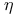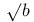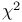Merzrath, E., refs., bivariate frequency-distributions and correlation 85
Mesokurtosis 82
Mesokurtosis in normal distribution 129
Milk, costs of production of, (Table 1.9) 9
Milk-yield, distribution of cows according to, (Table 1.25) 27
Milk-yield, distribution of cows according to, covariance and variances, (Exercise 14.1) 364
Milne — Thompson, L.M., Calculus of Finite Differences, footnote 69
Miner, J.R., tables of correlation coefficients 375
Miner, J.R., tables of correlation coefficients and refs. 386
MODE 35
Mode, relation with median and moan 35 46
Mode, standard error in Poarson distributions 225
Moments, preliminary 39
Moments, preliminary as characteristics of a distribution 83—84
Moments, preliminary in terms of factorial moments 57—58
Moments, preliminary of binomial 117 118
Moments, preliminary of hypergeometric 127
Moments, preliminary of normal distribution 129
Moments, preliminary, about one point in terms of those about another 49
Moments, preliminary, absolute moments see "Absolute"
Moments, preliminary, calculation of 50—54
Moments, preliminary, corrections for grouping 68—78
Moments, preliminary, corrections to multivariate 80—81
Moments, preliminary, definition 49
Moments, preliminary, distribution of 245 see "Second "Cumulants"
Moments, preliminary, factorial moments see "Factorial"
Moments, preliminary, generating functions for 54—56 90
Moments, preliminary, multivariate 79—80
Moments, preliminary, problem of moments 105—110
Moments, preliminary, relationship with cumulants 61—64
Moments, preliminary, Sheppard's corrections to 41
Moments, preliminary, standard errors of 204—211 225
Montel, P., theorem on convergent sequences of functions 100
Moore, G., data from, (Table 1.20) 24
Morant, G., refs., random occurrences in space and time 134
Morant, G., refs., random occurrences in space and time, data from (Table 14:1) 325
mth values, distribution of 217—222
Multiple correlation see "Correlation"
Multivariate, characteristic functions 104—105
Multivariate, correlation see "Correlation"
Multivariate, distributions 19—22
Multivariate, k-statistics 281—283
Multivariate, moments and cumulants 79—81
Multivariate, normal distribution 376—377
Multivariate, sampling distributions 250
Nair, U.S., distribution of mean difference 216 225
Nair, U.S., distribution of mean difference and refs. 228
Neyman, J., on theory of estimation, footnote 180
Neyman, J., on theory of estimation, footnote, refs., estimation 184
Neyman, J., on theory of estimation, footnote, representative method 202
Neyman, J., on theory of estimation, footnote, sampling from finite population 284 285
Nicholson, C., refs., distribution of a ratio 251
Normal distribution, (Example 10.10) 243
Normal distribution, (Example 10.3) 236—237
Normal distribution, as limit of binomial, (Example 4.6) 103
Normal distribution, as limit of Poisson distribution, (Example 4.8) 113
Normal distribution, as one of Pearson's types 141
Normal distribution, bivariate form see "Bivariate"
Normal distribution, characteristic function of, (Example 4.1) 94
Normal distribution, cumulants of, (Example 3.10) 67
Normal distribution, determined uniquely by its moments, (Example 4.7) 109—110
Normal distribution, distribution function of 129—130
Normal distribution, distribution of mean in samples from, (Example 10.2) 234—236
Normal distribution, distribution of measures of departure from, (Exercise 11.16) 288
Normal distribution, distribution of variance in samples from, (Example 10.5) 238—239
Normal distribution, generally 128—132
Normal distribution, in Central Limit Theorem 180—183
Normal distribution, in sampling of attributes 198—199
Normal distribution, moments of, (Example 3.4) 53—54
Normal distribution, multivariate form 376—377
Normal distribution, providing standard of kurtosis 82
Normal distribution, sampling of k-statistics from 274
Normalisation of frequency-functions 156—159
Norris, N., refs., inequalities among averages 47
Norton, J.P., data from Statistical Studies in the New York Money Market, (Table 1.26) 28
Ogburn, W.F., correlation of crime and religion and refs. 386
Ogburn, W.F., correlation of crime and religion, (Example 15.2) 375
Ogive of Galton see "Distribution curve"
Oldis, E., refs., significance of correlation coefficient, (under E.S. Pearson) 363
Pabst, M.R., distribution of Spearman's  401 401
Pabst, M.R., distribution of Spearman's  and refs., (under Hotelling) 436 and refs., (under Hotelling) 436
Paciello, U., refs., calculation of mean difference 47
Paired comparisons 421—436
Pairman, E., refs., corrections to abrupt distributions 85
Parameters, definition 29
Parameters, definition of dispersion 38—48
Parameters, definition of location 29—38
Partial: association 313—318
Partial: association, contingency 321—322
Partial: association, correlation see "Correlation"
Partial: association, regression see "Regression"
Pattern functions, in sampling k-statistics 262—265 277—278 279
Pattern functions, in sampling k-statistics, (Exercise 11.11) 287
Pea breeding, (Example 12.2) 299
Pearce, T.V., data from, (Table 1.23) 26
Pearse, G.E., data from, (Table 1.11) 10
Pearse, G.E., data from, (Table 1.11), refs., corrections when ordinates are infinite 86
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric 132—133
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, distribution of means from (ref. Irwin) 250
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, fitting of 143—145
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, generalisation by Romanovsky, refs. 160 161
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, generally 137—145
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, inflections of 138
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, quadrature of 145
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, recurrence relation for moments 138
Pearson distributions, as limit of hypergeometric, skewness of 138
Pearson, Coefficient of variation 43
Pearson, Coefficient of variation and of biserial 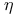 358 358
Pearson, Coefficient of variation, coefficient of contingency 319—320
Pearson, Coefficient of variation, grades and Spearman's  410 410
Pearson, Coefficient of variation, measure of skewness 81
Pearson, Coefficient of variation, sampling of contingency coefficients 321
Pearson, Coefficient of variation, sampling of tetrachoric r 356
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range 223 224
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, correlation coefficient 363
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, distribution of 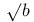 280—281 280—281
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, distribution of 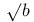 , (Exercise 11.17) 289 , (Exercise 11.17) 289
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, distribution of frequency constants in skew population 228
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, estimating standard deviation 228
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, polychoric coefficients, (under K. Pearson) 363
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, refs., range 228
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, sampling of correlation coefficient 346
Pearson, E.S., distribution of range, tests for normality 285
Pearson, Karl, data from, fecundity of mares, (Table 1.20) 24
Pearson, Karl, data from, height of fathers and sons, (Table 14.3) 327
Pearson, Karl, data from, quoting data by Elderton on alcoholism, (Exercise 14.12) 366
Pearson, Karl, data from, quoting data by Goring on crime, (Table 14.6) 356
Pearson, Karl, data from, trypanosomes, (Table 1.13) 12
Pearson, Karl, data from, whist deals, (Table 5.4) 128
Pearson, M.V., refs., mean character of ranked individuals 229
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman) 85
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman) of difference of Type III variates, (Exercise 10.6) 252
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), 15-constant frequency surface 160
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), distribution of 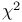 251 305 251 305
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), mean character of ranked individual 229
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), moments of hypergeometric 134
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), multiple contingency 322
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), probable error of biserial 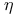 363 363
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), rank correlation 436
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), sampling of contingency coefficients 322
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), sampling of correlation coefficient, (under Co-operative Study) 363
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), skew variation 134
Pearson, Refs., corrections to abrupt distributions (under Pairman), standard errors of frequency constants 228—229
Pitman, E.J.G., refs., significance test applicable to samples from any population 436
Platykurtosis 82
Poincare, characteristic functions 113
Poisson distribution, generally 120—122
Poisson distribution, generally in mixed populations 122—124
Poisson distribution, generally, bivariate form, (Exercise 5.8) 130
Poisson distribution, generally, cumulants of, (Example 6.9) 66
| Poisson distribution, generally, distribution function of 122
Poisson distribution, generally, distribution of means from, (Example 10.9) 243
Poisson distribution, generally, moments of, (Exercise 3.3) 86
Poisson distribution, generally, normal distribution as limiting form of, (Example 4.8) 113
Poisson distribution, generally, sampling of attributes from, (Exercise 8.2) 203
Polynomials see "Tchebycheff — Hermite polynomials"
Populations, as basis of statistical theory 1
Populations, as basis of statistical theory, existent 18—19
Populations, as basis of statistical theory, hypothetical 19
Populations, as basis of statistical theory, types in sampling 186—187
Posterior probability 176
Potatoes and wheat, correlation of yields, (Example 14.3) 332—334
Potatoes and wheat, correlation of yields, (Table 14.4) 333
Potatoes, bias in estimates of yield, (Example 8.4) 189—190
Pretorius, S.J., data from, on Australian marriages and (Table 6.1) 150
Pretorius, S.J., data from, on Australian marriages on beans, (Table 1.13) 20
Pretorius, S.J., data from, on Australian marriages, (Table 1.8) 9
Pretorius, S.J., data from, on Australian marriages, refs., skew bivariate distributions 160
Principle of maximum likelihood 178 see
Principle of moments 83
Principle of moments in fitting Poarson's distributions 143
Prior probability 170
Probability, functions 14
Probability, generally 164—185
Probability, generally and statistical distributions 172—173
Probability, generally in a continuum 170—171
Probability, generally, basic rules of direct probability 166—170
Probability, generally, Bayes' theorem 175—178
Probability, generally, inverse probability 176
Probability, generally, logic of 165
Probability, generally, posterior and prior 176
Probability, generally, von Mises' approach 171—172
Problem of moments 105—110
Problem of moments, refs. 113—114
Product-moment correlation see "Correlation"
Quadrature of Pearson distributions 145
Quantiles, definition 36
Quantiles, graphical determination of 37—38
Quantiles, standard errors of 211—213
Quartiles, interquartile range as measure of dispersion 38
Quartiles, standard errors of 225
Radioactive element (polonium), distribution of particles from, (Example 6.4) 156
Radioactive element (polonium), distribution of particles from, (Table 6.2) 156
Ramsey, F.P., logic of probability 165
Ramsey, F.P., logic of probability, refs., The Foundations of Mathematics 184
Random variables, definition 173
Random variables, definition, addition of 173
Random, Sampling Numbers 192—197
Randomising machine, (Example 8.3) 189
Randomness 171
Randomness, random sampling, generally 186—203
Randomness, technique of 191—197
Range, definition 38
Range, distribution of 223—224
Rank correlation see "Correlation"
Ranking, estimation of 421
Rankings, problem of m see "m rankings"
Ratio, distribution of 248—249
Ratio, distribution of, Cramer's theorem (Exercise 10.8) 252
Ratio, distribution of, Geary's theorem (Exercise 10.9) 253
Ratio, distribution of, refs. 250—251
Rectangular population and (Example 10.12) 244
Rectangular population as one of Pearson's distributions 142
Rectangular population, distribution of geometric mean in samples from, (Example 10.13) 245—246
Rectangular population, distribution of mean of samples from, (Example 10.7) 240
Rectangular population, transformation of frequency-distribution to 18
Recurrence relations for moments of binomial 118
Registrar-General's Statistical Review of England and Wales, data from, (Table 1.1) 3
Registrar-General's Statistical Review of England and Wales, data from, (Table 1.11) 11
Registrar-General's Statistical Review of England and Wales, data from, (Table 1.3) 5
Registration districts, distribution according to births, (Table 14.2) 326
Regression, coefficients of 329
Regression, criterion for linearity of 335—336
Regression, definition 327—329
Regression, partials 368—379
Regression, sampling of coefficients of 336—337 347—349
Regression, sampling of partials 378—379
Regression, significance of 358—359
Regression, standard error of coefficients 337
Religion, correlation with crime, (Example 15.2) 375—376
Reserves and bank deposits, distribution of, (Table 1.26) 28
Residuals, in regression equations 369
Ritchie-Scott, A., refs., correlation coefficient of polychoric table 363
Romanovsky, V., refs., method of moments 86
Romanovsky, V., refs., method of moments and (Exercise 5.2) 135
Romanovsky, V., refs., method of moments, generalisation of Pearson distributions 160
Romanovsky, V., refs., method of moments, moments of hypergeometric 134
Room-space, distribution of families deficient in, (Table 1.24) 27
Rothamsted Experimental Station, data from, (Table 8.1) 187
Rutherford, Lord, data on emission of radioactive particles, (Example 6.4) 156
Saltus, in distribution function 14
Sampling distributions 173—175
Sampling distributions by characteristics functions 242—246
Sampling distributions by geometrical methods 236—242
Sampling distributions by induction 246—248
Sampling distributions of a ratio 248—249
Sampling distributions of a sum 246—247
Sampling distributions, approximations to 254—289
Sampling distributions, derivation by analytical methods 231—236
Sampling distributions, exact 231—253
Sampling distributions, multivariate 250
Sampling distributions, role in sampling problems 201
Sampling moments, generally 254—289 see "k-statistics"
Sampling preliminary 174
Sampling preliminary from attributes 197—202
Sampling preliminary from continuous population 197
Sampling preliminary with and without replacement 186—187
Sampling preliminary, lottery or ticket 192
Sampling preliminary, random sampling see "Random"
Sampling preliminary, randomness in 187—197
Sampling preliminary, sampling problem 186
Sampling preliminary, simple 174
Scale reading, bias in, (Example 8.2) 188
Scarlet fever, deaths from, (Table 1.3) 5
Schoolchildren, distribution according to intelligence and clothing, (Example 13.6) 320
Second Limit Theorem 110—113
Semi-interquartile range, as measure of skewness 38
Semi-interquartile range, as measure of skewness, standard error of 215
Seminvariant statistics 84—85 256
Seminvariant statistics, refs. (Dressel and Kendall) 285
Seminvariants 61 84—85
Seminvariants, refs. 84—85 see
Sentences, distribution of according to length, (Table 1.21) 25
Sheppard's corrections 68—74
Sheppard's corrections as average corrections 74—75
Sheppard's corrections for discrete data 77
Sheppard's corrections, (Exercise 3.13) 88
Sheppard's corrections, compared with sampling fluctuations 210
Sheppard's corrections, multivariate case 80—81
Sheppard's corrections, to cumulants 78
Sheppard's corrections, to factorial moments 77—78
Sheppard, W.F., tables of normal distribution 130
Sheppard, W.F., tables of normal distribution and refs. 134
Sheppard, W.F., tables of normal distribution, correlation coefficient, (Exercise14.4) 364
Shirley poppies, distribution of, (Table 1.5) 7
Shohat, J., refs., Stieltjes integrals 22
Shohat, J., refs., Stieltjes integrals, inequalities for moments 86
Shohat, J., refs., Stieltjes integrals, Second Limit Theorem 112 113 114
Shuffling of cards see "Card-shuffling"
Simple sampling 174
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments 59
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments and (Exercise 3.10) 87—88
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments on Gram — Charlier series 153
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments, corrections for moments when the distribution is symmetrical 85
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments, fitting of Pearson distributions 143
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments, refs., Frequency Curves and Correlation 85 160
Sir Elderton, William P., Hardy's method of calculating factorial moments, tables of 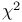 293 293
Sir Galton, Francis, data from Natural Inheritance, (Example 13.4) 314
Sir Hall, A.D., data on yield of grain, (Table 1.18) 23
Sir Hardy, G.F., calculation of factorial moments 59
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте