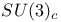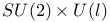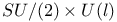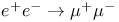|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Aitchison I.J.R. Ч An Informal Introduction to Gauge Field Theories |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
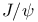 particles 119 121 particles 119 121
 -function 162Ч163 -function 162Ч163
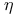 decay 155 decay 155
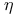 mass 155 mass 155
 scattering 110Ч112 scattering 110Ч112
 scattering, inelastic 120 scattering, inelastic 120
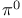 decay 148Ч155 decay 148Ч155
 -model 94Ч95 114 -model 94Ч95 114
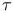 lepton 121 lepton 121
 parameter 38 121 parameter 38 121
't Hooft gauge fixing term(s) 66 99 104
Action principle 10
Adler Ч Weissberger relation 95 147
Algebra Lie of charges 24 92 95
Algebra Lie of currents 24 95
Algebra Lie of generators of group 20 34
Algebra Lie, matrix representation of 20 92
And departures from scaling 163
Anomalous dimension 158 162
Anomaly 16 126 148 153 160
Anomaly and 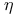 mass 155 mass 155
Anomaly and renormalisation 154
Anomaly and scale invariance 155Ч163
Anomaly and U(1) problems 155
Anomaly,  148Ч155 160 148Ч155 160
Anomaly, cancellation 155
Anomaly, cancellation in GSW theory 154Ч155
asymptotic freedom 2 122 162
Auxiliary field 45Ч47 56
Axial vector, charge 92
Axial vector, current 92 94
Axial vector, current and anomalies 148Ч155
Axial vector, current and Ward Ч Takahashi identities 146Ч147
Axial vector, current, non-conservation of 94 146
Axial vector, current, partial conservation of (PCAC) 94
Baryon, decay 123
Baryon, number conservation 124
Becchi Ч Rouet Ч Stora (BRS) transformation, Abelian 54Ч55
Becchi Ч Rouet Ч Stora (BRS) transformation, non-Abelian 54Ч56 147
Bogoliubov, quasiparticle operators 80Ч81
Bogoliubov, superfluid 79Ч83
Bogoliubov, transformation 82
Born graphs, high energy behaviour of 63Ч64 68 99 106
Bose condensate 79 82 83
BSC theory of superconductivity 83
Cabibbo, angle 115 144
Cabibbo, angle, generalised 121
Cabibbo, mixing 5
Callan Ч Treiman relation 95
Charge, algebra 24 95
Charge, axial vector 92
Charge, conserved, associated with symmetry 13Ч14 16 19Ч22
Charge, quantisation 36 124 144
Charge, renormalisation 137
Charge, renormalisation and vacuum polarisation 144
Charge, renormalised 137 144
Charge, unrenormalised 136Ч137 144
Charge, weak 5 145
Charged current 3 5
Charm 117 118
Charm-changing decays, selection rules in 118Ч119
Charmed mesons 118Ч119
Charmed mesons, mass prediction (GIM) 119
Chiral symmetry 2 71
Chiral symmetry and 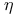 mass 155 mass 155
Chiral symmetry and 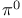 decay 148Ч155 decay 148Ч155
Chiral symmetry and anomalies 148 149Ч153
Chiral symmetry, hidden global 91Ч96 146
Colour 1 37
Colour and 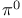 decay 153 decay 153
Colour, group 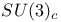 2 2
Commutation relations in canonical quantisation 12
Condensate (Bose) 79 82 83
Condensate (Bose), Cooper pair 100Ч101
confinement 163
Conservation law and anomalies 15Ч16
Conservation law and symmetry 13 16 19
Cooper pairs 100
Cooper pairs, wavefunction of 101
Correlation length in statistical mechanics 156 162
Coulomb interaction, instantaneous 57
Coulomb interaction, instantaneous in spontaneously broken theory 78Ч79 81
Coulomb interaction, instantaneous in superconductor 83
Coulomb interaction, instantaneous, modified by renormalisation 136
Counter terms 129Ч131 134 137Ч138 141 146 148
Covariant derivative, 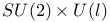 101 108Ч109 101 108Ч109
Covariant derivative, general 34
Covariant derivative, QED 25 31
Covariant derivative, regular representation 35 46
Covariant derivative, SU(2) doublet 32
Covariant derivative, SU(3) triplet 38
CP violation 120Ч121
Critical indices 162
Critical phenomena 162
Critical temperature 87 156
Curie temperature 76 85
Current as source in gauge theories 27 36
Current in vacuum 100
Current, algebra 24 95 146
Current, associated with spontaneously broken global symmetry 87 99
Current, associated with spontaneously broken local symmetry 99Ч100
Current, axial vector 92 94
Current, conservation and Ward identity 50 140Ч144
Current, conserved weak vector (CVC) 145
Current, conserved, associated with symmetry 14Ч19 21Ч24 27 71 73
Current, conserved, associated with symmetry and Coleman's theorem 72
Current, electromagnetic 27
Current, electromagnetic and gauge invariance 27
Current, hadronic weak 4 114Ч120
Current, leptonic 4
Current, screening 100
Current, weak for quarks 115
Current, weak neutral, strangeness changing 115
Current, weak neutral, strangeness changing and GIM mechanism 115Ч120
Current, weak vector 4 94 144Ч145
Current-current interaction 4 5
Cut-off 127Ч129 159Ч160
Deep inelastic lepton scattering and scale invariance 155Ч156 163
Degenerate ground states 75Ч77 82
Degenerate vacua 71
Dimension, anomalous 158 162
Dimension, scale 158
Dimensional analysis 156Ч157 162
Dimensional regularisation 127 133
Dimensional rescaling 157
Divergences, infra-red 127 139 148 160
Divergences, ultraviolet 6 15 64 126
Divergences, ultraviolet in 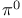 decay 152 decay 152
Effective charge 129
effective mass 128
Einstein 7Ч9
Equivalence, principle of 7
Euclidean region 160
Euler Ч Lagrange equations 10Ч11
Fabri Ч Picasso theorem 71Ч73
Fermi constant 110 114
Fermi theory 3 6
Fermion masses 38 93Ч95 113Ч114 120
Ferromagnet 75Ч78 85
Feynman gauge 44Ч45 48 57 64 67 127 133 135 139
Field tensor in QCD 38
Field tensor, electromagnetic 26 33 40
Field tensor, non-Abelian 33Ч35
Flavour 1 37 94 115 120Ч121
Flavour, octet of weak currents 115Ч116
Four-fermion theory, connection with GSW theory 110
Gap in electron energy spectrum in superconductor 83
Gauge fields, quantisation of 39Ч57
Gauge independence of physical amplitudes 148
Gauge invariance and local phase transformation 8 25 28Ч29 31
| Gauge invariance and mass of vector quanta 6Ч7 29Ч30 36Ч37 58Ч59
Gauge invariance and renormalisability 6 30 98
Gauge invariance in QED 2 26Ч29
Gauge invariance, hidden 5 7 9 30 36 58Ч59 96Ч104
Gauge invariance, non-Abelian 2 30Ч38
Gauge parameter 45Ч46 65 67Ч68 139
Gauge parameter, renormalisation of 139
Gauge principle 28Ч30 83 96
Gauge transformation in QED 26 28Ч29
Gauge transformation in Stuckelberg formalism 66 68Ч69
Gauge transformation, non-Abelian 30Ч33
Gauge, axial 57
Gauge, Coulomb 39 57
Gauge, covariant 46
Gauge, Feynman 44Ч45 48 57 64 67 127 133 135 139
Gauge, Landau 45
Gauge, Lorentz 39Ч40
Gauge, planar 57
Gauge, R 99 148
Gauge, U 99 104 148
Gauge-fixing term 38 45Ч46 57 65Ч66 113
Gauge-fixing term, 't Hooft 99 104
Gauge-fixing term, absence of counter-term for 139
Generations 107 120Ч121
Generator of 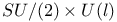 88 88
Generator of symmetry transformation 14Ч17 19Ч20 34
Georgi Ч Glashow electroweak model 63
Georgi Ч Glashow SU(5) 121Ч124
Ghosts 38 53 55Ч57 63 147
Glashow Ч Iliopoulos Ч Maiani (GIM) mechanism 117Ч118
Glashow Ч Salam Ч Weinberg (GSW) theory 1 30Ч31 36 58 60 62Ч63 70Ч71 87 90 105Ч124 145 154
Glashow Ч Salam Ч Weinberg (GSW) theory, connection with four-fermion theory 110
Global invariance 23 33
Global symmetry 71 83 85 87
Global transformation 8 23 31 69
Gluon 2 38
Gluon, exchange 2
Goldberger Ч Treiman relation 95
Goldstone, boson (massless modes in hidden symmetry) 73Ч83 86 88Ч89 93 96Ч97 99 139 155
Goldstone, boson (massless modes in hidden symmetry), 'swallowed' (in hidden gauge symmetry) 90
Goldstone, model 83Ч87
Goldstone, model, electromagnetic interactions in (Higgs model) 96Ч101
Goldstone, state 87
Goldstone, theorem 73 76Ч77
Grand unification 120Ч124
Gravity 7Ч9
Heisenberg interaction 76
Helmholtz free energy 84Ч85
Higgs, boson 98 103
Higgs, field 97 101 104 106
Higgs, field, mass 103 114
Higgs, mechanism 145
Higgs, meson 63
Higgs, model 96Ч101
Higgs, potential 121
Hypercharge, strong 37
Hypercharge, weak 106
Improper graphs 128
Inelastic electron scattering 120 155
Inelastic neutrino scattering 120 155
Invariance and conserved charge operators 20
Invariance, global 23 33
Invariance, local 23 33
Isospin and SU(2) group 28 33 89 94 102
Isospin, currents 94 145 147
Isospin, hadronic 22 30 37 94Ч95 115 145
Isospin, left-handed 92
Isospin, right-handed 92
Isospin, weak 30 94 105Ч106
IVB 109
Kibble model 78Ч79
Klein Ч Gordon equation 11
Landau mean field theory 85
Lepton mass 109 113Ч114
Lepton number 124
Lie algebra 20
Little group 89
Local invariance 23 33 145
Local non-Abelian symmetry 30Ч36
Local transformation 8 23 28 31 69
London equation 100
Loops and unitarity in non-Abelian gauge theories 52Ч53 56Ч57
Loops and unitarity in QED 55
Lorentz, condition 39 42Ч43 49
Lorentz, force 25
Lorentz, gauge 39Ч40
Low energy theorems 145Ч147
Mass of vector quanta and gauge invariance 7 29Ч30 36 105
Mass of vector quanta and renormalisability 7 58 68
Mass of vector quanta in GSW theory 110
Mass of vector quanta in hidden symmetry 83 98Ч104
Mass shift, due to renormalisation 128 130 138
Mass, unrenormalised 133
Massless states and hidden symmetry 74 76Ч77 79 81 85
Massless theories and scale invariance 156Ч158
Meissner effect 100
Minimal interaction in QED 25 29 31
Minimal interaction in Stuckelberg formalism 69
Momentum, canonically conjugate 11
Momentum, canonically conjugate to A∞ 41 45 57
Nambu Ч Goldstone realisation (of symmetry) 71
Nambu Ч Goldstone realisation of chiral symmetry 91 94 146
Negative norm states 39 42 67
Negative norm states, cancellation: in massive vector theory 68
Negative norm states, cancellation: in QED 44 68
Neutral weak current 3Ч5 63 105 109Ч112 115Ч120
Noether current 22 27 36 71 73 115
Noether current and BRS symmetry 56
Noether current and scale invariance 159
Noether's theorem 14 28
Non-Abelian gauge theories 2 30Ч38
Non-Abelian gauge theories and asymptotic freedom 162
Non-Abelian gauge theories, Feynman rules 39
Non-Abelian gauge theories, renormalisability 6 30
Non-Abelian symmetry 20
Non-Abelian symmetry, hidden global 87Ч91
Non-Abelian symmetry, hidden local 101Ч104
Non-Abelian symmetry, manifest local 29Ч36
Non-renormalisable theories 6 58 125
On-shell particle 128
One loop renormalisation 137Ч138
One particle irreducible graphs 128
One particle irreducible Green functions 160
One particle reducible graphs 128
Order parameter 77
Parity violation 4
Parity violation in 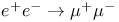 112Ч113 112Ч113
Parity violation in atomic physics 120
Parity violation in e-d scattering 120
Parity violation in electroweak interactions of hadrons 120
Parton model 115 120 163
PC AC 94Ч95 105
Penetration length 100
Phase angle, oscillations in 86 97
Phase transformation 8
Phase transformation, global 23 28 31
Phase transformation, local 23 25Ч26 28Ч36
Phase transformation, SU(2), SU(3) 8
Phase transformation, U(1) 8
Phase transition and hidden symmetry 85 87
Phase transition, Landau mean field theory of 85
Phase, hidden symmetry 101
Phonon-like modes in superfluid 81
Photon, mass 136
Photon, mass and hidden gauge symmetry 139
Photon, mass and infra-red divergences 139
Photon, polarisation vectors 42Ч43
Pion as Goldstone boson 94Ч95 146
Plasma frequency 82
Plasmons 82
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



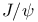 particles
particles  -function
-function 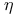 decay
decay  scattering
scattering 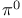 decay
decay  -model
-model 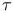 lepton
lepton  parameter
parameter