јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Chaikin P.M., Lubensky T.C. Ч Principles of condensed matter physics
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Principles of condensed matter physicsјвторы: Chaikin P.M., Lubensky T.C. јннотаци€: This book provides an overview of the physics of condensed matter systems. Assuming a familiarity with the basics of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics, the book establishes a general framework for describing condensed phases of matter based on symmetries and conservation laws. After surveying the structure and properties of materials with different symmetries, it explores the role of spatial dimensionality and microscopic interactions in determining the nature of phase transitions. Particular attention is given to critical phenomena and renormalization group methods. The properties of liquids, liquid crystals, quasicrystals, crystalline solids, magnetically ordered systems and amorphous solids are investigated in terms of their symmetry, generalized rigidity, hydrodynamics and topological defect structure. In addition to serving as a course text, this book is an essential reference for students and researchers in physics, applied physics, chemistry, materials science and engineering, who are interested in modern condensed matter physics.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /‘изика твЄрдого тела /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1995 оличество страниц: 699ƒобавлена в каталог: 12.08.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Stability exponents 268 Stability of homogeneous fluids 113Ч115 Stable fixed point 245 669 Static cross-section 31 Static scattering 32 Stationary state, hydrodynamic 422 Steam 3 Steric entropy 635Ч638 Sterically stabilized phases 638Ч640 642 Stochastic models see УModels stochasticФ Stochastic variable 375 StokesТ law 360 682 strain 11 316 682 Strain rate 447 682 Strain tensor, Eulerian 331 Strain tensor, Lagrangian 331 Strain tensor, linearized 317 Strain, inverse compressibility 328 Strength of crystals 518 Strength of vortex 497 Stress 682 Stress tensor 334 Stress tensor, Eulerian 338Ч341 Stress tensor, Lagrangian 334Ч337 Stress-strain relations 340 Striped phase 618 Structure and scattering 29Ч103 Structure factor 33 Structure function 32 Sum rules 357 398Ч399 Sum rules and moment expansions 398 Superconductivity 135 216Ч217 571 Supercooling 171 Superfluids 123 575 Superfluids, and xy symmetry 138 Superfluids, density 290 460 Superfluids, free energy density 575Ч576 Superfluids, helium 138 289 460Ч464 551Ч555 Superfluids, hydrodynamics 460Ч464 Superfluids, hydrodynamics, third sound in thin films 553 Superfluids, Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition in thin films 551Ч554 Superfluids, longitudinal and transverse response 575Ч577 Superfluids, velocity 460Ч464 Superheating 171 Superlattice peaks 87 Surface tension 481 486 635Ч638 Surfactants 636 638 susceptibility 231 341 Susceptibility, critical exponent 154 228 Symmetries, and order parameters 139 Symmetry group 39 133 Symmetry group, 139 231 Symmetry group, 137 139 231 289 Symmetry group, 138 156 230 231 Symmetry group, 138 156 202 298 Symmetry group, 135 139 152 231 Symmetry group, 137 139 Symmetry group, Euclidean 39 670 Symmetry group, U(1) 137 Symmetry, order parameters, and models 132Ч139 Symmetry, order parameters, and models, continuous symmetries 137Ч139 Symmetry, order parameters, and models, discrete symmetries 135Ч137 Symmorphic space group 57 Tangent plane 623 TDGL model 466 682 Temperature quench 483Ч484 Tension 335 Tetracritical point 181Ч182 235 253 682 Tetrahedra 7 191 TGB see УTtwist-grain-boundary phaseФ thermal conductivity 425 Thermal equilibrium 381Ч383 Thermal fluctuation 10 Thermodynamic critical field of the TGB phase 564Ч565 Thermodynamic equilibrium 417Ч419 Thermodynamic laws of 109Ч112 Thermodynamic stability 321 Thermodynamic sum rule 357 365 Thermodynamics of homogeneous fluids 108Ч117 Thermotropic liquid crystal 68 682 Thermotropism 58 Third sound 553 Three-phase coexistence 174 Time reversal 133 359 361 Time translations 133 Time-dependent Ginzburg Ч Landau model 466 682 Time-of-flight measurements 409 Topological defects 12 495Ч585 682 Topological defects, characterization 495Ч506 Topological defects, crystals disclinations 517Ч518 Topological defects, dislocation mediated melting 555Ч559 Topological defects, energies of 526Ч542 Topological defects, examples 506Ч526 Topological defects, Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition 542Ч555 Topological defects, nematic and hexatic liquid crystals 524Ч526 Topological defects, order parameters spaces and homotopy 501Ч506 Topological defects, periodic solids 512Ч515 (see also УDislocations disclinations and Torus 626 Transfer matrix 242 Translation vector 43 Translational invariance 35 329 Transport coefficients 425 Transverse strain 321 Triacontahedron 190 Triangular, lattice 51Ч53 255 520 Tricritical point 173Ч175 180 181 236 253 682 Tricritical point, three-state Potts critical point 256 Turbidity of nematics 307 Twist 299Ч306 561 687 Twist disclination 519 Twist wave vector 89 Twist-grain-boundary phase 561Ч573 682 Twist-grain-boundary phase, analogy with superconductivity 571Ч573 Twist-grain-boundary phase, X-ray scattering 568Ч571 Twisted nematic see УCholesteric liquid crystalФ Twisted nematic display 304 Two scale factor universality 234 Two-component fluids 453 Two-dimensional order 15 Two-dimensional order, Bravais lattice 50 Two-dimensional order, charge-density wave 80 Two-dimensional order, charge-density wave, smectic 311 Two-dimensional order, hexagonal solids 321 Two-dimensional order, orthogonal group 137 Two-dimensional order, orthogonal group 71Ч77 Two-fluid model 461 U(1) symmetry 289 (see also Уxy symmetryФ) Undamped oscillator 359 Undulations, smectic 315 Unit cell 43Ч46 Universality class 213 230 683 Unstable fixed point 245 Up-down symmetry 230 Upper critical dimension 213 215 228 264 Upper critical field 564 Ursell function 35Ч36 124 195Ч196 Vacancy 49 325 683 Vacancy, diffusion 459 Van der Waals attraction 18Ч20 683 Van der Waals equations of state 144 683 Van Hove theory 465 471 683 Variational mean-field theory 198 Velocity correlation function 385 Vesicle 70 73 683 Vicinal surface 648 Villain model 583 645 683 Villain model, duality 578Ч579 viscosity 387 447Ч448 683 Viscosity, kinematic 449 Viscosity, table of common materials 448 Viscous force 360 Volterra construction 515 517 519 683 Vortex energy 526 Vortices 495Ч499 504Ч506 Vortices, analogy with magnetism 530Ч531 Vortices, and the spin-wave stiffness 542Ч544 Vortices, energy 526Ч530 Vortices, helium films 551Ч555 Vortices, in xy-models 506Ч507 Vortices, Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition 544Ч551 Vortices, superfluid helium films 551Ч555 Vortices, vortex pairs 499Ч500 Walls, kinks and solitons 590Ч656 Walls, kinks and solitons, 597Ч599 Walls, kinks and solitons, domain walls in mean-field theory 595Ч601 Walls, kinks and solitons, dynamics 599Ч601 Walls, kinks and solitons, fluctuating walls 620Ч635 Walls, kinks and solitons, fluctuating walls, arrays 635Ч643 Walls, kinks and solitons, Frenkel Ч Kontorowa model 601Ч620 Walls, kinks and solitons, soliton, sine-Gordon 599 Wandering exponent 594 629 Water as example of condensed matter 3Ч15 Water, ice crystals 8 Water, ice crystals, dislocations 12Ч13 Water, Navier Ч Stokes equation 448 Water, phase diagram 4 Water, viscosity 448 Wave number cutoff 152 666 Wedge disclination 519 Weight function 221 Weiner Ч Khintchine theorem 355 683 Weiss molecular field theory 144 148 683 White noise source 383 466 Wigner Ч Seitz cell 44Ч46 50 52 683 Winding number 497 503Ч505 528 603 Wine bottle 289 Work hardening 521 683 Wulff construction 653 Wulff plot 654 684 Wurtzite 9 X-ray diffraction and scattering chapter 2 33 67 613Ч614 X-ray diffraction and scattering, from TGB phase 568Ч571 (see also УScatteringФ УBragg and X-ray structure factor 325 Xenon 79 Xenon, electron scattering 560 Xenon, on graphite 77 324Ч326 560 Xenon, on graphite, incommensurate phases 635 XY-model 288 289 495 502 506 524 544Ч545 684 xy-model, elasticity 289Ч290 xy-model, longitudinal and transverse response 575Ч577 xy-model, shear modulus 555 xy-model, vortex energy 526Ч530 xy-model, vortex unbinding 555 xy-symmetry 137 Yang Ч Lee edge 286 684 Yield stress 12 518 684 YoungТs modulus 337 533 557 684 YoungТs modulus, 2-D 632 УProblemsФ 103Ч107 209Ч212 283Ч287 347Ч352 411Ч416 492Ч194 585Ч589 656Ч661
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



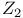 (Ising)
(Ising) 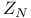
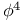 kink
kink