|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Pettifor D.G. — Bonding and structure of molecules and solids |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
 -tin, binding energy curve 47 -tin, binding energy curve 47
8-N rule 4 5 208—214
Actinides, structure 3
Alkali halides, structure 16
Alkali metal clusters 108—111
Alkaline-earths structure 3
Alkaline-earths, atomic energy levels 45
Alkaline-earths, trimers 106
Aluminium phosphide, bond order 205
Aluminium, atomic energy levels 44
Aluminium, band structure 119
Aluminium, band width 33
Aluminium, coordination number dependence of binding energy 132 133
Aluminium, core size 39
Aluminium, density of states 125 126
Aluminium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Aluminium, pair potential 154 159
Aluminium, screening cloud 144
Aluminium, structural stability 161—163
Aluminium, value of 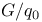 150 150
Angular dependence of bond order 204 205 213
Angular dependence of orbitals 41 42
Antibonding state 54 70 71 87
Antimony 5 9
Arsenic structure see also Structure types
Arsenic structure, relative structural stability 218
Ashcroft empty core pseudopotential see Pseudopotentials
Atomic eigenstates 35—45
Atomic energy level mismatch 53 64 102 191—195
Atomic preparation energy 186
Atomic radii of lanthanides 40
Atomic size 38—40
Axial ratio 9 166 236
Band centre 92
Band energy, definition 215
Band energy, sp band 186
Band gap, hybridization 199
Band gap, Kronig — Penney model 116
Band gap, NFE approximation 118—126
Band gap, octet compounds 57
Band magnetism see Magnetism
Band structure, aluminium 119
Band structure, d band 178
Band structure, definition 114
Band structure, iron 180
Band structure, Kronig — Penney 115
Band structure, p band 177
Band structure, s band 175
Band theory, canonical 178 233
Band theory, general principles 111—118
Band width, Al, Mg, Na 33
Band width, binary alloy 192 193
Band width, transition metals 183 189
Band width, valence 202
Band width, volume dependence 183—184
Band-structure energy, definition 147
Barium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Basis vector 116
Beryllium, atomic energy levels 45
Beryllium, density of states 125 126
Beryllium, dimer 72
Beryllium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Beryllium, structure 3
Bessel function, spherical 108
Bethe lattice 220
Bimodal versus unimodal behaviour see Moments
Binding energy curves of Ge and Si 47
Binding energy curves of hydrogen dimer 62
Binding energy curves of jellium 35
Binding energy curves of sodium 128
Binding energy curves of transition metal aluminides 48
Binding energy within first order perturbation theory 127—129
Binding energy within second-order perturbation theory 148—156
Binding energy, coordination number dependence 132 133 190
Binding energy, jellium 34
Black-body radiation 22—23
Bloch’s theorem 113 116 174
Body-centred cubic structure see also Structure types
Body-centred cubic structure, relative structural stability 161—164 169 215—223 224
Bohr radius xi 37
Bond angle of arsenic and black phosphorus 9
Bond charge density 56
Bond energy of d-valent metals 186 187
Bond energy of s-valent molecules 89 90
Bond energy of sp-valent elements 214
Bond energy, definition 85
Bond integrals, 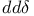 66 178 66 178
Bond integrals, 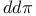 66 178 233 66 178 233
Bond integrals, 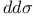 66 178 233 66 178 233
Bond integrals, 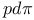 66 233 66 233
Bond integrals, 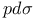 66 233 66 233
Bond integrals, 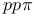 66 67 68 177 214 233 66 67 68 177 214 233
Bond integrals, 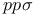 66 67 68 177 214 233 66 67 68 177 214 233
Bond integrals, 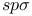 67 68 177 214 67 68 177 214
Bond integrals, 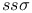 53 65 66 67 68 177 214 53 65 66 67 68 177 214
Bond length within second moment approximation 189
Bond length, first row dimers 69 73
Bond number 191
Bond orbitals 201—204
Bond order of four-atom s-valent molecules 97 98
Bond order of semiconductors 202—205
Bond order potentials within tight binding approximation 239—240
Bond order potentials, Tersoff 206
Bond order, angular dependence of 204
Bond order, definition 96
Bond order, saturated versus unsaturated bonds 97 208—214
Bonding state 54 70 71
Boron core size 39
Boron dimer 69 72
Boron structure 5
Boundary conditions for bottom of band 127 180
Boundary conditions for free atom 36
Boundary conditions for hard-wall 108
Boundary conditions for top of band 180
Boundary conditions, periodic 31
Bravais lattice 1 5 6 7
Brillouin zone, bcc 118
Brillouin zone, contact with Fermi sphere 166
Brillouin zone, fee 118
Brillouin zone, one-dimensional 113
Brillouin zone, simple cubic 117
Bulk modulus of sp-valent metals 130—131
Bulk modulus of transition metals 189
Cadmium atomic energy levels 45
Cadmium density of states 126
Cadmium equilibrium bulk properties 130
Cadmium telluride, bond order 205
Caesium chloride structure see Structure types
Caesium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Calcium atomic energy levels 45
Calcium structure 12
Calcium, density of states 126
Calcium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Calcium, pair potential 165
Canonical band theory 178 233
Carbon band gap 199
Carbon bond order 205
Carbon cohesion 10
Carbon core hardness 219
Carbon core size 39
Carbon dimer 69 71 72—73
Carbon dioxide 18 105
Carbon structure 5 11
Centre of gravity of d band 184
Centre of gravity of eigenspectrum see Moments
Chalcogenides 4 217
Charge density waves 145
Charge transfer 183
chemical potential 137
Chemical scale 234
| Chromium boride structure see Structure types
Chromium, magnetism 230
Clusters see also Molecules
Clusters, alkali metal 108—111
Cobalt, magnetism 230
Cohesive energy of elements 11
Cohesive energy of first-row dimers 69 72—74
Cohesive energy of sp-valent metals 130
Cohesive energy of transition metals 186 189
Cohesive energy, rectangular d band model 187—191
Compressibility sum rule 151
Compton effect 24—25
Conduction band, bottom of 127—129 182—183
Connectivity versus symmetry 9
Coordination polyhedra see Local coordination polyhedra
Copper bromide, band gap 57
Copper gold (CuAu) structure see Structure types
Copper, atomic energy levels 45
Copper, density of states 169
Copper, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Core contraction 40
Core radius of lanthanides 40
Core radius of sp-valent elements 38—40
Core radius, anomalous behaviour 73 81
Core radius, Ashcroft 130 183
Core radius, Zunger 39
Core-orthogonality constraints 122—124 186
Correlation diagram see Walsh diagram
Correlation energy 34
Covalency, degree of 57
covalent bond 50—57
Crystal field term 52 174
Crystal system 5 7
d band see also Band structure Band
D band, band parameters 183
D band, centre of gravity 184
D band, volume dependence 182
D bond energy see Bond energy
de Broglie wavelength 25
Degeneracy, lifting of 42 97 98 117—118
Degree of covalency 57
Degree of ionicity 57
Degree of normalized hardness and exceptions to 8-N rule 213
Degree of normalized hardness for s-valent molecules 85—91
Degree of normalized hardness, carbon versus silicon 81
Degree of normalized hardness, definition 79
Degree of normalized hardness, influence on structural stability 81 97 212
Delta function 138 203
Density functional theory 46
Density of states of free-electron gas 32 33
Density of states of s-valent elements 216
Density of states of sp-valent elements 216
Density of states of sp-valent metals 125 126
Density of states of transition metals 181
Diamond cubic structure see also Structure type
Diamond cubic structure, relative structural stability 215—223
Diamond hexagonal structure, relative structural stability 215—23
Diatomic molecule see Molecules
Dielectric constant, definition 139
Dielectric constant, poles of inverse 157
Dielectric constant, Thomas — Fermi approximation 139
dispersion relation 29
Dissociation of dimers 60—66
Double-counting 147 186
Effective charge 183
Effective coordination number 83—84
effective mass 183
Electron affinity 59
Electron diffraction 25—26
Electron phases 166 168—171
Electron spin 30
Electronegativity, Mulliken 59 60
Electronegativity, Pauling 59 60
Electronegativity, Philipps and Van Vechten 57
Electronic heat capacity 31 46 180 182
Electronic structure see Energy levels
Electrostatic energy for hydrogen dimer 64 65
Electrostatic energy for sp-valent metals 128—129
Embedded atom potential 131—134
Embedding function 131 132
Energy gap see Band gap
Energy level crossing, of sp dimers 71
Energy levels of 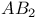 trimer 105 106 trimer 105 106
Energy levels of 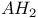 trimer 101 102 trimer 101 102
Energy levels of carbon dimer 71
Energy levels of first row dimers 72
Energy levels of hydrogen atom 42
Energy levels of jellium cluster 109 110
Energy levels of s-valent molecules 53 54 86 87 99
Energy levels of sd-valent atoms 44 45
Energy levels of silicon dimer 71
Energy levels of sp-valent atoms 43 44
Energy levels of sp-valent dimers 70 71
Energy-wave number characteristic 148
Equipartition of energy 22
Europium 3 40
Exchange energy 34
Exchange field 227
Exchange integral see Stoner exchange integral
Exchange-correlation energy for free-electron gas 34
Exchange-correlation energy for hydrogen dimer 64 65
Exchange-correlation enhancement factor 142
Exchange-correlation hole 34 35 46
Exchange-correlation potential 46
Exclusion principle see Pauli’s exclusion principle
Face-centred cubic structure see also Structure types
Face-centred cubic structure, relative structural stability 161—164 169 215—223 224
Fermi energy definition 33
Fermi energy variation across, 4d metals 185
Fermi energy, Fermi sphere, contact with Brillouin zone 166
Fermi surface, definition 120
Fermi surface, spanning of 145
Fermi temperature 33
Fermi wave vector, definition 32
Fluorine dimer energy levels 73
Fluorine dimer LDA predictions 69
Fourier analysis 26
Fourier component of potential, definition 119
Fourth moment see Moments
Free-electron gas, energy of 31—5
Free-electron gas, response function of 142
Friedel oscillations 144 153 166
Gallium arsenide, band gap 57
Gallium arsenide, bond order 205
Gallium, atomic energy levels 44
Gallium, core size 39
Gallium, density of states 125 126
Gallium, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Gallium, structural stability 164
Gallium, value of 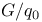 150 150
Gedanken experiment 27—28
Germanium, band gap 57 199
Germanium, binding energy curve 47
Germanium, bond order 205
Germanium, structure 4 5 219
Gold, atomic energy levels 45
Gold, equilibrium bulk properties 130
Graphite structure see also Structure types
Graphite structure, relative structural stability 215—223
Ground-state energy 46
Hall coefficient, positive 120
Halogens 4 217
Hamiltonian matrix 86 91
Hamiltonian matrix elements for s-valent dimer 52
Hamiltonian matrix elements with respect to hybrid orbitals 75
Hamiltonian operator 52
Hard-core ionic model 232—3
Hard-core potential 80
Hard-core radius 79
Hardness of potentials 79
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -tin, binding energy curve
-tin, binding energy curve 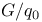
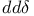
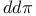
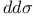
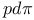
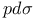
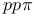
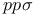
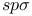
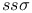
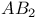 trimer
trimer 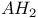 trimer
trimer