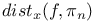|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Conte S.D., de Boor C. Ч Elementary numerical analysis - an algorithmic approach |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Acceleration 95ff. (See also УExtrapolation to the limitФ)
Adams Ч Bashforth method 373Ч376
Adams Ч Bashforth method, predictor form 383
Adams Ч Bashforth method, program 377
Adams Ч Bashforth method, stability of 392Ч394
Adams Ч Moulton method 382Ч388
Adams Ч Moulton method for systems 399
Adams Ч Moulton method, program 387
Adams Ч Moulton method, stability of 394
Adaptive quadrature 328ff.
AitkenТs 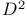 -process 98 196 333 -process 98 196 333
AitkenТs 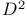 -process, algorithm 98 -process, algorithm 98
AitkenТs algorithm for polynomial interpolation 50
Aliasing 273
Alternation in sign 237
Analytic substitution 294ff 339
Angular frequency 271
Approximation 235ff.
Approximation, Chebyshev 235Ч244
Approximation, least-squares see УLeast-squares approximationФ
Approximation, uniform 235Ч244
Back-substitution 148 156 163
Back-substitution, algorithm 148. 163
Back-substitution, program 164
Backward error analysis 9Ч11 19 160 179Ч181
Base of a number system 1Ч4
Basis for n-vectors 140 141 196
Bessel interpolation 288
BesselТs function, zeros of 124Ч125 127
Binary search 87
Binary system 1Ч3
Binomial coefficient 57
Binomial function 57 373
Binomial theorem 58
Bisection method 74Ч75 8
Bisection method, algorithm 75
Bisection method, program 8 1Ч84
Boundary value problems 406Ч419
Boundary value problems, collocation method for 416Ч419
Boundary value problems, finite difference methods for 406Ч412
Boundary value problems, second-order equation 407ff.
Boundary value problems, shooting methods for 412Ч416
Breakpoints of a piecewise-polynomial function 284 319
Broken-line interpolation 284Ч285
BroydenТs method 222
Central-difference formula 298 407
Chain rule 28
Characteristic equation of a difference equation 350 391
Characteristic equation of a differential equation 348 392 394
Characteristic equation of a matrix 201
Characteristic polynomial of a matrix 202
Chebyshev approximation see УApproximation uniformФ
Chebyshev points 54 242Ч244 3
Chebyshev polynomials 32 239Ч241 255Ч256 293 317 354
Chebyshev polynomials, nested multiplication for 258
CholeskiТs method 160 169
Chopping 8
Compact schemes 160 169
Composite rales for numerical integration 319ff.
Condition 14Ч15
Condition number 175 177
Continuation method 218
Convergence acceleration 95ff. (See also УExtrapolation to the limitФ)
Convergence of a sequence 19ff
Convergence of a vector sequence 191 223
Convergence, geometric 22
Convergence, linear 95
Convergence, order of 102
Convergence, quadratic 100ff
Conversion, binary to decimal 2 6 113
Conversion, decimal to binary 3 6
Corrected trapezoid rale 309 310 321 323
Corrected trapezoid rale, program 324
Corrector formulas 379Ч388
Corrector formulas, Adams Ч Moulton 382Ч384
Corrector formulas, MilneТs 385
CramerТs rale 144 187
Critical point 209
Cubic spline 289 302
Cubic spline, interpolation 289Ч293
Damped NewtonТs method 219Ч220
Damping for convergence encouragement 219
Data fitting 245ff.
Decimal system 1
Deflation 117Ч119 124 203
Deflation for power method 207
Degree of polynomial 29 32
DescartesТ rale of sign 110Ч111 119
Descent direction 213
Determinants 144 185ff 201ff
Diagonally dominant see УMatrixФ
Difference equations 349ff 360 361 390 391 392
Difference equations, initial value 351
Difference equations, linear 349
Difference operators 61
Differential equations 346ff
Differential equations, basic notions 346Ч348
Differential equations, boundary value problems 406Ч419
Differential equations, EulerТs method 356ff.
Differential equations, initial value problems 347 354
Differential equations, linear, with constant coefficients 347Ч349
Differential equations, multistep methods 373ff.
Differential equations, Runge Ч Kutta methods 362ff.
Differential equations, stiff 401ff.
Differential equations, systems of 398Ч401
Differential equations, TaylorТs algorithm 354Ч359
Differential remainder for TaylorТs formula 28
Differentiation, Numerical 290 295Ч303
Differentiation, symbolic 356
Direct methods for solving linear systems 147Ч185 209
Discrete Fourier Transform 278
Discretization error 300 359 361 389
Dist 236
Divided difference 40 41ff 62ff 79 236
Divided difference, table 41ff.
DOUBLE PRECISION 7 11 18
Double precision, accumulation 396
Double precision, accumulation of scalar products 183
Double precision, accumulation, partial 3
DVERK subroutine for differential equations 370Ч372 400Ч401
Eigenvalues 189ff.
Eigenvalues, program for 194
Eigenvectors 189 191 194
Eigenvectors, complete set of 1
EISPACK 422
Equivalence of linear systems 149
Error 12ff.
EulerТs formula 30 269
EulerТs method 356 359Ч362 373 379 395
Exactness of a rale 311
Exponent of a floating-point number 7
Exponential growth 390 391
Extrapolation 54
Extrapolation to the limit 333ff 366 410
Extrapolation to the limit, algorithm 338Ч339 (See also УAitkenТs 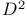 -processФ) -processФ)
Factorization of a matrix 160Ч166 169 187 229
False position method see УRegula falsiФ
Fast Fourier Transform 277Ч284
Fast Fourier transform, program 281Ч282
Finite-difference methods 406Ч411
Fixed point 88
Fixed-point iteration 79 88Ч99 108 223ff 381
Fixed-point iteration for linear systems 224Ч232
Fixed-point iteration for linear systems, algorithm 227
Fixed-point iteration for systems 223Ч234
Fixed-point iteration, algorithm 89
Floating-point arithmetic 7ff.
Forward difference, formula 297
Forward difference, operator D 56ff 373
Forward difference, table 58Ч61
| Forward-shift operator 57
Fourier coefficients 269
Fourier series 269ff.
Fourier transform, discrete 278
Fourier transform, fast 277Ч284
Fraction, binary 5
Fraction, decimal 4
Fractional part of a number 4
Fundamental theorem of algebra 29 202
Gauss elimination 145 149ff.
Gauss elimination for tridiagonal systems 153Ч156
Gauss elimination for tridiagonal systems, program 155
Gauss elimination, algorithm 152Ч153
Gauss elimination, program 164Ч166
Gauss Ч Seidel iteration 230Ч232 234 412
Gauss Ч Seidel iteration, algorithm 230
Gaussian rales for numerical integration 311Ч319 325Ч327
Geometric series 22
GershgorinТs disks 200
Gradient 209
Gram Ч Schmidt algorithm 250
Hermite interpolation 286
Hermite polynomials 256 318
Hessenberg matrix 197
HomerТs method see УNested multiplicationФ
Homogeneous difference equation 350Ч352
Homogeneous differential equation 347Ч348
Homogeneous linear system 135Ч140
Householder reflections 197
Ill-conditioned 181 249
IMSL (International Mathematical and Statistical Library) 370 421
Initial-value problem 347
Initial-value problem, numerical solution of 354Ч405
Inner product see УScalar productФ
Instability 15Ч17 117 376 385 389Ч394 402
Integral part of a number 4
Integral remainder for TaylorТs formula 27
Integration 303Ч345
Integration, composite rales 309 319ff.
Integration, corrected trapezoid rale 309 321
Integration, Gaussian rales 311Ч3 18
Integration, Gaussian rales, program for weights and nodes 316
Integration, midpoint rale 305 32
Integration, rectangle rale 305 320
Integration, Romberg rale 340Ч345
Integration, SimpsonТs rale 307 321 385
Integration, trapezoid rale 305 321
Intermediate-value theorem for continuous functions 25 74 89
Interpolating polynomial 38Ч71 295
Interpolating polynomial, difference formula 55Ч62
Interpolating polynomial, error 51ff.
Interpolating polynomial, Lagrange formula 38 39Ч41
Interpolating polynomial, Newton formula 40 41
Interpolating polynomial, uniqueness of 38
Interpolation by polynomials 31ff.
Interpolation by trigonometric polynomials 275Ч276
Interpolation in a function table 46Ч50 55Ч61
Interpolation, broken-line 284Ч285
Interpolation, global 293
Interpolation, iterated linear 50
Interpolation, linear 39
Interpolation, local 293
Interpolation, optimal 276
Interpolation, osculatory 63 67 68 286
Interpolation, quadratic 120 202 213Ч214 416
Interval arithmetic 18
Inverse interpolation 51
Inverse iteration 193Ч195
Inverse of a matrix 133 166
Inverse of a matrix, approximate 225
Inverse of a matrix, calculation of 166Ч168
Inverse of a matrix, program 167
Iterated linear interpolation 50
Iteration function for fixed-point iteration 88 223
Iteration methods for solving linear systems 144 209 223ff.
Iterative improvement 183Ч184 229
Iterative improvement, algorithm 183
Jacobi iteration 226 229 234
Jacobi polynomials 317
Jacobian (matrix) 214 216 404
Kronecker symbol 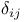 201 201
Lagrange form 38
Lagrange formula for interpolating polynomial 39 295 312
Lagrange polynomials 38 147 259 275 295
Laguerre polynomials 256 318
Least-squares approximation 166 215 247Ч251 259Ч267
Least-squares approximation by polynomials 259ff 302
Least-squares approximation by polynomials, program 263Ч264
Least-squares approximation by trigonometric polynomials 275
Lebesque function 243 244
Legendre polynomials 255 259 260 315
Leibniz formula for divided difference of a product 71
Level line 212
Line search 213Ч214 215
linear combination 134 347
Linear convergence 95 98
Linear independence 140 347 417
Linear operation 294
Linear system 128 136 144
Linear system, numerical solution of 147ff
LINPACK 422
Local discretization error 355 359
Loss of significance 12Ч14 32 116 121 265 300
Lower bound for 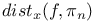 236Ч237 245 236Ч237 245
Lower-triangular 13 1
MaehlyТs method 119
Mantissa of a floating-point number 7
Matrix 129ff
Matrix, addition 133
Matrix, approximate inverse 225
Matrix, bandtype of banded 350
Matrix, conjugate transposed 142
Matrix, dense 145
Matrix, diagonal 131
Matrix, diagonally dominant 184 201 217 225 230 231. 250 289
Matrix, equality 129
Matrix, general properties 128Ч144
Matrix, hermitian 142 206
Matrix, Hessenberg 197
Matrix, Householder reflection 197
Matrix, identity 132
Matrix, inverse 133 166Ч168
Matrix, invertible 132 152 168 178 185 188 229
Matrix, multiplication 130
Matrix, norm 172
Matrix, null 134
Matrix, permutation 143 186
Matrix, positive definite 159 169 231
Matrix, similar 196
Matrix, sparse 145 231
Matrix, square 129 135
Matrix, symmetric 141 198 206
Matrix, trace 146
Matrix, transpose 141
Matrix, triangular 131 147 168 178 186 234
Matrix, triangular factorization 160Ч166
Matrix, tridiagonal 153Ч156 168 188 198 204Ч206 217 230
Matrix, unitary 197
Matrix-updating methods for solving systems of equations 221Ч222
Mean-value theorem for derivatives 26 52 79 92 96 102 298 360
Mean-value theorem for integrals 26. 304 314 320
Midpoint rule 305
Midpoint rule, composite 321 341
MiillerТs method 120ff 202Ч204
MilneТs method 378 385 389
Minimax approximation see УApproximation uniformФ
Minor of a matrix 188
Modified regula falsi 77 78 84Ч86 205
Modified regula falsi, algorithm 77
Modified regula falsi, program 84Ч86
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



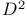 -process
-process