јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Callaghan P. Ч Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopyјвтор: Callaghan P. јннотаци€: Although nuclear magnetic resonance is perhaps best known for its spectacular utility in medical tomography, its potential applicability to fields such as biology, materials science, and chemical physics is being increasingly recognized as laboratory NMR spectrometers are adapted to enable small scale imaging. This excellent introduction to the subject explores principles and common themes underlying two key variants of NMR microscopy, and provides many examples of their use. Methods discussed are not only important to fundamental biological and physical research, but have applications to a wide variety of industries, including those concerned with petrochemicals, polymers, biotechnology, food processing, and natural product processing. The wide range of scientists interested in NMR microscopy will want to own a copy of this book.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1991 оличество страниц: 492ƒобавлена в каталог: 28.06.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Absorption imaging 18Ч20 Acceleration 354 Acetabularia 242 Active shielding 471Ч472 Adhesives 257 Aerosol OT 349 Aliasing 11 Anderson Ч Weiss theory 63 415 Angiography 423 433 Angular momentum, quantization 21 Angular momentum, vector 35 Animal tissue, imaging 244Ч254 Animal tissue, spectrum of proton relaxation times 233Ч234 Anisotropic diffusion 344Ч350 Apodization filter 185Ч189 Apparent diffusion coefficient 372Ч373 Artefacts 5 209 Artefacts, chemical shift 278Ч280 Artefacts, diffusion 451 456 Artefacts, gradient induced phase shifts 452Ч456 Artefacts, phase 453 Artefacts, zero-filling 453Ч454 Autocorrelation function 334 376 Average propagator 332 Average propagator for diffusion and flow 333 Average propagator for restricted diffusion in the long timescale limit 376Ч380 Back-projection 20 Bandwidth 11 Bandwidth, of r.f. pulse 57 Bandwidth, optimal 191Ч192 Belosov Ч Zhabotinsky reaction 276 Best 155 Binomial sequence 292 294 Bipolar gradient 355 426 436 Bloch decay 48 306 Bloch equations 39 Bloch vector 53 Bolus tagging 423 Broadening regimes 185 Brownian motion 157Ч162 331Ч334 Brownstein Ч Tarr model 408Ч413 Bryophyllwn tubiflore 237 Capillary flow 443Ч446 Carbon imaging 301Ч306 Cardiac cycle 434 Cardiac gating 247 Carr Ч Purcell echo train 65 Carr Ч Purcell Ч Meiboom Ч Gill (CPMG) sequence 75Ч76 Cartesian and polar coordinates 19 122 CE-FAST 151Ч152 422 Cell imaging 251Ч254 Central limits theorem 159 Ceramics 257 Chapman Ч Kolmogoroff equations 406 Chemical exchange magnetic resonance imaging 296 Chemical selection 98 141Ч143 283Ч287 Chemical shift 49Ч50 Chemical Shift Imaging 280Ч282 Chemical shift, artefacts 278Ч280 Chemical shift, contrast and higher-dimensional strategy 280Ч281 Chemical shift, image displacement 278 Chemical shift, isotropic 50 Chemical shift, selective multislice images 141 Chemical shift, tensor 50 Chemical waves 276 Chemically selective excitation see УChemical selectionФ Chess 141 283 287 Chromatographic and electrophoretic separation 458 Coherence 32Ч33 Coherence peaks 392 398 Coherence time for turbulence 363Ч367 451 Coherence transfer 79Ч85 288 301Ч304 Coherent noise cancellation 67 Coherent superposition 13 Collimated sources 17 Conditional probability 330Ч332 406 438 Conditional probability flux 331 Conjugate space 2Ч4 18 Connection matrix 388Ч389 Continuity theorem 331 contrast 22 25 267Ч296 Contrast, 277 Contrast, 270Ч277 Contrast, 271 Contrast, agents 277Ч278 Contrast, chemical shift 278Ч287 Contrast, factor 97 Convolution 8Ч9 45 135 386 Convolution, broadening 14 74 Convolution, due to apodization filter 186 Convolution, integral 8 20 Convolution, theorem 8 Correlation function 415 see УSelf-correlation Correlation function, dipolar 60 Correlation function, fluctuating field 415 Correlation function, lattice 394 Correlation function, Van Hove 330 Correlation function, velocity 335Ч337 correlation length 363 394 414 Correlation regularity 393 Correlation time 335 414 416 Correlation time, exchange 231 Correlation time, for translation 335 Correlation time, rotational 61 230 Couette flow 362 CPMAS 317 CRAMPS 310 313 Crusher pulses 137 Cryofluid freezing 277 Current control 463 Curvilinear diffusion 401Ч403 Cyclops 67Ч68 430 Dante 120Ч121 308 426 438 Demagnetizing field 209 Density matrix 31 Deuterium imaging 299 318 diamagnetic susceptibility 208Ч224 Diffraction 3Ч4 Diffraction, analogy 337Ч341 386Ч399 Diffraction, effect 398 Diffraction, intensity 3 Diffraction, pattern 13 Diffraction, phase problem 3 Diffraction, scattering centres 4 Diffusion see also УSelf-diffusionФ УMutual УPseudo-diffusionФ Diffusion, artefact 451 Diffusion, bounded 337 Diffusion, dephasing and echo attenuation effects 201 204Ч206 217Ч224 Diffusion, in polymer gels 401 Diffusion, restricted 328 346 371Ч401 449 Diffusion, resulting point spread function 204 Diffusion, spectrum 335 344 357 Diffusion, tensor see УDiffusion spectrumФ Diffusive broadening 204 Diffusive broadening, influence according to k-space direction 206 Diffusive contrast 434 438Ч458 Diffusive envelope 392 Diffusive linewidth see УDiffusive broadeningФ Diffusive resolution limit 205 Digger 117 287 Diode duplexor 461 Dipolar interactions 46Ч49 58Ч64 306 Dipolar line-narrowing 85Ч91 Dipolar linewidth 86 Dirac delta function 4 dispersion 43 73 129 Dispersion, image 133 Dispersion, spectrum 43 73 129 Distortion 124 209Ч217 224Ч225 Double quantum coherence 54Ч57 290 318 Driven Equilibrium Fourier Transform method 79 Droplet size distribution 350 382 Dynamic displacement 332 339Ч341 Dynamic displacement profile 440Ч441 449 451 Dynamic equilibrium 65 77Ч79 Dynamic NMR microscopy 438Ч457 Dynamic NMR microscopy, contrast 440 Dynamic NMR microscopy, digital computation 441 Dynamic NMR microscopy, resolution 438 Dynamic nuclear polarization 308 Dynamic viscosity 443 e.m.f. induced in the receiver coil 174Ч177 echo see also УGradient echoФ УSolid УSpin УStimulated Echo attenuation 157Ч169 328 Echo attenuation, 'pathological' 387 Echo attenuation, Carr Ч Purcell train 161 Echo attenuation, diffusion and flow 164 Echo attenuation, steady gradient 160 Echo planar imaging 152Ч157 435 Echo planar imaging, comparison with FLASH 157 Echo planar imaging, diffusive effects 206Ч208 Echo planar imaging, echo summation 143 147 194Ч197 Echo planar imaging, optimum conditions 208 Echo planar imaging, optimum sensitivity 147 Echo planar imaging, raster 153 Echo planar imaging, unequal sampling intervals 156 Echo planar imaging, with bipolar encoding gradient 436 Echo summation 143 147 194Ч197 Echo summation, diffusive effects 206Ч208 Echo summation, optimum conditions 208 Echo summation, optimum sensitivity 147 Echo, even and odd 366 Echo, negative time 128 Echo, spin and gradient 105 113 116 Eddy currents 470Ч471 Eddy gradient compensation and suppression 471 Effective field 37 98 Effective gradient 167Ч168 354 428 433 Elastomer, imaging 263Ч267 Elastomer, spin echo and gradient echo imaging 267 Elastomer, structural morphology 267 Electric quadrupole interactions 25 Electron spin resonance 22 Embryogenesis 251 Emission imaging 17 21 energy levels 30 Ensemble averaging 25 31 Epoxy resin composites 257 Ernst angle 66 Erythrocyte membrane permeability 233 Evolution, during selective excitation 102Ч113 Evolution, of a nuclear spin quantum state 28 Evolution, of polarization states 72 81Ч85 301Ч306 Evolution, of the density matrix 31 Evolution, operator 28 Evolution, time 97 Evolution, under effective gradient 353Ч357 Evolution, with average Hamiltonian 87Ч90 Exchange 221 232 296 298 408 Exponential filter 185Ч186 Extreme narrowing 61 Fade 152 422 FAST 151 422 Fast motion limit 64 Fast-exchange averaging 221 FI and PR 18Ч20 122Ч128 FI and PR, comparison of methods 224 Fick's law 331 FID see УFree Induction DecayФ Field inhomogeneity 45 Filter, bandpass 11 Filter, optimal 186 Filtered back projection see УProjection reconstructionФ УFI Filtered profile 127 Filtered transform 20 129 FISP 152 Flash 148Ч149 435 FLASH, advantages 149 FLASH, relaxation contrast 149 FLASH, snapshot 149 FLASH, spoiled 149 FLEET 152 Flow measurement 163Ч169 341Ч342 421Ч449 Flow measurement, direct visualization of motion 426 Flow measurement, effect of gradient non-uniformity 455 Flow measurement, effect of self-diffusion 433 Flow measurement, nulling the stationary signal component 429 Flow measurement, periodic motion 434 Flow measurement, phase shift 420 426Ч424 Flow measurement, range of velocities 421 Flow measurement, replenishment effects 446 Flow measurement, slice selection gradient effects 421 Flow measurement, steady state 420 422 Flow measurement, time of night 420 423Ч426 Flow measurement, using CPMG train 435 Flow measurement, using DANTE sequence 426 Flow measurement, using stimulated echo 423 Flow, compensation using even echoes 449 Flow, random 362Ч367 Flow, suppression of phase shifts 435 Flow, through porous media 363 Flow, visualization 362 Fluorine imaging 296 Forced rayleigh scattering 436 Form factor 392 Fourier filtration 18 20 Fourier imaging 122Ч124 Fourier transformation 2Ч8 13 94Ч95 Fourier transformation, antisymmetric 12 Fourier transformation, Cartesian coordinates 95 Fourier transformation, complex transformation 11 Fourier transformation, conjugate transformations 10 Fourier transformation, conjugate variables 2 Fourier transformation, Cooley and Tukey 11 Fourier transformation, discrete 10Ч11 Fourier transformation, in dynamic NMR microscopy 441 Fourier transformation, inverse 8 20 95 Fourier transformation, inverse in polar form 127 Fourier transformation, one-dimensional 19 Fourier transformation, optical microscopy 12Ч15 Fourier transformation, real and imaginary 11Ч12 Fourier transformation, relationship between average propagator and echo amplitude 340 Fractal behaviour 404Ч405 Fractal dimension 405 Free induction decay (FID) 42Ч43 Free Induction Decay (FID), Gaussian 48 Frequency domain 95 Full Ч Width Ч Half Ч Maximum 42 Full Ч Width Ч Half Ч Maximum of dynamic, displacement profile 442 Gadolinium-diethylene-triaminepenta-acetic acid 278 Gaussian, assumption 356 Gaussian, lineshape 48 Gaussian, pulses 100 Geen et al pulse 116 Gradient coil 461Ч463 Gradient coil, double and single screening 470Ч477 Gradient coil, gradient uniformity under screening 475 Gradient coil, saddle, Maxwell pair, quadrupolar, Helmholtz, and planar 470 475 Gradient coil, target field approach 474 Gradient, current 461Ч465 Gradient, echo 105 113Ч125 136Ч138 Gradient, frequency domain treatment 358 Gradient, linearity 463 Gradient, modulated 353Ч362 Gradient, phase cycling 429 431 Gradient, power supplies 463 Gradient, pulse matching 452 Gradient, reversal 113 138 Gradient, rise time 137 470Ч471 Gradient, spectrum 358
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



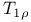
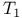 and
and