
Spin-splitting zeros and g-factor measurement 403Ч404 439 440 441 447 448 450
Spin-wave stiffness 244 247 272Ч274
Spin-waves 93 99 230 238 243Ч248 267 270Ч277
Spiral waves 27 135
Spontaneous magnetization 127 196
Square-well pseudopotentials 176
Sr, electronic structure of 179 214Ч215
Standard potential 160 181Ч182 204 207 209 212 213 214 215 221 223
Static field technique for dHvA measurement 493 502Ч503
Stoner coefficient of  term 266 267 271 term 266 267 271
Stoner enhancement factor/parameter 64 66Ч67 92 235 248
Stoner enhancement factor/parameter, for  93 93
Stoner enhancement factor/parameter, for transition metals 194Ч196
Stoner excitations 228Ч229 245 265Ч276
Stoner theory 194Ч196 227 228Ч230 248
Stoner-RPA theory 229Ч230
Stress, effect on Fermi surface 278Ч318 see "Dilation" "Hydrostatic "Pressure" "Tetragonal "Uniaxial
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental methods, direct 284Ч286
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental methods, indirect 286Ч291
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental results 297Ч317
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental results, for Cu 304Ч309
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental results, for Pb 297Ч304
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, experimental results, for W 309Ч317
Stress, effect on Fermi surface, theoretical models 291Ч296
Strong scattering and the Fermi surface in alloys 325Ч326
Subtraction Principle 400Ч401 500 505
Sum rule 94
Sum rule, Friedel 348 349 353 374
Superconducting solenoids 486Ч489 493
Superconducting temperature 78
Superconductivity and  77Ч79 84 77Ч79 84
Superconductivity and domain nucleation 130Ч131 133Ч135
Surface conductivity 16
Surface energy 129 130Ч132 133Ч134
Surface impedance 24 31
Surface scattering 122Ч123
Surface tension 134
susceptibility 60Ч61 62Ч67
Susceptibility and the electron-phonon interaction 68 72Ч73
Susceptibility for 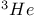 84 86 87 89Ч92 84 86 87 89Ч92
Susceptibility for alkali metals 447 452
Susceptibility tensor 229 232
Susceptibility tensor and spin density fluctuations 229Ч230 232
Symmetry directions 286 424 426Ч431 484
T-matrix 328Ч332 343Ч347 350Ч352 354 365 374
TA 212
Tb 221
TC 179 219
Temperature dependence of boson particle numbers 4
Temperature dependence of, dHvA amplitude 83 250Ч251 366
Temperature dependence of, dHvA phase 250Ч251
Temperature dependence of, Dingle temperature 478
Temperature dependence of, Fermi surface in ferromagnets 243Ч251 265Ч271
Temperature dependence of, impurity scattering in Rh(Fe) 474Ч476
Temperature dependence of, lifetimes 81Ч82
Temperature dependence of, magnetization in ferromagnets 228 230Ч231
Temperature dependence of, magnetoresistance oscillations 143Ч145
Temperature dependence of, magnetothermal oscillations 140Ч141
Temperature dependence of, relaxation time 96Ч97
Temperature dependence of, residual magnetization 271Ч277
Temperature dependence of, resistivity 18 145 475
Temperature dependence of, self-energy 82Ч83 334 364 366Ч367 460
Temperature dependence of, sound wave attenuation and velocity 97Ч99
Temperature dependence of, transport coefficients of pure metals 19
Temperature modulation technique 239
| Temperature of electron gas, measurement of 121
Tetragonal shear 280 281Ч283
Tetragonal shear, response of Fermi surface to 303 307Ч308 317
Tetragonal shear, response of Fermi surface to, for Cu 308
Tetragonal shear, response of Fermi surface to, for Pb 303Ч304
Tetragonal shear, response of Fermi surface to, for W 311Ч315
Th, electronic structure of 209Ч210
thermal conductivity 76 109 112
Thermal mass 338 348
Thermal neutron scattering 231Ч233
Thermodynamic properties of itinerant ferromagnets 243Ч248
Thermoelectric effects 106 117Ч120
Thermoreflectance 202 213
Thin oxide barrier tunnelling 74
Thin plate resonance 31
TI 217
Torque measurements 288 289 303 310 315 367 see
Torquemeter 289
Torsion balance measurements 138Ч139 142 144
Transition metals see also "Individual metals"
Transition metals as solute in dilute alloys 476Ч478
Transition metals, cohesive properties of 186 189Ч193
Transition metals, effects of magnetic impurities in 474Ч477
Transition metals, electronic structure of 149Ч224
Transition metals, g-factors 450 451
Transition metals, strain dependence of Fermi surface 278 295 309Ч317
Transport properties 44 76Ч77 94Ч101 318
Transport properties, path-integral approach to 102Ч123
Transverse sound waves 283 291
tunnelling 39 74Ч76 78 84
Turning points in dHvA waveforms 380 424 484 485
Two-band model 379 476
Two-centre approximation 173
Ultrasonics see "Sound waves"
Ultraviolet photoemission 153 198
Umklapp processes 18Ч19 22 34
Uniaxial tension, Fermi surface dependence on 278 279 303 305Ч312
Uniaxial tension, Fermi surface dependence on, direct experiments 286
Uniaxial tension, lattice strain produced by 280Ч282
V 212 213
Valence difference 353
VBH approximation 252Ч256
Vector mean feee path 109Ч114 123
Vector mean feee path for non-uniform fields 120
Vector mean feee path, path-integral calculation of 114Ч117
Vector mean feee path, physical interpretation 110
Vector projection technique 397 413Ч420 443 444Ч445
Volume of Fermi surface 99Ч101 234 236Ч237 238
von Barth Ч Hedin (vBH) approximation 252-256
W, band structure and optical properties 213Ч214
W, Fermi surface 152 211 212Ч213 257 268
W, Fermi surface, stress dependence of 279 288 289 309Ч318
Wave-function renormalization 76Ч77 100 331Ч332 344 348 366 380Ч381 391
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect 393Ч478 see dHvA
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect and electron spin effects 403Ч405
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect and g-factor measurement 438Ч455
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect and magnetic impurity effects 405Ч412 456Ч478
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect and magnetic interaction effects 412Ч420
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, dephasing effects 395 420Ч437 445
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, dephasing effects, due to field inhomogeneity 436Ч437
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, dephasing effects, due to lattice dislocations 431Ч435
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, dephasing effects, due to mosaic structure 422Ч431 445 508
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, Fourier analysis of 136 399 400Ч402 485 497Ч502 503
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, Fourier analysis of, fast Fourier transform 497Ч502
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, information content in 393Ч399
Waveshapes in the dHvA effect, measurable quantities for 400Ч403
White tin, uniaxial tension measurements on 286
Wigner Ч Seitz cells 55 160 161Ч162 180 188
Wigner Ч Seitz rule 170 177
X-rays, fine structure near absorption edges 154 198 209
X-rays, use in specimen orientation 482Ч483
Y, electronic structure of 175 179 216 217
Yb as solute in Au-based alloys 471 473 474
Yb, electronic structure of 214 221
Young's modulus 290
Zeeman splitting 396 398 403 407
Zero padding in fast Fourier transforms 498
Zero sound 87 94 97Ч99
Zero-crossing points 493Ч494 496 504Ч505
Zn 301 396
Zn, alloys of 361 397 478
Zn, g-factor 439 449 453
Zr 179 217
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 term
term