|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Macmillan N., Creelman D. Ч Detection Theory: A User's Guide |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Isobias curve, empirical 39Ч40
Isobias curve, monotonicity of 40Ч41
Isosensitivity curve see "ROC"
Jittering 181
jnd (just-noticeable difference) 22 120Ч121
Joint distribution 146
KaernbachТs adaptive method 277 282 292 293
Least-squares estimation 354
Lie detection 6 49
Likelihood ratio for unequal-variance model 67Ч69
Likelihood ratio in multi-interval designs see "Response bias under specific designs"
Likelihood ratio, as response bias measure see "B''" " " "
Likelihood ratio, as ROC slope 33Ч34
Likelihood ratio, Choice Theory see " " " "B''" " " "B''"
Likelihood ratio, decision rule 42Ч44
Likelihood ratio, SDT see " " "
Log-odds transformation 95Ч96
Log-odds transformation and Choice Theory 95Ч96
Log-odds transformation and logistic regression 337Ч339
Logarithms 357Ч358
Logistic distribution 108Ч109 349
Logistic distribution, as psychometric function 275 284 see Choice "Log-odds
Logistic regression 337Ч339
mAFC 246
mAFC in adaptive methods 293
mAFC vs 2AFC 249 251 293
mAFC vs other designs 253Ч255
mAFC, as an example of multidimensional identification 249Ч250
mAFC, decision space 249Ч250
mAFC, psychometric functions 253
mAFC, response bias 250Ч251
mAFC, sensitivity 250 426Ч430
mAFC, statistical properties of d' 329Ч330
mAFC, threshold model 251Ч252
Market research 250Ч251
Matching experiment 182Ч183
Matching experiment, brightness 271Ч272
Matching-to-sample see "ABX"
Maximum (-output) rule 154Ч158 see
Maximum-likelihood estimation 291 354Ч355
Maximum-likelihood estimation of empirical thresholds 284Ч285 294
Maximum-likelihood estimation of ROCs 70 330
Mean (-shift) integrality 195Ч196
Mean category scale 130Ч131
Memory as limitation in perception 133Ч135 175Ч179
Minimum (-output) rule 154Ч158
MISS xviii 4 142Ч144
MLE see "Maximum-likelihood estimation"
Monte Carlo techniques see "Computer simulations"
Multidimensional Signal Detection Analysis (MSDA) 260Ч262 433
Multiple-choice exams 249Ч252
Multiple-look experiments 206Ч207
Noise, external see "Variance external"
Noise, internal see "Variance internal"
Nonparametric analysis 100Ч104 130Ч132
Normal distribution 35 320Ч322 348Ч349 374Ч378
Normal distribution, as psychometric function 117Ч120 274 see "z-transformation"
Normal distribution, bivariate 144Ч152 322Ч323 349Ч351
Oddity 235Ч238
Oddity vs other designs 253Ч255
Oddity, decision space 236Ч237
Oddity, differencing model 236Ч237
Oddity, independent-observation model 237
Oddity, sensitivity 236Ч238 420Ч425
Oddity, statistical properties of d' 329Ч330
Oddity, threshold model 238
One-interval design 1 see "Yes-no
One-interval design vs other designs see "Specific design"
Optimality see "Decision rule likelihood "Ideal
p(c) (proportion correct) 7
p(c) (proportion correct) and d' 9Ч13
p(c) (proportion correct), as sensitivity measure in 2AFC 170Ч175
p(c) (proportion correct), as sensitivity measure in identification 131Ч132 see
p(c) (proportion correct), as sensitivity measure in yes-no 7
Parameter estimation 319
Parameter Estimation by Sequential Testing see "PEST"
Parameter estimation, pooled sensitivity and bias 331Ч337
Parameter estimation, proportions 320Ч322
Parameter estimation, response bias 328
Parameter estimation, ROC points 322Ч323
Parameter estimation, sensitivity 323Ч330 see "Maximum-likelihood
payoffs 71
Perceptual dependence and independence 149 260 262
Perceptual integrality 195Ч196 260Ч262
Perceptual separability 195Ч196 260Ч262
Perfect performance see "Sensitivity near-perfect"
PEST 282Ч287
PEST vs other methods 291
PEST, MOUSE and RAT modes 286
PEST, stepping rules 282Ч283
Point of subjective equality see "PSE"
Poisson distribution 301Ч302
Pooled data 331Ч337
Presentation probabilities 7
Presentation probabilities and bias 42Ч44
Presentation probabilities and ROC generation 72
Presentation probabilities in one-dimensional classification 129Ч130
probability 343Ч351
Probit analysis 274 293 see as
Product rule 151 350
Projection of multidimensional distributions 146Ч149
Proportion correct see "p(c)"
PSE 120Ч121 273
Pseudo-d' 122 124
Psychometric function 119 272Ч276
Psychometric function in 2AFC 273Ч274
Psychometric function in mAFC 253 see "Normal "Weibull
Psychometric function, shape of 273Ч276
Psychometric function, slope 293
Psychophysics vs psychoacoustics 312Ч313
Psychophysics, history 22Ч24
Quest 284Ч286
QUEST vs other methods 286 291
Radiology see "X-ray reading"
Random variables 345Ч349
Range-frequency model 130
Rating experiment 2 51Ч70
Rating experiment, calculating response rates 53Ч57
Rating experiment, decision space 64Ч69
Rating experiment, design 51Ч52
Rating experiment, graphing data 55Ч57
Rating experiment, response sets 52 see
Receiver operating characteristic see "ROC"
Recognition 1
Recognition of faces 3Ч6
Recognition of letters 246Ч249
Recognition of odors 51Ч57 64Ч66
Recognition of words 40 57Ч59 90Ч92 160Ч161 166Ч170 185 193Ч194
Rectangular distribution see "Underlying distributions in threshold theory"
Relative operating characteristic see "ROC"
Reminder paradigm 180Ч182 255
Reminder paradigm vs other designs 181Ч183 see
Response bias 27Ч44 362 366
Response bias in below-chance performance 41
Response bias in multi-interval designs see "Response bias under specific design"
Response bias measures 362 363 366
Response bias measures and sensitivity measures 41Ч42
Response bias measures for rating experiment 64Ч69
Response bias measures in multi-interval designs see "Response bias under specific design"
Response bias measures, characteristics of 28Ч29
Response bias measures, Choice Theory see "b" "b'" "B''" " "
Response bias measures, comparisons of 36Ч42
Response bias measures, nonparametric see "B''" "
| Response bias measures, SDT see "c" "c'" "
Response bias measures, threshold theory 85Ч86 see "False-alarm as "Yes
Response bias, as criterion location 29Ч31
Reversal (in adaptive methods) 283Ч286
Reward function see "Payoffs"
ROC 10 51Ч77
ROC for group data 337
ROC in multi-interval designs see "ROC under specific design"
ROC in z-coordinates 11 55Ч59 see ROC" "Rating
ROC slope (linear coordinates) 11 33Ч34
ROC slope (z-coordinates) 14 59 330Ч331
ROC slope (z-coordinates) and sensitivity 74Ч77
ROC slope (z-coordinates) and uncertainty 76
ROC slope (z-coordinates) in multi-interval designs see "ROC under specific design"
ROC slope (z-coordinates), nonunit slope 57Ч59
ROC slope (z-coordinates), unit slope 14
ROC space 10
ROC, empirical 55Ч59 66Ч77
ROC, fitting to data 70 330 433
ROC, generation methods 71Ч72
ROC, implied 9Ч13
ROC, regularity 11 18
ROC, symmetry 14
ROC, threshold 12Ч13 83Ч84 89Ч92 110
ROC, Type-2 73Ч74
Roving discrimination see "Designs roving"
S see "ROC slope (z-coordinates)"
S',(sensitivity measure for rating design) 104
Same-different 214Ч228
Same-different vs other designs 216Ч217 228 253Ч255
Same-different, decision space 215Ч218 222Ч224
Same-different, differencing model 221Ч227
Same-different, hit and false-alarm rates 215 223
Same-different, independent-observation model 216Ч217
Same-different, isobias curves 219Ч220 226Ч227
Same-different, response bias 218Ч220 225Ч227
Same-different, ROC 220 223Ч225
Same-different, sensitivity 216Ч220 223Ч225 380Ч419
Same-different, statistical properties of d' 329Ч330
Same-different, threshold model 217Ч218
Sampling distribution 351Ч352
Saturated model see "Logistic regression"
Sensitivity 3 361 363 365
Sensitivity in multi-interval designs see "Sensitivity under specific design"
Sensitivity measure in ROC space 12 59Ч64
Sensitivity measures 3 361 362 365 see "
Sensitivity measures and bias measures 41Ч42
Sensitivity measures for nonunit-slope ROCs see "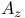 " " " " " " " " " "
Sensitivity measures for unit-slope ROCs see "d'" "
Sensitivity measures in Choice Theory see " " "
Sensitivity measures in classification, one-dimensional see "Classification one-dimensional sensitivity"
Sensitivity measures in multi-interval designs see "Sensitivity under specific design"
Sensitivity measures in SDT see "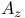 " "d'" " " " " " "d'" " " " "
Sensitivity measures in threshold theory 82Ч89
Sensitivity measures, area-based see "A'" " "Area "
Sensitivity measures, characteristics of 5Ч7
Sensitivity measures, nonparametric see "A'" " "S'"
Sensitivity, as mean difference in decision space 18Ч20
Sensitivity, as perceptual distance 15
Sensitivity, medical use of term 6
Sensitivity, near-chance 8Ч9 40Ч41
Sensitivity, near-perfect 8Ч9 129 224Ч225 321 336
Separability 194Ч195
Sequential effects 183
Simulations see "Computer simulations"
Simultaneous detection and identification 255Ч259
Simultaneous simple and compound detection 200Ч202
Specificity 6
Staircase procedure 281Ч282
Standard stimulus 113Ч114 see
State diagram 81
Statistical bias 352
Statistical bias of d' estimates 323Ч325
Statistical bias of pooled sensitivity estimates 331Ч335
Statistical bias of threshold estimates 290
Statistics 351Ч355
Statistics and detection theory 319Ч341 see "Maximum-likelihood "Parameter
Stimulus repetition see "Compound detection" "Multiple
Subliminal perception 105Ч106 258Ч259
Sweat factor 290
Target proportion (of an adaptive method) see "Adaptive methods target
Threshold and response bias 287Ч289
Threshold theories 81Ч94 104Ч107
Threshold theories for multi-interval designs see "Specific design"
Threshold theories, double high-threshold 88Ч94
Threshold theories, low threshold 86Ч88
Threshold theories, single high-threshold 82Ч86
Threshold theories, three-state 110
Threshold, compared with criterion 22Ч23
Threshold, empirical 119Ч120 269Ч296
Thurstonian scaling see "Classification one-dimensional"
Time order errors 176Ч177
Trace coding 178Ч179
Trace-context theory 133Ч135 178Ч179 310Ч311
Trading relations 114 124Ч126
Training, effects of 46
Transformations, arcsine 103
Transformations, log-odds 95
Transformations, logarithmic and exponential 274 357Ч358
Triangular method see "Oddity"
Type-I error 44
UDTR 278 281 289
UDTR vs other methods 292
UDTR, decision rule 278
Unbiased performance see "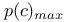 " "
Uncertain detection 188Ч202
Uncertain detection on one dimension 189Ч191
Uncertain detection vs identification see "Simultaneous detection and identification"
Uncertain detection, independent-observation rule 197Ч199
Uncertain detection, optimal model 199
Uncertain detection, summation rule 196Ч197
Uncertainty see also "Uncertain detection"
Uncertainty, extrinsic vs intrinsic 188
Underlying distributions 16
Underlying distributions and transformations 19Ч20
Underlying distributions in Choice Theory 98Ч100
Underlying distributions in multi-interval designs see "Decision space under specific design"
Underlying distributions in SDT 16Ч20
Underlying distributions in threshold theory 82Ч91
Underlying distributions with unequal variances 57Ч64 173Ч175
Underlying distributions yes-no 16 see
Underlying distributions, multidimensional 144Ч152
Unsaturated model see "Logistic regression"
Up-Down Transformed Method see "UDTR"
Variance (in statistics) see "Confidence interval under specific statistic"
Variance, external 297Ч298 302Ч303
Variance, internal 297Ч298 302Ч303
Variance, internal, context 134Ч135
Variance, internal, sensory 134Ч135 178Ч179
Variance, internal, trace 178Ч179 see incomplete"
Visual search 311
Wald rule in adaptive methods 278Ч280
Weibull function 275Ч276
X-ray reading 28Ч35
Yes rate 92Ч93
Yes-no design 1Ч50 361Ч362
Yes-no design in adaptive methods 271Ч272 293
Yes-no design vs other designs 167Ч168 175Ч176 181Ч182 228 234 253Ч255
Z-transformation 8
z-transformation for one-dimensional classification 117Ч128
z-transformation for psychometric functions 117Ч121
z-transformation for ROCs 11Ч12 55Ч64
z-transformation, variance of 325Ч327
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 "
" "
"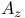 "
" "
"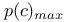 "
"