|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Oden J.T. Ч Finite Elements: An Introduction (Vol. 1) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
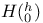 11 16 11 16
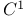 basis functions 233Ч237 basis functions 233Ч237
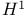 55Ч56 43 147 223Ч224 244 55Ч56 43 147 223Ч224 244
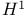 norm 57 norm 57
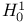 7Ч11 16 20 23 56Ч58 60 241 7Ч11 16 20 23 56Ч58 60 241
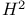 231 231
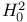 235Ч236 235Ч236
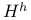 58 224 232 235 58 224 232 235
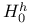 16 23 39 16 23 39
A-posteriori estimates 36
A-priori estimates 36
Accuracy, of finite element approximation 36Ч39 189 197 see УErrorsФ
Admissible functions see УTest functionФ
Admissible functions, for one-dimensional problems 7
Admissible functions, for three-dimensional problems 223
Admissible functions, for two-dimensional problems 57 147
Admissible functions, fourth-order problRems 231Ч232
Approximation, best Galerkin 14Ч15
Approximation, interpretation of 31Ч36
Approximation, of systems 241
Approximation, of three-dimensional problems 224
Approximation, of time-dependent problems 249
Approximation, of two-dimensional problems 162 165
Approximation, of two-point problems by finite elements 73Ч76
Area coordinates 201Ч205
Area coordinates, and nonlinear maps 202
Area coordinates, definition 201
Backward difference scheme 251
Banded matrix 26
Banded matrix, elimination of 118Ч121
Banded matrix, storage of 118Ч121 209
Bandwidth, definition of 119
Basis functions, 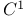 -type 232 234 236Ч237 -type 232 234 236Ч237
Basis functions, for Galerkin's method 11Ч15 59
Basis functions, for model two-point problem 15Ч23
Basis functions, global 33 67 69 157 234
Basis functions, Hermite 233Ч237
Basis functions, Lagrange polynomial 67 195 204
Basis functions, on rectangles 159 236Ч237
Basis functions, on triangles 154 157 237
Basis functions, piecewise-constant 22
Basis functions, piecewise-linear 17 20 25 30 38 67Ч68 85 154 157
Basis functions, piecewise-polynomial 16
Basis functions, piecewise-quadratic 23
Beam bending 238Ч239
Bicubic rectangle 237
Biharmonic equation 235Ч236 239
Body forces 44
Boundaries, parametric definition of 141Ч142 193
Boundaries, smoothness of 132
Boundary condition data, input of 104 212Ч223
Boundary conditions, calculation and flowchart of 216
Boundary conditions, clamped plate 235
Boundary conditions, compatability of 229Ч230
Boundary conditions, convective 216
Boundary conditions, essential 43 49 55Ч56 60 81 138 140 223 231Ч232
Boundary conditions, for biharmonic equation 235
Boundary conditions, for fourth-order problems 229Ч230
Boundary conditions, for general two-point problems 42 79Ч84
Boundary conditions, in CODE2 218Ч229
Boundary conditions, inCODEl 107Ч109
Boundary conditions, natural (definition) 49 138 146 231Ч232
Boundary integrals, computation of 191Ч192
Boundary, restriction of shape functions 191
Brick element 226
Capacitance matrix see УMass matrixФ
Chain rule, in area coordinates 205
Chain rule, in shape function transformation 189
Charge 4
Classical boundary-value problem 3 8 40Ч52 62 224 228Ч229 235 240
Compatability condition for, data in two-point problems 83 141 228Ч230
Complete polynomials, integration error for 160Ч161 205Ч208
Completeness, and rate of convergence 197Ч198
Conservation principle 43 47 49Ч51 83 136 138 141 246Ч247
Conservation principle, of electric flux 44
Conservation principle, of energy 44
Conservation principle, of linear momentum 44 242Ч243 247
Conservation principle, of mass 44
Constitutive equation 43 44 46 49 136 140 243 247
Constitutive equation, Stokes' law 44
Convergence in an 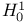 sense 11 sense 11
Convergence rates 36Ч37 189 197 see УErrorsФ
Coordinate function, derivatives 189 201
Coulomb's law 44
Cube element 225Ч227
Cubic triangle 240
Curvilinear coordinates, from master element map 176Ч177
Darcy's law 44
Data, management of 90
Data, of a boundary-value problem 1 140 229Ч230
Deformations, calculation of 127Ч130
Deformations, of an elastic bar 44
Degrees-of-freedom 12 15 59 235Ч237
Degrees-of-freedom, definition of 12
Degrees-of-freedom, for beam element 238
Degrees-of-freedom, for fourth-order problems 235Ч237
Degrees-of-freedom, symbolism 236Ч237
Derivatives, directional 133
Derivatives, of element transformation 183
Diffusion 247
Dirac delta 2 4 46 48 84 144 167 232
Divergence theorem 136 137 143 145
Divergence, definition of 134
Elastic modulus 246
Elasticity 242 244 246Ч247
Electrostatics 44
Element calculations, flow chart of 30
Element calculations, for ODE system 242
Element calculations, general 187Ч194
Element calculations, transformation to master element 177
Element calculations, two-dimensional 175Ч121
Element flux vector 166
Element matrices, assembly of 91
Element matrices, calculation of 26 74Ч76 91 187 190
Element matrices, for time dependent problems 251
Element transformations, in three dimensions 225Ч226
Element transformations, in two dimensions 175Ч187
Energy, conservation of 247
Energy, first variation of 61Ч64
Energy, functional 60Ч64
Energy, norm 36 38 57 114
Energy, second variation of 61Ч64
Energy, strain 32Ч33 36
entropy 247
Equilibrium equations 243
Errors, analysis of 37Ч38 57
Errors, asymptotic estimates of 35
Errors, estimates 35Ч38 70
Errors, estimates for two-point problems 84Ч85
Errors, estimates, a-posteriori 36
Errors, estimates, a-priori 36
Errors, in Galerkin approximation 14
Errors, interpolation 67
Errors, log-log-plots of 37
Errors, measures 38
Errors, pointwise 38 124
Errors, quadrature 190
Errors, residual 53
Essential boundary condition see УBoundary conditionsФ
Evolution problems see УTime dependent problemsФ
Extrapolation 33Ч34
Finite element mesh, definition 16
Finite element method, definition 1
Finite element, definition 1 16
Flow through pourous media 44 247
Fluid flow 44 242
Flux 43 45Ч46 48Ч49 73 74 76Ч77 80 247
Flux, electric 44
Flux, flow rate 44
Flux, heat flux 44
| Flux, jump in 46
Flux, shear stress 44
Forward difference scheme 250
Fourier series 10
Fourier's law 44 247
Fourth-order problems 222 228Ч240
Fourth-order problems, essential boundary conditions 231Ч232
Fourth-order problems, natural boundary conditions 231Ч232
Fourth-order problems, two-dimensional 235Ч239
Fourth-order problems, two-point problem 228Ч235
Fully discrete method 250
Functional, definition 60
Galerkin approximation, finite element subspace for 23 58
Galerkin approximation, for the general one-dimensional boundary value problem 58Ч60 73
Galerkin approximation, for the model problem 10Ч15
Galerkin's method, definition 12
Gauss' theorem see УDivergence theoremФ
Gaussian elimination 109Ч111
Gaussian quadrature 23 95 190 206
Global matrices 105Ч107 228
Gradient, definition of 133
Green Ч Gauss Theorem 148
Green's formula 143 148
Heat conduction 44 247
Heat sources 44
Hermite interpolation 233Ч237
Hooke's law see УConstitutive equationФ
Hyperbolic equation 248
Ill-posed problem 48 55 230Ч238
Implicit time integration 251Ч252
Initial-value problems 41 248Ч252
Integrals, coordinate transformation of 190
Integrals, on boundaries 191Ч192
Integration, exact for tetrahedra 228
Integration, exact for triangles 207Ч208
Integration, points, definition of 93
Integration, rules for one dimension 75 91Ч95
Integration, rules for quadrilaterals 199
Integration, rules for triangles 205
Interpolant, finite element 22 72
Interpolant, of data 75
Interpolation, error 67
Interpolation, error, rate of convergence 161
Interpolation, Hermite 233Ч235
Interpolation, higher-order 64
Interpolation, Lagrange 65 67
Interpolation, of one-dimensional problems 64Ч73
Interpolation, of problem data 191
Interpolation, piecewise-linear 21
Inverse map 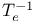 179 179
Invertibility of map 179 182
Isoparametric elements 193
Isotropic 136
Jacobian, for boundary integrals 191Ч192
Jacobian, geometric interpretation of 181Ч182 201Ч202
Jacobian, invertibility condition on 179 182Ч186 194
Jump conditions 46 48 62 73 78 139Ч140 148Ч149
Lagrange, basis functions 67
Lagrange, families 65 67 72Ч73 157 159
Lagrange, interpolation 65 67 72
Lagrange, triangles 203Ч204
Laplaces equation 142
Laplacian operator 143 236
Line source 149 167
Linear momentum, conservation of 242Ч243 2
Linear space 10
Load, vector 23 26 28 62 76 85 164 225
Load, vector for Galerkin's method 12 59
Map 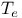 , construction of 179Ч187 , construction of 179Ч187
Map 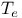 , criteria for 179Ч181 , criteria for 179Ч181
Map 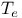 , curved elements 207 , curved elements 207
Map 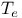 , invertibility conditions 185 , invertibility conditions 185
Map 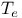 , using finite element shape functions 180 , using finite element shape functions 180
Mass matrix 250
Master element, calculations on 188Ч193
Master element, in one dimension 65
Master element, in three dimensions 225Ч226
Master element, in two dimensions 175Ч179
Master element, integration 190
Master element, map 176Ч177 235
Master element, shape functions 188
Master element, square 181
Master element, triangle 181 200
Material, modulus 43 45 47 136
Material, modulus-dielectric permittivity, permeability, thermal conductivity, viscosity, Young's modulus of elasticity 44
Material, properties 89Ч99 104
Mesh, construction by master elements 175Ч178
Mesh, finite element 16 23 72Ч73 77 150 223
Mesh, parameter h 36
Mesh, refinement 21 36 125
Midstep time integration 252
Mixed boundary conditions 83
Modulus of elasticity 44 127 242
Natural boundary conditions, definition of 49 138 146 231Ч232
Natural boundary conditions, for beam bending 239
Natural boundary conditions, for fourth order problems 231Ч232
Natural boundary conditions, in one dimension 80
Natural boundary conditions, in three dimensions 223
Natural boundary conditions, in two dimensions 141
Natural boundary conditions, relation to conservation principle 139Ч140
Neumann, boundary conditions 82
Neumann, problem 82 85
Nodal, displacements 168
Nodal, points 16 23 72
Nodal, values 33
Norm, 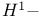 57 57
Norm, definitions of 35
Norm, energy 35 38 57
Norm, maximum 35Ч36
Norm, mean-square 35Ч36 38
Numerical integration see УIntegrationФ
Orthogonality 14 38
Parabolic equations 247
Parametric map 193
Pascal's triangle 157 204
Penalty method 121Ч123
Plane, strain 127
Plane, stress 127 242Ч246
Plate bending 235
Point loads see УDirac deltaФ
Point source see УDirac deltaФ
Poisson's ratio 242 246
Post processing 88 100-11 210Ч225
Principle, conservation see УConservation principleФ
Principle, of superposition 41
Principle, of virtual work 244 246
Quadratic element 196Ч197
Quadrature see УIntegrationФ
Quadrature, error 190
Quadrature, Gauss see УGaussian quadratureФ
Quadrature, points 198Ч199 205Ч206
Quadrature, rules for quadrilaterals 198Ч199
Quadrature, rules for triangles 205Ч206
Quadrature, weights 190 192
Quadrilateral elements 195Ч199 207
Quintic triangle 237
Rate of convergence 36Ч37 84Ч85
Rate of convergence, of interpolation error 161
Refinement of mesh 21 36 125
Residual, for fourth order problems 229
Residual, for the model problem 5
Residual, for time dependent problems 248
Residual, of the differential equation 6 53 144
Self-adjoint, boundary-value problem 26
Self-adjoint, operator 63Ч64
Semi-discrete method 249Ч250
Shape functions, calculation 95Ч96 217 219
Shape functions, definition 26
Shape functions, derivative calculation 95Ч96 189 216Ч227
Shape functions, for one dimension 26Ч27 65Ч68 72Ч74
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



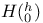
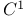 basis functions
basis functions 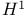
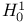
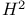
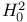
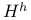
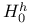
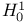 sense
sense 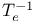
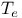 , construction of
, construction of