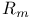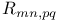|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Davies J.H. — The physics of low-dimensional semiconductors : an introduction |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
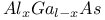 , band gap 88 , band gap 88
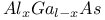 , change in nature of conduction band 88 , change in nature of conduction band 88
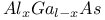 , table of properties 412 , table of properties 412
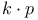 theory 261—263 theory 261—263
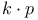 theory at edge of band 262 theory at edge of band 262
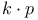 theory, estimate of theory, estimate of 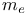 263 263
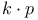 theory, interband matrix element 262 263 theory, interband matrix element 262 263
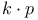 theory, modified Schroedinger equation 262 378 theory, modified Schroedinger equation 262 378
 -doping 356 368 -doping 356 368
 -function barrier 158 -function barrier 158
 -function trick in response functions 322 374 -function trick in response functions 322 374
 -function well 124 147 -function well 124 147
2DEG see "Two-dimensional electron gas"
Acceptors 36
Adiabatic approximation 186
Aharonov — Bohm effect 232—233
AIAs, crystal structure 58
AIAs, X-valleys 68
Airy equation see "Stokes equation"
Airy functions 129 209 415—416
Airy functions, asymptotic form 415
Airy functions, zeros 415
Airy functions, zeros of derivative 416
Alloy scattering 80 325 363
Anderson localization 241
Anderson’s rule 85
Angular momentum, Quantum number 136
Angular momentum, rules in quantum mechanics 381
Band alignment, band alignment, Anderson’s rule 85
Band alignment, classification 86—87
Band alignment, GaAs — AlAs 86—88
Band alignment, InAs — GaSb 86
Band alignment, lattice-matched examples 87
Band alignment, staggered 86
Band alignment, straddling 86
Band alignment, type I 86
Band alignment, type II 86
Band alignment, type III 86
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers 329—342
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, behaviour at surface 331
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, calculation of electrostatic potential 332—333
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, need for self-consistent calculation 331
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, relation between Fermi levels and gate bias 332
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, simple model 331
Band diagram through modulation-doped layers, threshold voltage 335
Band engineering 85—88
Band gaps in higher dimensions 56
Band gaps, alignment at heterojunction 85 86
Band gaps, breakdown (Zener tunnelling) 53
Band gaps, complex band structure 181
Band gaps, direct 67 88
Band gaps, indirect 67 88
Band gaps, location in 1D 49 282
Band gaps, nature of electronic states 181
Band gaps, origin 47
Band gaps, plotted against lattice constant 81
Band gaps, relation to Bragg reflection 47
Band gaps, relation to reciprocal lattice vectors 49
Band gaps, wave functions above and below 50
Band gaps, width from nearly free electron method 283
Band structure in quantum well 384—387
Band structure of common semiconductors 63—68
Band structure of common semiconductors,  -valley 67 -valley 67
Band structure of common semiconductors, L-valleys 68
Band structure of common semiconductors, light and heavy holes 65
Band structure of common semiconductors, top of valence band 64
Band structure of common semiconductors, valence band 63
Band structure of common semiconductors, X-valleys 67
Band structure, 1D 47 48 55
Band structure, cosine approximation 50
Band structure, different zone schemes 47
Band structure, display in higher dimensions 62
Band structure, distinction between insulators and metals 54
Band structure, effective mass 51
Band structure, free electrons in GaAs 62
Band structure, Kane model 377—383
Band structure, nearly free electron method 280—284
Band structure, reduction to first Brillouin zone 47
Band structure, surface states 69
Band structure, tight-binding method 275—280
Bernard — Durrafourg condition for optical gain 396
Bessel functions 137 299
Bessel functions, asymptotic form 137
Bessel's equation 137
Binding energy 119
Bloch oscillation 53 214
Bloch wave vector (or wave number) 46
Bloch's theorem 46
Bohr magneton 223
Bohr radius 111 139 354
Boltzmann distribution 32
Born approximation 295
Bose — Einstein distribution 38 303
Bragg reflection 47
Bras and kets 251
Brillouin zone 46
Brillouin zone in higher dimensions 56
Brillouin zone, common semiconductors 61
Brillouin zone, notation for special points 61
Broken gap 86
Burstein shift 327
Canonical momentum 208 213
Capacitance of modulation-doped layers 335 336
Capacitance of modulation-doped layers, as probe of density of states 335
Causality 372 417
Centre of symmetry 60
Centrifugal potential 136 140 223
Charge density from wave function 9
chemical potential 38
Circulator 192
classical turning points 264
Coherent transport 150
Coherent transport with many leads 188—195
Coherent transport with many leads, coefficients 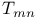 and and 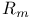 189 189
Coherent transport with many leads, coherent and incoherent contributions 192
Coherent transport with many leads, contact resistance 195
Coherent transport with many leads, four leads 193—194
Coherent transport with many leads, four-probe resistance 194 195
Coherent transport with many leads, invasive effect of voltage probe 192
Coherent transport with many leads, Landauer conductance 195
Coherent transport with many leads, Landauer — Buettiker formula 189 190
Coherent transport with many leads, modes and channels 188
Coherent transport with many leads, perfectly transmitting wire 195
Coherent transport with many leads, resistance 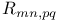 193 193
Coherent transport with many leads, sum rule for 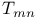 189 190 189 190
Coherent transport with many leads, symmetry of conductance matrix 190 192 204
Coherent transport with many leads, t-matrix 189
Coherent transport with many leads, three leads 190—193
Coherent transport with many leads, two- and four-probe measurements 188 194—195
Coherent transport with many leads, two-probe resistance 194
Coherent transport with two leads 184—188
Coherent transport with two leads, conductance from t-matrix 185
Coherent transport with two leads, inodes and channels 184
Coherent transport with two leads, perfectly transmitting wire 195
Coherent transport with two leads, quantum point contact 185—188
Coherent transport with two leads, t-matrix 185
Coherent transport, distribution of incoming electrons 199 200
Coherent transport, inelastic scattering 200
Coherent transport, many leads 188—195
Coherent transport, perfect leads 184
Coherent transport, power dissipation 199
Coherent transport, scattering centre and leads 183
Coherent transport, two leads 184—188
Collisional broadening 294
Commutation relation 19 252
Complete set 250
Complex band structure 181 379
Composite fermions 245
Conductance, quantum unit 165
Conduction band 6
| Conduction band of common semiconductors 66—68
Conduction band,  -valley 67 -valley 67
Conduction band, L-valleys 68
Conduction band, X-valleys 67
Conductivity tensor 216
Conductivity tensor in high magnetic field 218
Conductivity, complex 309
Conductivity, Drude model 53
Conductivity, Kramers — Kronig relations 310
Conductivity, significance of real and imaginary parts 310
Constants of motion 20 252
Contact resistance of reservoir 195
Correlation between electrons 347
Coulomb blockade 174
Coulomb potential energy in Fourier space, 2D 354
Coulomb potential energy in Fourier space, 2D (out of plane) 355
Coulomb potential energy in Fourier space, 3D 350
Coulomb well 2D 139 400
Coulomb well 3D 140 399
Cross-section, impurity scattering 298
Cross-section, short-range potential 300
Cross-section, total, differential, and transport 299
Crystal momentum 46 51 214
Crystal structure, body-centred cubic 57 58
Crystal structure, centre of symmetry 60
Crystal structure, diamond 58
Crystal structure, face-centred cubic 57 58
Crystal structure, planes and directions 59—60
Crystal structure, simple cubic 57 58
Crystal structure, symmetry group 60
Crystal structure, zinc-blende 58
Current 1D tunnelling systems 163—165
Current 2D and 3D tunnelling systems 165—167
Current continuity equation 10 152
Current density from wave function 10
Current density in terms of momentum operator 14
Current density with vector potential 208
Current density, decaying waves 12
Cyclotron energy 147
Cyclotron frequency 219 220
Cyclotron radius 219
Cylindrical well 136—137
Cylindrical well, energies 137
De Broglie relation 3
Debye — Hueckel screening 352
Deformation potential 303
Degenerate distribution of particles 33
Degenerate energy levels 21
Degenerate perturbation theory 273—275
Degenerate perturbation theory, square quantum dot 273—275
Density of states, 1D crystal 54
Density of states, apparent thickness in capacitance 334
Density of states, definition 22
Density of states, effective in classical semiconductor 35
Density of states, free electrons (1D) 25 27
Density of states, free electrons (2D) 27 43
Density of states, free electrons (3D) 26 27
Density of states, general definition 27
Density of states, local 29
Density of states, optical joint 315 392
Density of states, thermodynamic 351 352
Diagonalization 252
Diamagnetic current 208
Diamond lattice 58
dielectric constant 105 349
Dielectric function 350 351 354
Dielectric function for Q = 0 (3D) 353
Dielectric function of plasma 353 375 421
Dielectric function, complex 309
Dielectric function, Kramers — Kronig relations 310
Dielectric function, Lindhard 353
Dielectric function, plasmons 353
Dielectric function, significance of real and imaginary parts 310
Dielectric function, Thomas — Fermi (2D) 354
Dielectric function, Thomas — Fermi (3D) 351
Dipole matrix element 320
Dirac notation 251
Direct gap 67 69 88
Dispersion relations 373
Donors 36
Donors,  -doping 356 368 -doping 356 368
Donors, DX centre 337
Donors, hydrogenic model 111 337
Donors, potential from remote donor (in 2D) 355
Donors, screening (2D) 355 357
Donors, screening (3D) 351
Double-barrier potential 90 168
Drude model 52 216
Drude model, response function 419—421
DX centres 337—340
DX centres, effect on band diagram 337—339
DX centres, effect on density of 2DEG 338
DX centres, effective potential well 337
DX centres, occupation freezes at low temperature 337
Edge states 235 237
Edge states in integer quantum Hall effect 239
Edge states, classical behaviour 235
Effective Hamiltonian 110
Effective Hamiltonian at bottom of conduction band 110
Effective Hamiltonian for donor 110
Effective Hamiltonian in heterostructures 113
Effective mass in cosine band 50
Effective mass in general energy band 51
Effective mass, anisotropic for holes in quantum well 385
Effective mass, density of states 67
Effective mass, longitudinal and transverse 67 198
Effective mass, negative 52
Effective mass, optical 8
Effective mass, reduced 306
Effective-mass approximation 107—111 385 394
Effective-mass approximation at bottom of conduction band 110
Effective-mass approximation for donor 110
Effective-mass approximation, envelope function 109
Effective-mass approximation, extension to heterostructures 111—114
Effective-mass approximation, Hamiltonian 110
Effective-mass approximation, limitations 111
Effective-mass approximation, matching at heterojunctions 112
Eigenstates 13 20—22
Eigenstates, completeness 21 250
Eigenstates, degenerate 21
Eigenstates, expansion of arbitrary state 21 22
Eigenstates, orthogonality 20 250
Eigenvalues, eigenvectors, eigenfunctions, and eigenstates 13 251
Einstein relation 3
Electric field with crossed magnetic field 229—231
Electric field, conduction in a narrow band 215
Electric field, current density 213
Electric field, density of states 210—212
Electric field, Franz — Keldysh effect 212
Electric field, length and energy scales 209
Electric field, local density of states necessary 210
Electric field, narrow electronic band 214—215
Electric field, potentials 207
Electric field, quantum-confined Stark effect 258
Electric field, Schroedinger equation 208
Electric field, wave functions with scalar potential 208—210
Electric field, wave functions with vector potential 213—214
Electric-dipole approximation 312
Electromagnetic potentials 207
Electron affinity 85
Electron gas 37
Electron-hole pair 397
Electronic structure of 2DEG 342—349
Electronic structure of 2DEG, comparison of different approximations 343
Electronic structure of 2DEG, Fang — Howard model 347—349
Electronic structure of 2DEG, quantum mechanics of many electrons 344—347
Electronic structure of 2DEG, simple approximation for energy level 336
Electronic structure of 2DEG, thickness of 2DEG 343
Electronic structure of 2DEG, triangular-well approximation 342—344
Energy bands, cosine approximation 280
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 , band gap
, band gap 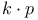 theory
theory 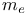
 -doping
-doping  -valley
-valley 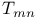 and
and