|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Galwey A.K. Ч Thermal Decomposition of Ionic Solids |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Controlled atmosphere 221
Controlling step, decompositions of solids 528 554 557Ч560
conversion functions 567G
Coordinated water 217
Coordination bond rupture 530 532
Coordination compound 493
Coordination compounds, decomposition mechanisms 494Ч495
Coordination compounds, decompositions 493Ч522
Coordination compounds, hydrates as 494
Coordination compounds, thermal stabilities 517Ч520
Coordination number 493
Coordination polyhedron 494
Copper acetate, decomposition 449
Copper ammine chromate, decomposition 509
Copper ammine sulfate, decomposition 509
Copper azide, decomposition 335 339
Copper carbonate, decomposition 356
Copper carboxylate, decomposition, metal sublimation 444 449
Copper carboxylate, decompositions, copper¬Ѓ intermediates 43 449 458 469 473 484
Copper chloride piperazinium hydrate, dehydration 509
Copper chloride pyrimidinium hydrate, dehydration 509
Copper formate tetrahydrate, dehydration 249
Copper formate, decomposition 442Ч445 448 484
Copper formate, decomposition mechanism 443Ч445
Copper formate, decomposition, copper(1) intermediate 443Ч444
Copper fumarate, decomposition 473 484
Copper hexaammine halides, decompositions 508Ч509
Copper hydride, decomposition 316
Copper hydroxide, dehydration 281
Copper hypophosphite, decomposition 398
Copper maleate, decomposition 473 484
Copper malonate, decomposition 472Ч474 484 542Ч543
Copper nitrate, decomposition 394
Copper nitride, decomposition 320
Copper oxalate, decomposition 457Ч458 485Ч486
Copper oxides, decomposition 300
Copper permanganate, decomposition 389
Copper squarate, decomposition 469 484
Copper sublimation in copper carboxylate decompositions 444 449
Copper sulfate pentahydrate, dehydration 123 223 227Ч229
Copper sulfate trihydrate, dehydration 227Ч229
Copper sulfate, decomposition 401Ч402 407
Copper sulfide, decomposition 322
Copper(II) salts, cation reductions 545
Copper(II) salts, decompositions 545
Copper, basic halides, decompositions 376
Covalent bond rupture 530 544
Covalent crystal decompositions 531
Crack development 96 98 111 234
Cracking, potassium bromate decomposition 371
Cracking, potassium metaperiodate decomposition 369
Cracking, potassium permanganate reaction 381Ч382
Crystal bulk 569G
Crystal cracking 270 274 276 282
Crystal imperfections 8Ч15
Crystal imperfections in decompositions of solids 526 529 556
Crystal lattice 2
Crystal strain 271
Crystal structure 174Ч175
Crystal structures and stabilities 555
Crystal surface 569G
Crystal, charge-carrying species 191
Crystalline hydrates 217
Crystallographic shear 306Ч307
Crystals, covalent 5
Crystals, ionic 5
Crystals, metallic 6
Crystals, molecular 5
Crystolysis 3 111 527 537 569G
Crystolysis and related reactions 551Ч552
Crystolysis reactions, literature content 548
Cyano coordination compounds, decompositions 510Ч511
Deceleratory kinetic rate equations 102Ч111
Deceleratory period 106Ч110 143
Decomposition enthalpy 60 66
Decomposition of solids, steps 536 554
Decomposition products 53 55Ч56 58 62
Decomposition products, primary 53Ч54
Decomposition, classification of mechanisms 200Ч202 207Ч208
Decomposition, oxides 291Ч308
Decomposition, reversible, enthalpies 60
Decomposition, stoichiometry 53 60 63Ч64
Decompositions 25Ч26
Decompositions of coordination compounds 493Ч522
Decompositions of solids, chemical features 528 554
Decompositions of solids, controlling step 528 554 557
Decompositions of solids, reaction precursors 529 554
Decompositions with melting 547 554
Decompositions, ammonium salts 415Ч435
Decompositions, carbonates 345Ч361
Decompositions, dissociation pressure 52
Decompositions, endothermic 50 53 66Ч68
Decompositions, exothermic 50 66
Decompositions, Group IA metal permanganates 546 552
Decompositions, irreversible 200
Decompositions, irreversible, oxyacid salts 404
Decompositions, metal carboxylates 441Ч486
Decompositions, metal formates 441Ч448
Decompositions, metal salts of organic acids 441Ч486
Decompositions, oxyacid metal salts 381Ч409
Decompositions, oxyhalide salts 365Ч377
Decompositions, reversible 50 60 200
Decompositions, reversible, oxyacid salts 404
Defect mobility 16Ч25
Dehydration 31 217Ч268
Dehydration and cobalt oxalate decomposition 454
Dehydration kinetics 217Ч268
Dehydration mechanisms 218 256Ч260
Dehydration nuclei 221Ч222 258Ч259
Dehydration nuclei, shapes 232 237
Dehydration of 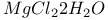 and oxidation of and oxidation of 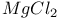 546 546
Dehydration, calcium oxalate monohydrate 559
Dehydration, experimental 219Ч221
Dehydration, explosive 261
Dehydration, Group IA metal cyanoferrates 510
Dehydration, hydroxides 269Ч290
Dehydration, initial 65
Dehydration, isotope effects 261
Dehydration, reversible 269
Dehydration, topotactic 257Ч260
Dehydration-anation reactions 260
Dehydration-rehydration 233
Dehydrations in mixed coordination compounds 500 506 517 522
Dehydrations,  and and  546 546
Dehydrations, classifications 256Ч259
Dehydrations, cobalt(III) diammine compounds 513
Dehydrations, copper chloride coordination compounds 509
Dehydrations, homogeneous 257
Dehydrations, hydroxyhalides 375Ч376
Dehydrations, lignite and alums 546
Dehydrations, lithium potassium tartrate hydrates 547
Dehydroxy lation reactions 281Ч2
Dehydroxy lation, hydroxides 269Ч290
Dehydroxy lation, inhomogeneous 270
Dehydroxylation, electric field 271
Dehydroxylation, homogeneous 270
Dense initial nucleation 234
Desorption, caesium from graphite compound 320
Desorption, oxygen 292
Diammine cobalt(III) compounds, decompositions 512Ч513
Diammine isomerization in solid coordination compounds 513
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 63 66
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) 63
Diffraction measurements 537 554
Diffraction using synchrotron radiation 537 553
Diffusion 75 96Ч100 282 284
Diffusion coefficients 22 99
Diffusion control rate equations 96Ч111
Diffusion in potassium metaperiodate decomposition 369
Diffusion processes, hydroxyhalide decompositions 375
| Diffusion reactions 96Ч101
Diffusion, Fick's laws 97Ч99
Diffusion, intracrystalline 96Ч100 102
Diffusion, lattice 292
Diffusion, surface 43
Diffusion, water 231 242 250 258
Diffusion, water vapour 243 251
Dislocation detection, X-ray topography 184Ч185
Dislocation generation in sodium chlorate 370
Dislocations 9 12Ч15 24 37Ч38 42 46
Dislocations, Burger's vector 382
Dislocations, edge 12Ч13
Dislocations, screw 12Ч14
Dissociation, surface 42
Dissociations 568Ч569G
Dissociations, oxides 291Ч308
Dissociative evaporation, azides 340
Dissociative vaporization, equimolar 308
Dissociative vaporization, isobaric 308
Dissolution-recrystallization 279
Distinguishability of kinetic equations 141 143Ч144 147 149 540
Dolomite, decomposition 350 358
Dopants in barium bromate decomposition 372
Doping 12
Doping of crystals 192Ч193
Doping, cadmium carbonate decomposition 355
Doping, cobalt oxide 304
Doping, silver carbonate decomposition 354
Dunwald Ч Wagner rate equation 99
Elastic surface layer 230Ч231
Electrical conductivity 38 190Ч192
Electron diffraction 277
Electron mobility 16 22Ч25
Electron probe microanalysis 184
Electron spin resonance spectroscopy (ESR) 181
Electron transfer 44 127 530 532 544
Electron transfer in complex azide decompositions 502
Electron transfer, carboxylate decompositions 443 457 462 480
Electron transfer, oxides 291
Electron traps, 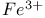 ions in barium azide 332 ions in barium azide 332
Electronic activation 75
Electronic energy 128 134
Electrons and positive holes 8Ч10 16Ч22
Ellingham diagrams 55Ч58
Energy band levels 191 199
Energy chain branching 381Ч382
Energy chains 79Ч80 96
Energy distributions, interface 127Ч129
Energy levels, spectral studies 534 538 559
Enthalpy of decomposition 60 69
Enthalpy of dehydration 222Ч223
Etch pits 14 42 230
Ethylenediamine chromium(III)compounds, decompositions 513Ч514
Ethylenediamine cobalt(III) compounds, decompositions 512Ч513
Ethylenediamine nickel compounds, decompositions 514
Evolved gas analysis (EGA) 61 539
Exciton formation in azide decomposition 341
excitons 9Ч10 20Ч21
Experimental conditions 140
Experimental errors 141 162 167
Experimental methods 29 60Ч67 69 174Ч194 277Ч278
Experimental methods, spectroscopic 177Ч178
Exponential rate equations 94 103
Extended imperfections 306Ч308
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) 182Ч183
Extent of reaction (a) see also Уfractional reactionФ 30 60
F-centre 11
Fermi level 128
Fermi level, azide decompositions 332 334 340
Fermi Ч Dirac statistics 127Ч128
Fick's laws of diffusion 22
Field-emission spectroscopy 177Ч178
First-order rate equation 90Ч91 100 108
Flynn and Wall method of kinetic analysis 160
Flynn method of kinetic analysis 157
Formates as heterogeneous catalysis intermediates 447Ч448
Formates, metal, decompositions 441Ч448
Formates, metal, hydrates, dehydrations 249Ч250
Formic acid, nickel catalyzed decomposition 441Ч442 447
Fractional reaction (a) 30 60 87 139Ч140 570G
Frank net 14
Freeman and Carroll method of kinetic analysis 158
Frenkel point defects 9Ч11 24
Frenkel-type defects in dehydration 511
Frequency factor (A) 117Ч134 222 567G
Friedman method of kinetic analysis 157
Fulminates, decompositions 338Ч9
Fumarates, metal, decompositions 469 471Ч475
G thiosulfates, decompositions 403
Gas analyses 205
Gas chromatography (GC) 62
Gas pressure, accumulatory 61
Geometric and diffusion control rate equations 98Ч100
Geometric interpretation of kinetics 141 165
Geometric interpretations, microscopy 186Ч190
Geometric rate equations 91Ч94 102Ч111
Germ nucleus 77Ч78
Ginstling Ч Brounshtein rate equation 98
Glass 4
Glass transition 67
Glossary of subject-specific terms 567Ч571
Grain boundaries 8 24
Group IA and Group IIA metal oxides 297
Group IA metal formates, decompositions 446Ч447
Group IA metal hexacyanoferrates, decomposition 510
Group IA metal percarbonates 254Ч255
Group IA metal peroxocarbonates 254Ч255
Group IIA metal acetates, decompositions 450
Group IIA metal formates, decompositions 447
Group IIA metal hydrides, photodecomposition 315
Growth nucleus 25 76Ч78 239 258Ч259
Growth, restricted, nuclei 85Ч86
Growth, unrestricted, nuclei 84Ч85
Halides, metal, decompositions 374
Heating a crystalline solid 49
Hedvall effect,  reaction 356Ч357 reaction 356Ч357
Hertz Ч Knudsen Ч Langmuir equation 41Ч42 45
Hertz Ч Knudsen Ч Langmuir sublimation model 559Ч560
Hertz Ч Knudsen Ч Langmuir volatilization 307Ч308
Heterogeneity of reactant crystals 556
Heterogeneous catalysis 47 130
Heterogeneous catalysis and crystolysis 544 560
Heterogeneous catalysis, intermediates 324
Heterogeneous reactions, oxides 294 307Ч308
Heterogeneous/homogeneous kinetics 527 557 560
Hexaammine chromium(III) compounds, decomposition 504Ч505
Hexaammine chromium(III) thiocyanate, decomposition 505Ч506
Hexaammine cobalt(III)compounds, decompositions 495Ч498 515
Hexaammine copper halides, decompositions 508Ч509
Hexaammine nickel perchlorate, decomposition 508
Hexacyanoferrates, metal, decompositions 510Ч511
Hydrate structures 218Ч219
Hydrates 31 218
Hydride decompositions, reversible 314
Hydrides, decompositions 313Ч317
Hydrides, surface properties 314
Hydrogen bonding 218
Hydrogen desorption, hydrides 314
Hydrogen evolved during dehydroxylation 282
Hydrogen mobility in hydrides 314
Hydrogen peroxide of crystallization 254
Hydroxides, dehydrations 269Ч288
Hydroxy halides, metal, decompositions 375
Hydroxy halides, two-metal salts, decompositions 375Ч376
Hydroxy metal salts, dehydrations 287
Hydroxystannates, metal, decomposition 277
Imperfection interactions 306Ч307
Imperfection loss and annealing 558
Imperfections 8Ч15 33 250
Imperfections and electrical conductivity 191Ч192
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



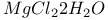 and oxidation of
and oxidation of 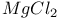
 and
and 
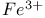 ions in barium azide
ions in barium azide  reaction
reaction