|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Myers J.L., Well A.D. Ч Research design and statistical analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
kurtosis 31Ч32
Kutner, M.H. 56 737
Latin-square designs 457Ч477 see
LaVange, L.M. 363 737
Least absolute deviation criterion 548 see also Regression
Least-squares criterion 51Ч52 60
Lee, D.M. 629 737
Lee, W-C. 493Ч494 735
Leeuw, J. de 551 735
Lehmann, E.L. 372 735
Leighton, J. 424 734
Lepine, D. 335 739
Leroy, A.M. 56 542 585 739
Levene, H. 161 185 222 735
Levenetest 161 185 222
Leverage of 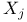 528 584 726 528 584 726
Levin, J.R. 253 724 736
Levine, D.W. 122 735
Lindauer, P. 436 735
Lindeman, R.H. 507 736
Lindquist, E.F. 205 217 736
Line graphs 25
Linear combinations 136Ч139 722 see Regression
Linear equation 44
Linear independence 616
Linear relations 43Ч44
Linn, R.L. 403 736
Lix, L. M. 221 225Ч226 736
Location see central tendency
Lorch, R.F. 444 549 607 736 737
LOWESS 42 533
Ludwig, T.E. 479 741
Lunney, G.H. 217 736
MacGillivray, H.L. 32 729 731
Mahalanobis distance 545Ч548 see
Main effect contrasts see Contrasts among means
Main effects 202 289Ч293 307 325
MannЧ Whitney U test 220
Mans, E. 522 736
Marascuilo, L.A. 220 724 736
Marginal probability see Probability
Matched-pair design see Repeated-measures design
Matthews, C.E. 726 736
Matthews, K.A. 4 738
Mauchly test for sphericity 357
Mauchly, J.W. 357 736
Maxwell, S.E. 209 361 370 403 428Ч429 588 590Ч591 736
McCann, J. 163 737
McLean, R.A. 403 734
Mead, R. 333Ч334 736
Meade, M.L. 339 739
Mean of a linear combination 137Ч138
Mean of a population 79Ч80
Mean of a sample 11 20Ч23
Mean, harmonic mean 340
Mean, properties of 22
Mean, standard error of the mean (SEM) 24Ч25
Mean, trimmed mean 24 111 222
Mean, weighted mean 22
Measurement error and correlation 486
Measurement error and regression 531Ч532
Measures of importance see Effect size
Median 11 13Ч15
Median, depth of 13Ч15
Mendoza, J.L. 357 739
Meng, X-L. 501 736
Merenda, P.F. 507 736
Merriam, P.A. 726 736
Micceri, T. 12 106 493 736
Midsummary scores 30
Miller, D.J. 531 737
Miller, R.G. 179 737
Miller, R.G., Jr. 252 737
Min FТ 370 384Ч385
Missing scores, estimating 349Ч350 465
Mittlehammer, R.C. 531 726 737
Mixed designs 191 386Ч408 see
Mixed-normal distribution 111
Moderator variable 601
Morrison, D.F. 360 737
Morrow, L.M. 6 737
Mosteller, F. 33 179 732 734 737 739
Mulaik, S.A. 212 733 740
Muller, K.E. 363 737
Multicollinearity 570Ч572 596Ч598 see
Multifactorial ANOVA designs see Analysis of variance
Multilevel modeling 551 see also Regression
Multiple correlation coefficient, R 200Ч201 524 565Ч580;
Multiple regression see Regression
Multivariate analysis of variance (Manova) 359Ч361 see
Murray, J.E. 363Ч364 367 371 437 737
Muticorr program 501
Myers, J.L. 163 193 203 217 234 246 318 357 359 376 396 412 415 429 444Ч445 464 469 549 607 626 724 725 729 731 736 737 738
Myers, N.A. 61 75 84 737
Nachtscheim, C.J. 56 737
Namboodiri, N.K. 476 737
Negatively biased test 216 333
Nested factors 389Ч390 437 see Hierarchical
Neter, J. 56 531 542 585 737
Newman, D. 255 737
Neyman, J. 424 734 735
Nicewander, W.A. 46 738
Nonadditivity see Analysis of variance
Noncentral distributions, the F 210
Noncentral distributions, the t 147Ч148
Noncentrality parameters 148 162 210Ч211 317 491 588Ч590
Nonorthogonal designs 319Ч324 623Ч629
Nonparametric tests 152 217 219Ч220 372Ч377
Noon, S.N. 492Ч493 732
Normal approximation to the binomial 128Ч129
Normal distribution see Distributions
Normal equations in regression 60
Normality assumption 124 178 184Ч185 217 287
Notation and summation operators see Appendix A 641Ч648
Nuisance variable see Variable
Null hypothesis see Hypothesis testing
Observational study 3
Ockene, I.S. 726 736
Odeh, R.E. 372 737
Oilman, D.O. 225 731
Olkin, I. 146 210 501 586Ч587 733 735 737
Omega squared, 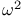 see Effect size see Effect size
Omnibus null hypothesis 192 233
Omnibus null hypothesis for correlation matrices 500
One-tailed tests see Hypothesis testing
Orthogonal contrasts 259Ч260
Orthogonal designs 621Ч623
Orthogonal polynomials see Trend analysis
Oshima, T.C. 220 737
Outer fence 16
Outliers 15Ч17 55Ч56 542Ч548
Overall, J.C. 428 731
Overall, J.E. 627 629 737 738
Overton, R.C. 548 738
Owens, J.F. 4 738
OТBrien, E.J. 469 731
pairwise comparisons see Contrasts among means
Parks, C.D. 436 443 740
Part correlation see Correlation
Partial correlation see Correlation
Partial F tests 582Ч583 see
Partial regression coefficients 564 see
Partial slope coefficients 564 see
Partitioning variability 196Ч197 230Ч231 388Ч390 437-444 517Ч518 525 573Ч577
Pearson, E.S. 726 738
Pedhazur, E.J. 489 502 593 738
Peritz, E. 255 738
Perlmutter, J. 257 738
Peterson, N.L. 493 733
Petrie, G. 436 735
| Phi coefficient see Correlation
Planned contrasts see Contrasts among means
Point estimates 89 113
Point-biserial correlation coefficient see Correlation
Pollatsek, A. 477 738
Polynomial analysis of covariance see Analysis of covariance
pooling 332Ч334 441Ч443 see Hierarchical
Population parameters 2
Populations 2
Populations, distinguished from samples 2
Positively biased test 217
Post hoc contrasts see Contrasts among means
Power for analysis of covariance 430
Power for bivariate regression 527Ч528
Power for multifactor between-subjects ANOVA 318Ч319
Power for multiple regression 587Ч591 726
Power for one-factor between-subjects ANOVA 212Ч215
Power for one-sample t test 147Ч151
Power for repeated-measures designs 363
Power for t test of two independent means 157Ч158
Power for test of a single correlation 495Ч496
Power for test of the equality of independent correlations 498
Power for tests using the binomial distribution 83Ч86
Power for z test 119Ч122
Power transformation 223Ч224 351Ч352
Power, a priori calculation 147
Power, factors affecting power 121Ч122
Power, functions for the binomial distribution 85
Power, GPOWER see GPOWER
Power, post hoc calculation 147
Power, specific alternative hypothesis 84
Power, SYSTAT power module 493 497 725
Pretest-posttest designs 402Ч403
Probability distributions see Distributions
Probability of unions of events 69
Probability plot 287
Probability, conditional 69Ч70 97Ч99
Probability, definition 68 72
Probability, density function 101
Probability, introduction to 67Ч72
Probability, joint 68
Probability, marginal 68
Probability, posterior 98
Probability, prior 98
Probability, rules of 71 72
Pseudogroup procedure 444
Pun, F.C. 592 738
Pure error 537Ч539
Quasi-F tests 368Ч370 444Ч445 451Ч452
R2 program 586
Raaijmakers, J.G.W. 473 738
Raekkoenen, K. 4Ч5 738
Ragosa, D. 522 738
Ramey, C.T. 363 737
Ramey, S.L. 363 737
Ramsey, P.H. 255 738
Randies, R.K. 111 734
Random assignment 4
Random coefficients modeling see Multilevel modeling
random selection 68
Random-effects variables 192
Random-effects variables as opposed to fixed effects variables 202 371Ч372
Rank-transformation F test 219 373
Rasmussen, J.L. 496 738
Ratcliff, R. 121 738
Raudenbush, S. W. 551 730
Raw-score formulas see Computational formulas
Reference group see Coding of categorical variables
Regression analysis see Regression
Regression with categorical variables 614Ч637
Regression, adjusted (shrunken) multiple correlation coefficient R 524 577Ч580
Regression, bivariate regression 51Ч54 519Ч561
Regression, bivariate regression, coefficients are unbiased estimators 558Ч559
Regression, bivariate regression, coefficients as linear combinations of the Y scores 557Ч559
Regression, bivariate regression, egression from the mean 522
Regression, bivariate regression, inference, see Regression Inference about bivariate regression
Regression, bivariate regression, least absolute deviation criterion 548
Regression, bivariate regression, least-squares criterion 51Ч52 60
Regression, bivariate regression, partitioning of variability 517Ч518 525
Regression, bivariate regression, regression coefficients 522Ч523
Regression, bivariate regression, regression toward the mean 519Ч522
Regression, bivariate regression, standardized coefficients 525
Regression, bivariate regression, two-group ANOVA as a special case 529Ч531
Regression, capitalization on chance 577Ч580
Regression, checking for violations of assumptions independence, and the Durbin-Watson statistic 533 541Ч542
Regression, checking for violations of assumptions, linearity 537Ч539 598Ч599
Regression, checking for violations of assumptions, using residuals 536Ч538
Regression, coding of categorical variables 615Ч621 727
Regression, coding of categorical variables, dummy coding 617 620Ч621 727
Regression, coding of categorical variableseffect coding 617Ч621
Regression, coefficients as linear combinations of Y scores 559Ч561
Regression, cross-validation 577Ч580
Regression, curvilinearity, testing for 598Ч601
Regression, direct and indirect effects 596
Regression, factorial designs 621Ч629
Regression, factorial designs, nonorthogonal designs 623Ч629
Regression, factorial designs, orthogonal designs 621Ч623
Regression, homogeneity of regression slopes 630Ч631
Regression, independent slopes, testing for equality 548Ч549
Regression, inference about bivariate regression 522Ч532
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, estimators of regression coefficients 530 (table)
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, homoscedasticity 522 539Ч540
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, independence 541Ч542
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, inference about 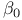 and and 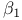 523Ч527 523Ч527
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, inference about a new value of Y at 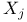 528Ч529 528Ч529
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, inference about the population regression line 528
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, leverage of 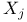 528 528
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, models for regression, model for nonexperimental research 531Ч532
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, models for regression, model with fixed-effect predictors 522
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, normality 540Ч541
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, power calculations 527Ч528 see
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, robust regression 548
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, standard error of estimate 524Ч525
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, standard errors for 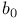 and and 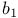 525Ч526 525Ч526
Regression, inference about bivariate regression, standard errors for 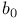 and and 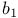 derivation 559Ч560 derivation 559Ч560
Regression, inference about multiple regression confidence intervals for the squared multiple correlation coefficient 585Ч587
Regression, inference about multiple regression, inference about a single coefficient 581Ч582
Regression, inference about multiple regression, inference about predictions of Y 583Ч584
Regression, inference about multiple regression, models and assumptions 580
Regression, inference about multiple regression, power 587Ч591
Regression, inference about multiple regression, testing the hypothesis that all the partial coefficients are zero 581
Regression, interactions 601Ч606
Regression, interactions between a quantitative and a dichotomous variable 604Ч606
Regression, interactions between quantitative variables 601Ч604
Regression, matrix algebra approach to see Supplementary Materials folder of CD
Regression, measurement error 531Ч532
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity) 570Ч572 596Ч598
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity), centering 598
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity), condition index 597
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity), tolerance 570Ч571 597
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity), variance inflation factor 571 597
Regression, multicollinearity (collinearity), variance proportions 597Ч598
Regression, multilevel modeling 551
Regression, multiple correlation coefficient R 524 573Ч578
Regression, multiple regression 562Ч608
Regression, multiple regression, analysis of covariance as a special case 632Ч634
Regression, multiple regression, analysis of variance as a special case 615Ч629 634Ч637
Regression, multiple regression, explanation versus prediction 593Ч594
Regression, multiple regression, general linear model 614Ч637
Regression, multiple regression, inference see Regression Inference
Regression, multiple regression, interpretation of the coefficients 572Ч573 593-596
Regression, multiple regression, multiple correlation coefficient 573Ч580
Regression, multiple regression, partial F tests 582Ч583
Regression, multiple regression, partial regression coefficients 564
Regression, multiple regression, partial slope coefficients 564
Regression, multiple regression, partitioning of variability 573Ч577
Regression, multiple regression, specification errors 594Ч596
Regression, multiple regression, specification errors, including irrelevant variables 595Ч596
Regression, multiple regression, specification errors, omitting relevant variables 594Ч595
Regression, multiple regression, standard error of estimate 565Ч567
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



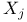
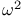
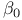 and
and 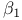
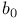 and
and