|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Macmillan N., Creelman D. Ч Detection Theory: A User's Guide |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
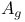 (area under the multipoint ROC) 64 330 (area under the multipoint ROC) 64 330
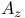 (area under the SDT ROC) 63 172 330Ч331 (area under the SDT ROC) 63 172 330Ч331
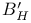 (area-based measure of response bias) 103 (area-based measure of response bias) 103
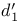 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 59Ч60 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 59Ч60
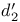 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 59Ч60 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 59Ч60
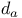 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 61Ч62 330Ч331 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 61Ч62 330Ч331
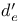 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 62Ч63 (sensitivity measure in SDT) 62Ч63
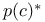 (proportion correct with unequal presentation probabilities) 7 (proportion correct with unequal presentation probabilities) 7
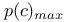 (unbiased proportion correct) 153 (unbiased proportion correct) 153
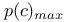 (unbiased proportion correct) in 2AFC 170Ч175 (unbiased proportion correct) in 2AFC 170Ч175
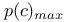 (unbiased proportion correct) in yes-no 153 171Ч172 see (unbiased proportion correct) in yes-no 153 171Ч172 see
 (sensitivity measure in Choice Theory) 95Ч96 (sensitivity measure in Choice Theory) 95Ч96
 (sensitivity measure in Choice Theory) and d' 95Ч96 (sensitivity measure in Choice Theory) and d' 95Ч96
 (normal distribution likelihood ratio) 33Ч35 67Ч69 (normal distribution likelihood ratio) 33Ч35 67Ч69
 (normal distribution likelihood ratio), calculation of 374Ч375 (normal distribution likelihood ratio), calculation of 374Ч375
 (logistic distribution likelihood ratio) 98 (logistic distribution likelihood ratio) 98
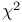 (chi-square) distribution 103 (chi-square) distribution 103
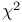 test 353Ч354 test 353Ч354
 (contingency statistic) 103 (contingency statistic) 103
 (normal density) see "Normal distribution" (normal density) see "Normal distribution"
 (normal distribution function) see "Normal distribution" (normal distribution function) see "Normal distribution"
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice) 166Ч179
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice) vs one-interval 167Ч168 175Ч176 181Ч182
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice) vs other designs 181Ч183 234 251 253Ч255
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), advantages 179
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), decision space 168Ч170
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), hit and false-alarm rates 167
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), response bias 170 287Ч289
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), ROC 173Ч174
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), sensitivity 168 170Ч175 426Ч430
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), statistical properties of d' 328Ч329
2AFC (two-alternative forced-choice), unbiased performance 170Ч171
3AFC (three-alternative forced-choice) 249Ч252 426Ч430
3AFC (three-alternative forced-choice) vs other designs 251Ч255
A priori probabilities see "Presentation probabilities"
A' (area under the one-point ROC) 100Ч103
Absolute judgment 113 see one-dimensional" "Classification multi-dimensional" "Identification absolute"
ABX 229Ч235
ABX vs other designs 234Ч235 253Ч255
ABX, decision space 231Ч234
ABX, differencing model 233Ч234
ABX, hit and false-alarm rates 230
ABX, independent-observation model 230Ч233
ABX, response bias 232Ч233
ABX, ROC 232Ч233
ABX, sensitivity 232Ч233 380Ч400
ABX, threshold model 234Ч235
Accuracy see "Sensitivity"
Adaptation level 129Ч130
Adaptive methods 267Ч296
Adaptive methods for slope estimation 293Ч294
Adaptive methods vs nonadaptive methods 269Ч270 276
Adaptive methods, components of 277
Adaptive methods, decision rules 277Ч280
Adaptive methods, evaluation of 289Ч292
Adaptive methods, stepping rules 281Ч285
Adaptive methods, stopping rules 285Ч286
Adaptive methods, target proportion 277 280Ч281 see "Bekesy "HallТs "KaernbachТs "Maximum-likelihood "PEST" "QUEST" "UDTR" "Wald
Adaptive Probit Estimation (APE) 294
Animal experiments 229Ч233 271Ч272
AOC 206Ч209
Area theorem 170Ч171
Area under the ROC 170Ч175
Area under the ROC for multipoint ROC see "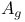 " "
Area under the ROC for one-point ROC see "A'"
Area under the ROC in SDT see "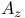 " "
Attention, capacity model 207Ч209
Attention, divided 188 204Ч205
Attention, incomplete 46Ч47
Attention, operating characteristic see "AOC"
Attention, selective 188 203Ч204 see "Uncertainty"
Audiology 269Ч270
AX design see "Same-different"
b (criterion measure in Choice Theory) 97
b' (relative criterion measure in Choice Theory) 98
B'' (area-based measure of response bias) 103Ч104
Bayesian rule 285
Bekesy audiometry 269Ч270
Best PEST 284Ч285
Binomial distribution 320Ч323 345Ч348
Boundary theorem 251Ч252
c (criterion measure in SDT) in multi-interval designs see "Response bias under specific design"
c (criterion measure in SDT), calculation of 20Ч21 29 374Ч375 427Ч430
c (criterion measure in SDT), confidence intervals 328
c' (relative criterion measure in SDT) 31Ч33
c' (relative criterion measure in SDT) in multi-interval designs see "Response bias under specific design"
Categorical perception 133Ч135 137Ч138
Categorization 113
Category scaling 113 see one-dimensional"
Ceiling effects see "Sensitivity near-perfect"
Central limit theorem 352
Chance line in ROC space 10
Chance performance see "Sensitivity near-chance" "Chance "ROC
Channels (perceptual) 192
Choice axiom 94
Choice theory 94Ч100
Choice Theory and logistic regression 337Ч339
Choice Theory, 2AFC 168
Choice Theory, classification, one-dimensional 115
Choice Theory, mAFC 247Ч249
City-block metric see "Distance city-block"
Classification for studying attention and interaction 187Ч211
Classification in discrimination designs 214Ч243
Classification vs discrimination 132Ч135
Classification, multidimensional 367
Classification, one-dimensional 2 113Ч135 367
Classification, presentation probability effects 131
Classification, range effects 131
Classification, response bias 116Ч119 127Ч130
Classification, ROC 127Ч128 131
Classification, sensitivity 116Ч119 127Ч130
Classification, two-response 115Ч126
Comparison designs 165Ч184 see "2AFC"
Comparison stimulus 113Ч114
Compound detection 141Ч142 152Ч161
Compound detection, maximum and minimum decision rules 156Ч157
Compound detection, optimal rule 158Ч159 see
Computer programs 431Ч434
Computer simulations of adaptive methods 290
Computer simulations of Wald rule 279Ч281
Conditional-on-Single-Stimulus (COSS) design 306Ч309
Condorcet group 309
confidence intervals see "Parameter estimation"
Consciousness and detection theory 47 106 259
Constant ratio rule 247Ч249 see "Choice
Constant stimuli, method of 120 see one-dimensional"
Context coding 134Ч135
Correct rejection 4 142Ч144
Correction for guessing for psychometric function 276 287Ч289
Correction for guessing in 2AFC 172Ч173 287Ч289
Correction for guessing in mAFC 251Ч252
Correction for guessing in yes-no 82
Correlation 351
Correlation between decision axes in ABX 233Ч234
Correlation between decision axes in oddity 236Ч237
Correlation between decision axes in TannerТs model 191Ч193
Correlation between sensitivities in roving discrimination 221
Correlation between successive intervals or trials 183
Correspondence (experiment) xvii
Criterion location 17 29Ч31
Criterion location in Choice Theory see "b"
Criterion location in SDT see "c"
Criterion location in threshold theory see "False-alarm rate as "Yes
Criterion location, relative 33
Criterion location, relative in Choice Theory see "b'"
Criterion location, relative in SDT see "c'"
Criterion location, relative in threshold theory see "Error ratio"
Criterion location, relative in unequal variance model 67Ч68
Criterion location, variability of 46Ч47
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT) 8
| d' (sensitivity measure in SDT) and  95Ч96 95Ч96
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT) and p(c) 9Ч13
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT) in multi-interval designs see "Sensitivity under specific designs"
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT), calculation of 8Ч9 20Ч21 374Ч375 431Ч434
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT), confidence intervals 325Ч330
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT), cumulative 114
d' (sensitivity measure in SDT), total 114
Data zeroes see "Sensitivity near-perfect"
Decision boundary 145
Decision goals 42Ч44
Decision rule 17 42Ч44
Decision rule, likelihood ratio 42Ч44
Decision rule, nonoptimal 46Ч47 see "Independent-observation "Integration
Decision space 16
Decision space for multi-interval designs see "Decision space under specific design"
Decision space for one-interval designs 16 82Ч91 98Ч100 116Ч119 142Ч144 see
Decision space, multidimensional 152Ч153 191Ч193
Decision theory, statistical 23Ч24
Decisional separability 154 260Ч262
Decisional separability in 2AFC 170
Decisional separability in reminder paradigm 180Ч181
Degrees of freedom 353Ч354
Density function 348Ч349
Designs (for discrimination measurement) xviii 360 364
Designs (for discrimination measurement), comparisons among 234 252Ч255 263Ч264
Designs (for discrimination measurement), fixed 177Ч179 216 230
Designs (for discrimination measurement), multi-interval see "ABX" "mAFC" "Oddity" "Same-different" "2AFC"
Designs (for discrimination measurement), one-interval see "Rating experiment" "Yes-no"
Designs (for discrimination measurement), roving 177Ч179 221 233 see multidimensional" "Classification one-dimensional" "Compound "Identification" "Simultaneous "Simultaneous "Uncertain "Specific
Detection 1
Detection of X-rays 28Ч39 256Ч259 see "Simultaneous
Detection, auditory 115Ч119 176 251 259 270Ч271 302Ч303
Detection, bimodal 141Ч142 152Ч159 196Ч202
Detection, visual 300Ч302
Deviation limit see "Wald rule in adaptive methods"
df see "Degrees of freedom"
Dice game 298Ч300 314
Difference threshold see "jnd"
Differencing models 181 see
Dimensionality, perceptual 114Ч115
Discrimination 1
Discrimination vs classification 132Ч135
Discrimination, color 227
Discrimination, frequency modulation, auditory 182
Discrimination, frequency, auditory 176 182 228 234
Discrimination, intensity, auditory 127Ч129 176Ч178 189Ч191 234
Discrimination, intensity, visual 271Ч272 300
Discrimination, line length 40 120 228 303
Discrimination, number 234 300
Discrimination, orientation 227
Discrimination, phase of visual gratings 114
Discrimination, phase, auditory 176 228 234
Discrimination, pictures 214Ч220
Discrimination, pluck bow 234
Discrimination, shape 229Ч233
Discrimination, size 234
Discrimination, speech 106 228
Discrimination, taste 228 235Ч236 255
Discrimination, tone sequences 308
Distance, city-block 15 193
Distance, Euclidean 15
Distance, measures 15 173
Distribution discrimination 234 298Ч300 304Ч308
Distribution function 348Ч349
Distributions see "Binomial distribution" " "Logistic "Normal "Poisson "Rectangular
Efficiency of d' estimates 325Ч327
Efficiency of pooled sensitivity estimates 335Ч337
Efficiency of real vs ideal observers 303
Efficiency of statistics 352
Efficiency of threshold estimates 290Ч291
Equivalence of measures 7
Error ratio 93
Euclidean distance see "Distance Euclidean"
Exponentials 357Ч358
external noise see "Variance external"
False alarm xviii 4 142Ч144
False fame 123Ч124
False memory 120Ч123
False-alarm rate 5
False-alarm rate in multi-interval designs see "Hit and false-alarm rates under specific design"
False-alarm rate in rating experiment 53Ч54
False-alarm rate in yes-no 5
False-alarm rate, as response-bias measure 85Ч86
False-alarm rate, calculated from parameters 44Ч46
Feature-complete factorial design 246 260
Feedback 129Ч130
Filtering see "Attention selective"
Fixed discrimination see "Designs fixed"
Floor effects see "Sensitivity near-chance"
Forced choice 166 see "3AFC" "mAFC"
Gamer paradigm 194Ч195 205Ч206
Gaussian distribution see "Normal distribution"
General Recognition Theory 259Ч262 304Ч308 see "Multidimensional "Perceptual "Perceptual
Generalized linear models 337Ч339
Group decisions 308Ч310
HallТs adaptive method 294
Hierarchical models 310Ч311
Hit 4 142Ч144
Hit rate 5
Hit rate in multi-interval designs see "Hit and false-alarm rates under specific design"
Hit rate in rating experiment 53Ч54
Hit rate in yes-no 5
Hit rate, as sensitivity measure 6
Hit rate, calculated from parameters 44Ч46
Hypnosis 27Ч28
Hypothesis testing 319 353Ч354
Hypothesis testing and decision rules 44
Hypothesis testing and discrete thinking 106
Hypothesis testing with logistic regression models 337Ч339
Hypothesis testing, independence 353Ч354
Hypothesis testing, proportions 320Ч322
Hypothesis testing, response bias 328
Hypothesis testing, ROC points 322Ч323
Hypothesis testing, sensitivity 325Ч330
Ideal observers 267 290 299Ч303
Identifiability 104
Identification 2
Identification operating characteristics see "IOC"
Identification vs detection 191Ч193
Identification vs uncertain detection 255Ч259
Identification, absolute 113 245
Identification, curvature 260Ч262
Identification, intensity, auditory 127Ч130
Identification, multidimensional 245Ч266
Identification, multidimensional of objects 246Ч249
Identification, multidimensional, sensitivity 246Ч249
Identification, one-dimensional 126Ч135
Identification, one-dimensional, sensitivity 127Ч132
Identification, orientation 260Ч262
Identification, speech 106 124Ч126
Identification, X-rays 256 see "Simultaneous
Implied ROC see "ROC"
Importance ratio 43
Independence of events 344Ч345
Independence of perceptual channels or dimensions 191Ч193 see "Independent-observation "Perceptual "Perceptual
Independent-observation models 198Ч202 see
Information theory 132
instructions 71Ч72
Integrality 194Ч195
Integration models 200Ч202
Internal noise see "Variance internal"
Interstimulus interval see "ISI"
IOC (identification operating characteristic) 256Ч258
ISI (interstimulus interval) 176Ч177
Isobias curve 35Ч41 93Ч94 98
Isobias curve for Choice Theory measures 98
Isobias curve for SDT measures 35Ч41
Isobias curve for threshold measures 93Ч94
Isobias curve in multi-interval designs see "Isobias curve under specific design"
Isobias curve in same-different 219Ч220 226Ч227
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



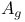 (area under the multipoint ROC)
(area under the multipoint ROC) 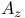 (area under the SDT ROC)
(area under the SDT ROC) 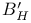 (area-based measure of response bias)
(area-based measure of response bias) 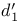 (sensitivity measure in SDT)
(sensitivity measure in SDT) 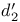 (sensitivity measure in SDT)
(sensitivity measure in SDT) 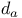 (sensitivity measure in SDT)
(sensitivity measure in SDT) 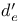 (sensitivity measure in SDT)
(sensitivity measure in SDT) 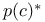 (proportion correct with unequal presentation probabilities)
(proportion correct with unequal presentation probabilities) 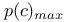 (unbiased proportion correct)
(unbiased proportion correct)  (sensitivity measure in Choice Theory)
(sensitivity measure in Choice Theory)  (normal distribution likelihood ratio)
(normal distribution likelihood ratio)  (logistic distribution likelihood ratio)
(logistic distribution likelihood ratio) 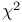 (chi-square) distribution
(chi-square) distribution  (contingency statistic)
(contingency statistic)  (normal distribution function)
(normal distribution function)