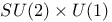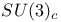|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Aitchison I.J.R. Ч An Informal Introduction to Gauge Field Theories |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Poisson bracket 11 14
Polarisation states, elimination of unphysical 39 44 46Ч47 49Ч52 56 58Ч59 145 147 154
Polarisation states, longitudinal: absence of, in massless theory 43 62
Polarisation states, longitudinal: and high energy behaviour 61 63Ч64
Polarisation states, scalar 43
Polarisation states, sum over: massive theory 61
Polarisation states, sum over: massless theory 49 62
Polarisation vectors for massive vector particle 60Ч61
Polarisation vectors for massless vector particle 42Ч43 49
Polarisation, vacuum 133Ч136
Propagator, electron 127Ч133
Propagator, gauge field quanta 41Ч42
Propagator, massive vector 59
Propagator, massive vector in hidden gauge symmetry 65 67 99
Propagator, massless vector 41 44Ч45 48 57 65 133Ч137
Propagator, renormalisation 127Ч137
Propagator, scalar field 41
Proper graphs 128
Proper Green functions 160
Proton decay 123
QCD 1 30 36Ч38 93 114 121
QCD and asymptotic freedom 2 162Ч163
QCD, infra-red behaviour 148 163
QCD, renormalisability 6
qed 1
QED, divergences in 6
QED, renormalisability 6
QED, renormalisation 126Ч139
Quantisation in Coulomb gauge 57
Quantisation of massive vector fields 58Ч70
Quantisation of massless vector fields 39Ч57
Quantisation of non-Abelian gauge theories 47 53Ч57
Quantisation, canonical 10Ч11
Quantisation, path-integral 11 53
Quark-lepton mass ratios 123Ч124
Quarks 1
Quarks in GSW theory 114Ч120
Quarks, charges of 124
Quarks, masses of 95 114 123Ч124
Quarks, weak currents for 115
Quasiparticles (Bogoliubov) 80Ч82
R-gauge 99
Regularisation 126
Regularisation and gauge invariance 133Ч134
Regularisation and scale invariance 159
Regularisation and Ward identity 146 148 153Ч154
Regularisation, cut-off 127 159
Regularisation, dimensional 127 133 159
Regularisation, Pauli Ч Villars 133 152
Renormalisability 6Ч7
Renormalisability of massive vector theory 59Ч64 68 105
Renormalisability of theories with hidden gauge invariance 30 98Ч99 105Ч106
Renormalisation 6 125Ч163
Renormalisation and anomalies 150 154Ч155
Renormalisation and mass-shift 128 130
Renormalisation and scale invariance 155Ч163
Renormalisation of charge 136Ч137 144
Renormalisation of coupling strength and weak angle 122
Renormalisation of non-Abelian gauge theories 147Ч148
Renormalisation of QED 138Ч139
Renormalisation, conditions 159Ч160
Renormalisation, group 161
Renormalisation, multiplicative 146
Renormalisation, point 160Ч162
Renormalisation, universality of coupling preserved under 144 147
Representation, adjoint 20
Representation, matrix 20Ч21
Representation, regular 20Ч21 34 46
Rotational invariance 12Ч15
Scale dimension 158Ч162
Scale invariance 7 126 155Ч163
Scale invariance and deep inelastic lepton scattering 155Ч156
Scale invariance and massless theories 156Ч158
Scale invariance and renormalisation 158Ч163
Scale invariance and Ward identities 159Ч162
Scale invariance in statistical mechanics 155Ч156
Scales of symmetry breakdown 123
Scaling behaviour 162
Scaling behaviour, departures from, in asymptotically free theories 162
Schwinger terms 51 146
Seagull terms 51 146
Self-energy of electron 127
Self-energy of photon 133Ч136
Simple group 121
Slavnov Ч Taylor identities 147Ч148 154
Source currents 27 36
Spin waves in ferromagnet 77
Statistical mechanics, correlation length 156
Statistical mechanics, critical point 156 162
Statistical mechanics, scale invariance in 155
Strangeness 115
Strangeness-changing weak neutral currents 115Ч120
Strong interactions see "QCD"
Structure constants 20 34
Structure function 155
Stuckelberg formalism 65Ч68
Subsidiary condition 44 46
Superconductor 83 87 100
Superfluid (Bogoliubov) 79 86Ч87
Superfluid (Bogoliubov), transition temperature 79
Superheavy mass scale 122Ч123
Sutherland Ч Veltmann result (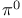 decay) 148Ч149 153 decay) 148Ч149 153
Symmetry and conservation laws 12Ч14
Symmetry and dynamics 7Ч9
Symmetry and gauge theories 7
Symmetry, 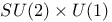 5 36 101Ч106 108 112 114Ч123 145 5 36 101Ч106 108 112 114Ч123 145
Symmetry,  92 94 92 94
Symmetry,  and fourdimensional rotations 92Ч93 and fourdimensional rotations 92Ч93
Symmetry, 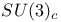 37 121 37 121
Symmetry,  123 123
Symmetry,  37 145 37 145
| Symmetry,  116 116
Symmetry, Abelian 20
Symmetry, algebra 38
Symmetry, breakdown: radiatively induced 101 see hidden"
Symmetry, chiral 2 71 91Ч96
Symmetry, gauge, hidden, and photon mass 139
Symmetry, global 8 28
Symmetry, global, Abelian, hidden 83Ч87
Symmetry, global, chiral, hidden 91Ч96
Symmetry, global, non-Abelian, hidden 87Ч91
Symmetry, hidden 15 30 36 58Ч59 65 68Ч103
Symmetry, hidden, phase 85 101
Symmetry, local 8 28
Symmetry, local, Abelian, hidden 96Ч101
Symmetry, local, manifest 28Ч36
Symmetry, local, non-Abelian, hidden 101Ч104
Symmetry, manifest 10Ч23 36
Symmetry, Nambu Ч Goldstone realisation see "Symmetry hidden"
Symmetry, non-Abelian 8 20 30Ч36
Symmetry, not unitarily implementable see "Symmetry hidden"
Symmetry, partial 105
Symmetry, spontaneously broken see "Symmetry hidden"
Symmetry, SU(2) 5 20Ч22 28 30Ч33
Symmetry, SU(3) 38
Symmetry, SU(5) 121Ч124
Symmetry, unitarily implementable see "Symmetry manifest"
Symmetry, Wigner Ч Weyl realisation see "Symmetry manifest"
Transformation, Bogoliubov 82
Transformation, BRS: Abelian 54Ч55
Transformation, BRS: non-Abelian 54Ч56
Transformation, gauge in QED 26
Transformation, gauge in Stuckelberg formalism 69
Transformation, global 8 23 31
Transformation, local 8 23 28 31
Transformation, scale 156Ч158
Transformation, symmetry, generators of 14Ч17 19
U(1), gauge symmetry 8 28 96
U(1), hidden local 96Ч101
U(1), problem(s) 155
U(1), symmetry group 20 35Ч36 81 85Ч86 88Ч89
U-gauge (unitary gauge) 99 104
Unified theories 7 9 105 120Ч124
Unitarity and anomalies 154
Unitarity and elimination of unphysical polarisation states 47Ч53
Unitarity and Slavnov-Taylor identities 147Ч148
Unitarity and Ward identities 47Ч51
Unitarity, violation: and negative norm states 39
Unitarity, violation: and renormalisability 59Ч64
Universal strength and gauge theory 5 35 118 145 147
Universal strength of weak interactions 5 145
Unrenormalised charge 136 144
Unrenormalised field 132
Unrenormalised mass 132
Upsilon T particle 121
V-A theory 4 107
VACUUM 18
Vacuum and Fabri Ч Picasso theorem 71Ч72
Vacuum as ground state 75 85
Vacuum in QED 43Ч44
Vacuum in Stuckelberg model 70
Vacuum, current 100
Vacuum, expectation value, non-vanishing 73
Vacuum, polarisation 133Ч136
Vacuum, polarisation and charge renormalisation 144
Vacuum, quantum fluctuations in 128Ч129 131
Vacuum, role in hidden symmetry 75
Vector boson, intermediate (IVB) 109
Vector boson, mass in GSW theory 110
Vector field (gauge), mass of 29 30 36 70
Vector field (gauge), massive and renormalisability 58 60Ч64
Vector field (gauge), massive and unitarity violation 60Ч64
Vector field (gauge), massive, propagator for 58
Vector field (gauge), quantisation of: massive 58Ч70
Vector field (gauge), quantisation of: massless 39Ч57
Vector potential, electromagnetic 8 25Ч26 39Ч40
Vertex, electron-photon 140
Vertex, renormalisation constant 137 140 144
Vertex, renormalised 141
W boson 3 90 103 105Ч106 110 118
W boson, mass 4 110
W boson, width 110
Ward Ч Takahashi identities 140Ч148
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and BRS transformations in non-Abelian gauge theories 54Ч56 147Ч148
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and BRS transformations in QED 54
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and current conservation 50 140 142
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and regularisation procedure 146 148
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and renormalisability 53 125 147Ч148 154
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and scale invariance 159Ч162
Ward Ч Takahashi identities and unitarity 47Ч51 53 126
Ward Ч Takahashi identities for axial currents 146Ч148
Ward Ч Takahashi identities in QED 53Ч54 133 138 152
Ward Ч Takahashi identities,  140 142 144 147 140 142 144 147
Ward Ч Takahashi identities, anomalous 153
Wave function renormalisation constant 131Ч132 144
Weak angle 103Ч104 108 110 112 120
Weak angle in SU(5) 122
Weak angle, higher-order corrections to 110
Weak interaction 105 124
Weak interaction, range 3Ч4
X boson 123
Yang Ч Mills theory 8
Yang Ч Mills theory of strong interactions (QCD) 36
Yang Ч Mills theory, one coupling constant in 35
Yang Ч Mills theory, quadrilinear couplings in 33
Yang Ч Mills theory, trilinear couplings in 33
Yang Ч Mills theory, universality in 35
Yukawa interaction 3Ч6
Yukawa interaction and lepton mass 113
Yukawa interaction and quark mass 120
Z∞ boson 4 63 90 103 105Ч106 110 117 119
Z∞ boson, mass 4 110
Z∞ boson, width 110
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



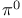 decay)
decay)