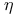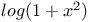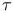"Cocked-hat" as synonym for unimodal 29
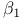 , , 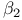 (skewness and kurtosis) 81 (skewness and kurtosis) 81
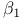 , , 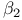 (skewness and kurtosis), (Exercise 11.17) 289 (skewness and kurtosis), (Exercise 11.17) 289
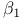 , , 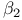 (skewness and kurtosis), generalised (skewness and kurtosis), generalised  82 82
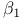 , , 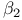 (skewness and kurtosis), sampling distributions of 279Ч280 (skewness and kurtosis), sampling distributions of 279Ч280
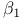 , , 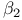 (skewness and kurtosis), standard errors of 225 (skewness and kurtosis), standard errors of 225
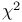 -distribution as square contingency 319 -distribution as square contingency 319
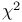 -distribution in -distribution in 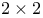 tables 303 tables 303
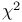 -distribution, correction for continuity 303Ч304 -distribution, correction for continuity 303Ч304
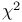 -distribution, generally 290Ч307 -distribution, generally 290Ч307
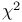 -distribution, properties of 292Ч297 -distribution, properties of 292Ч297
 -function, in summing Poisson series 122 -function, in summing Poisson series 122
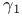 , , 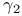 (skewness and kurtosis) 82 (skewness and kurtosis) 82
 , as criterion of type in Pearson distributions 140 , as criterion of type in Pearson distributions 140
Abortion, distribution of women according to term of, (Table 1.23) 26
Abrupt distributions, corrections for grouping to 79
Abrupt distributions, corrections for grouping to, refs. 85Ч86
Absolute moments 56
Absolute moments, Liapounoff's inequality for, (Exercise 3.14) 88
Accidents, exemplified by Poisson distribution 124
Adyanthaya, N.K., refs., distribution of frequency constants in small samples, (under Pearson) 228
Age, correlation with highest audible pitch, (Example 14.1) 331
Age, correlation with highest audible pitch, (Table 14.1) 325
Agreement, coefficient of 427Ч429
Agreement, coefficient of, significance of 429Ч435
Agricultural Research Institute, Oxford, data from Report of, (Table 1.9) 9
Alcoholism and crime, Goring's data on and health, (Exercise-14.12) 366
Alcoholism and crime, Goring's data on, (Table 14.6) 356
Ammon O., data from (hair and eye-colour), (Table 12.4) 300
Anthropometric Committee of British Association, data from Report of, (Table 1.10) 10
Anthropometric Committee of British Association, data from Report of, (Table 1.7) 8
Antimode, definition of 35
Approximations to sampling distributions see "Sampling distributions"
Aroian, L.A., fitting of Type B distribution to data, (Example 6.4) 156
Aroian, L.A., fitting of Type B distribution to data, refs., Type B series 160
Arrays, in bivariate distributions 327
Association, generally 308Ч323
Association, generally, coefficients of 310Ч313
Association, generally, illusory 317Ч318
Association, generally, partial 313Ч317
Asymmetrical distributions 10 see
Attributes, sampling of 197Ч201
Attributes, sampling of in finite populations, (Exercise 8.3) 203
Attributes, sampling of in Poisson distribution, (Exercise 8.2) 203
Australian marriages, 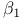 and and 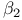 of, (Example 3.1) 82 of, (Example 3.1) 82
Australian marriages, distribution of, (Table 1.8) 9
Australian marriages, moments of, (Example 3.1) 50Ч52
Average see "Moan"
Average corrections to moments 74Ч75 see
b, (sampling value of 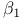 , measure of skewness) 279Ч280 , measure of skewness) 279Ч280
B-function, in summing binomial 120
Babington Smith, B., data from, on random numbers, (Table 8.3) 189
Babington Smith, B., data from, on random numbers, distribution of Spearman's  , problem of m rankings, method of paired comparisons 436 , problem of m rankings, method of paired comparisons 436
Babington Smith, B., data from, on random numbers, Random Sampling Numbers 193 197
Babington Smith, B., data from, on random numbers, refs., (under Kendall) 202
Baker, G.A., distribution of means in Type A series, (Exercise 10.7) 252
Bayes' theorem 175Ч177
Bayes' theorem in estimating proportion of attributes 200
Bayes' theorem, (Exercise 8.5) 203
Bayes' theorem, comparison with maximum likelihood 178Ч180
Bayes' theorem, postulate 176Ч178
Bayes, T., refs., doctrine of chances 183
Beans, distribution of, (Table 1.15) 20
Beans, distribution of, fitting of Pearson distribution to, (Example 6.1) 143Ч144
Beans, distribution of, Gram Ч Charlier series fitted to, (Example 6.2) 151
Beans, distribution of, histogram of, (Figure 1.4) 20
Bernouilli numbers, footnote 69 71 78
Bernouilli polynomials, definition of 58
Bernstein, S., refs., extension of central limit theorem 183
Bias in sampling 187Ч190
Bias in sampling in choosing plants, (Example 8.1) 187Ч188
Bias in sampling in cropreporting, (Example 8.4) 189Ч190
Bias in sampling in reading randomising machine, (Example 8.3) 189
Bias in sampling in scale reading, (Example 8.2) 188
Binomial distribution, general properties 116Ч120
Binomial distribution, general properties and (Exercise 5.7) 136
Binomial distribution, general properties in sampling of attributes 198
Binomial distribution, general properties with negative index 125Ч126
Binomial distribution, general properties, 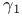 and and 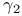 of, (Example 3.17) 82 of, (Example 3.17) 82
Binomial distribution, general properties, arising from mixed population 122Ч124
Binomial distribution, general properties, bivariate form 133Ч134
Binomial distribution, general properties, cumulants of, (Exercise 5.1) 135
Binomial distribution, general properties, distribution function of 119Ч120
Binomial distribution, general properties, distribution of means of, (Example 10.8) 243
Binomial distribution, general properties, factorial moments of, (Exercise 3.6) 87
Binomial distribution, general properties, incomplete moments of, (Exercises 5.2 and 5.3) 135
Binomial distribution, general properties, limiting form, (Example 4.6) 103
Binomial distribution, moments of 117
Binomial distribution, moments of (Example 3.2) 52
Birth-rates, distribution of in Local Government Areas, (Table 1.1) 3
Birth-rates, distribution of in Local Government Areas, frequency polygon of, (Table 1.1) 4
Biserial 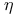 356Ч358 356Ч358
Bivariate binomial distribution 133Ч134
Bivariate Poisson distribution, (Exercise 5.8) 136
Bivariate, frequency-distributions 19Ч22
Bivariate, moments and cumulants 79Ч81
Bivariate, moments and cumulants, k-statistics and cumulants 281Ч283
Bivariate, moments and cumulants, standard errors of 211
Bivariate, normal distribution 22
Bivariate, normal distribution as limit of bivariate binomial 133Ч134
Bivariate, normal distribution, (Example 3.15) 79Ч80
Bivariate, normal distribution, correlation and regression of 334Ч336
Bivariate, normal distribution, moments of, (Exercise 3.15) 89
Bivariate, normal distribution, multivariate form 376Ч377
Borel, E., refs., Traite du Calcul des Probabilites 22 183
Bose, S.S., distribution of variance ratio, (Exercise 14.8) 365
Bowley, A.L., refs., F.Y. Edgeworth's Contributions to Mathematical Statistics 160
Bowley, A.L., refs., F.Y. Edgeworth's Contributions to Mathematical Statistics, representative method 202
Brood-mares, distribution of fecundity in, (Table 1.20) 24
Call discount rate, distribution of weekly returns according to, (Table 1.26) 28
Camp, B.H., refs., distribution functions of binomial and hypergeometric 134
Card-shuffling, tested by 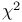 , (Example 12.1) 297Ч299 , (Example 12.1) 297Ч299
Card-shuffling, tested by 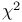 , tested by rankings, (Example 16.5) 420 , tested by rankings, (Example 16.5) 420
Carleman, T., criteria for uniqueness in the problem of moments 109
Carleman, T., criteria for uniqueness in the problem of moments, refs., Les functions quasi-analytiques 114
Carver, H.C., Sheppard corrections for discrete variables 85
Cauchy distribution, (Example 10.15) 247
Cauchy distribution, (Example 3.12) 67Ч68
Cauchy distribution, characteristic function of, (Example 4.2) 95Ч96
Cauchy distribution, distribution of mean of samples from, (Example 10.1) 233Ч234
Cave, B.M., refs., sampling of correlation coefficient (under Co-operative Study) 363
Census of Population, data from Housing Report, (Table 1.24) 27
Census of Production, data from, on size of firms, (Table 1.17) 23
Central limit theorem 180Ч183
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions 54
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions in sampling distributions 242Ч246
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions, conditions for a function to be 98Ч99
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions, general theory of 90Ч115
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions, limiting properties of 99Ч104
Characteristic functions, as moment-generating functions, multi-variate 104Ч105
Charlier, C.V.L., Types A and B series 147 see
Charlier, C.V.L., Types A and B series, refs., expansion of frequency functions 160
Cheshire, L., refs., significance of correlation coefficient, (under E.S. Pearson) 363
Chi-square see "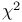 " "
Cholera, inoculation against, (Example 13.1) 309
Cholera, inoculation against, (Example 13.2) 311Ч312
Cholera, inoculation against, (Example 13.3) 313
Cholera, inoculation against, (Table 12.6) 302
Church, A.E.R., sampling moments 256
Church, A.E.R., sampling moments, refs. 284Ч285
Circular triads, in preferences 423
Class-frequency, definition 2
Class-interval, definition 2
Class-interval, definition, ambiguities in 5
Cloudiness, distribution of days according to, (Table 1.11) 10
Co-operative Study on correlation coefficient, refs. 363
Cochran, W.G., refs., 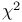 -distribution 305 -distribution 305
Coefficients of association, contingency, correlation, etc. see "Association" "Contingency" "Correlation"
Coin-tossing, as example of sampling of attributes, (Example 8.9) 198
Colligation, coefficient of 311
| Combinatorial method, in sampling of k-statistics see "k-statistics"
Comrie, L.J., refs., Tables of arc, tan x and 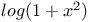 160 160
Concentration, coefficient of 43
Concentration, coefficient of and (Figure 2.3) 44
Concentration, coefficient of, curve of 43-44
Concordance, coefficient of 411 see
Consistence, coefficient of 425
Contingency 318Ч322
Contingency, coefficient of 319
Continuity correction to 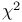 303Ч305 303Ч305
Continuous frequency functions 13
Continuous frequency functions, sampling from 197
Continuum, probability in 170
Cornish, E.A., refs., moments and cumulants in specification of distributions 160
Corrections for grouping in calculation of moments 30 41
Corrections for grouping in calculation of moments, refs. 85Ч86 see
Corrections for grouping in calculation of moments, when distribution is abrupt 79
Correlation 363
Correlation ratios, definition 351
Correlation ratios, definition for ranked data (Wallis) 437
Correlation ratios, definition, relation with multiple correlation 381
Correlation ratios, definition, sampling distribution in uncorrelated normal population 352Ч353
Correlation, coefficient of multiple correlation 380Ч381
Correlation, coefficient of multiple correlation, sampling of 381Ч385
Correlation, coefficient of partial 368Ч379
Correlation, coefficient of partial in multivariate normal distribution 376Ч378
Correlation, coefficient of partial in terms of coefficients of lower orders 372
Correlation, coefficient of partial, (crime and religion, Example 15.2) 375Ч376
Correlation, coefficient of partial, definition 370
Correlation, coefficient of partial, examples of, (weather and crops, Example 15.1) 373Ч375
Correlation, coefficient of partial, geometrical interpretation 372Ч373
Correlation, coefficient of partial, sampling distribution of 378Ч379
Correlation, coefficient of product-moment, generally 324Ч367
Correlation, definition 329
Correlation, Fisher's transformation of 345
Correlation, in bivariate normal distribution 334
Correlation, intra-class 358Ч362
Correlation, rank, coefficient 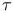 391Ч393 391Ч393
Correlation, rank, coefficient 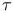 , sampling of 403Ч408 see , sampling of 403Ч408 see
Correlation, rank, generally 388Ч421
Correlation, rank, generally, sampling of 394Ч403
Correlation, sampling of 336Ч348
Correlation, Spearman's coefficient 388Ч391
Correlation, standard error of, (Example 9.6) 211
Correlation, tables of (David) 345
Correlation,calculation of 330Ч334
Covariance, definition 79
Covariance, definition, calculation of 330
Covariance, definition, distribution of in normal samples 339Ч342
Covariance, definition, notation for 204
Cows, distribution of according to age and milk-yield, (Table 1.25) 27
Craig, C.C., corrections to moments of discrete distribution 77
Craig, C.C., corrections to moments of discrete distribution, (Exercise 3.13) 88
Craig, C.C., corrections to moments of discrete distribution, refs. 85
Craig, C.C., corrections to moments of discrete distribution, sampling of cumulants 256
Craig, C.C., corrections to moments of discrete distribution, sampling of cumulants, refs. 285
Cramer, H., convergence of Gram Ч Charlier series 151Ч152 159
Cramer, H., convergence of Gram Ч Charlier series, central limit theorem 181Ч183
Cramer, H., convergence of Gram Ч Charlier series, distribution of a ratio (Exercise 10.8) 252
Cramer, H., convergence of Gram Ч Charlier series, distribution of a ratio (Exercise 10.8), refs., Random Variables and Probability Distributions 114 183 250
Cramer, H., convergence of Gram Ч Charlier series, refs. 160
Crime and alcoholism, Goring's data on, (Table 14.6) 356
Crime, Goring's data on, correlation with religion, (Example 15.2) 375
Crop-reporters, bias in, (Example 8.4) 189Ч190
Crops, correlation with weather, (Example 15.1) 373
Cuckoo's eggs, distribution of length of, (Exercise 14.13) 366
Cumulants and (multivariate case) 80Ч81
Cumulants of normal distribution 129
Cumulants, calculation of 65Ч68
Cumulants, definition 60
Cumulants, existence of 64Ч65
Cumulants, generating functions for 90
Cumulants, in bivariate case 80
Cumulants, invariantive properties of 61
Cumulants, relations with moments 61Ч64
Cumulants, Sheppard's corrections to 78
Cumulative function 90
Curve of concentration see "Concentration"
Dairy farms, distribution according to coats of milk-production, (Table 1.9) 9
David, F.N., distribution of difference of Type III variates, (Exercise 10.6) 252
David, F.N., distribution of difference of Type III variates, (Exercise 10.6), refs. 363
David, F.N., distribution of difference of Type III variates, (Exercise 10.6), Tables of the Correlation Coefficient 345
Davies, O.L., refs., estimation of standard deviation 228
de Finetti, B., refs., calculation of moan difference 47
de la Vallee Poussin, C.J., refs., Cours d'analyse, footnote 233
Deaf-mutes, distribution of children of, (Table 1.19) 24
Deaths, from scarlet fever, (Table 1.3) 5
Deaths, from scarlet fever, distribution of, according to age at death, (Table 1.12) 11
Deciles, definition 36
Deciles, definition, interdecile range 38
Deciles, definition, standard errors of 225
Degrees of freedom, in 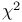 -distribution 292 -distribution 292
Degrees of freedom, in 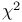 -distribution in contingency table 299 -distribution in contingency table 299
Demoivre, A., discoverer of normal distribution 131
Denjoy, A., theorem on uniqueness of quasianalytic functions, (Exercise 4.10) 115
Dice, throws with, Weldon's data (Table 1.14) 19
Dice, throws with, Weldon's data, (Example 8.10) 199
Dice, throws with, Weldon's data, (Table 1.16) 23
Dice, throws with, Weldon's data, (Table 12.5) 301
Digits, distribution of, from telephone directory, (Table 1.4) 6
Direct probability see "Probability"
Dirichlet integrals, in Inversion Theorem 91Ч92
Discontinuous frequency-functions 12
Discontinuous frequency-functions, variate, examples of distribution according to 6Ч7
Dispersion, measures of 38Ч48 see
Distribution curve 36Ч37
Distribution, determination by moments 105Ч110
Distribution, determined by characteristic function 91Ч94
Distribution, functions 12Ч15
Distribution, limiting properties of 99Ч104 110Ч113
Distribution, relation with probability 172Ч173
Distribution, standard distributions 116Ч163 see Distributions"
Doerge, K., refs., axiomatisation of von Mises' theory of probability 183
Doodson, A.T., relation of mean, median and mode 35 46
Doodson, A.T., relation of mean, median and mode, refs. 47
Dressel, P.L., refs., seminvarians 84Ч85 285
Edgeworth, F.Y., citing Weldon's dice data, (Table 1.14) 19
Edgeworth, F.Y., citing Weldon's dice data, form of Gram Ч Charlier series 148Ч149
Edgeworth, F.Y., citing Weldon's dice data, refs., law of error 160
Edwards, J., refs., Integral Calculus, footnote 68
Edwards, J., refs., Integral Calculus, footnote and footnote 221
Eells, W.C., formulae for probable errors of correlation coefficients 410
Eells, W.C., formulae for probable errors of correlation coefficients, refs. 436
Egyptian skulls, distribution of, (Table 1.22) 25
Elderton, E.M., data on health of son and alcoholism of father, (Exercise 14.12) 366
Estimates, of proportions of attributes 199Ч200
Estimates, of proportions of attributes in large samples generally 201Ч203
Estimates, of proportions of attributes of a ranking 421
Euler Ч Maclaurin sum formula 69
Expectation 84 see
Extreme values of sample, distribution of 217Ч222
Eye-colour, rotation with hair-colour in parent and child, (Example 13.4) 314
Eye-colour, rotation with hair-colour, (Example 12.3) 299
Factorial moments 56Ч60
Factorial moments in terms of ordinary moments 57Ч58
Factorial moments of binomial 118
Factorial moments of hypergeometric, (Exercise 5.4) 135
Factorial moments, calculation of 58Ч60
Factorial moments, definition 66
Factorial moments, generating function for 90
Factorial moments, Sheppard's corrections to 77Ч78
Families deficient in room space, distribution of, (Table 1.24) 27
Fathers, height of, distribution of sons according to, (Table 14.3) 327
Fay, E.A., data from Marriages of the Deaf in America, (Table 1.19) 24
Fecundity, distribution of brood-mares according to, (Table 1.20) 24
Feeding and teeth in infants, (Example 12.5) 304
Fieller, E.C., refs. distribution of a ratio 250
Filon, L.N.G., refs., (under Pearson), standard errors of frequency constants 229
Finite populations, sampling from 283Ч284
Finney, D.J., sampling of variance ratio, (Exercise 14.8) 365
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



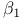 ,
, 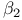 (skewness and kurtosis)
(skewness and kurtosis) 
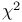 -distribution as square contingency
-distribution as square contingency  tables
tables  -function, in summing Poisson series
-function, in summing Poisson series  ,
,  (skewness and kurtosis)
(skewness and kurtosis)  , as criterion of type in Pearson distributions
, as criterion of type in Pearson distributions  , problem of m rankings, method of paired comparisons
, problem of m rankings, method of paired comparisons