|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hughes B.D. — Random Walks and Random Environments: Random Environments (том 2) |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Random resistor problem, one-dimensional 319—320
Random walk in random environment 386—496
Random walk in random environment, one-dimensional discrete-time, recurrent See Sinai's problem
Random walk in random environment, one-dimensional discrete-time, transient See Temkin's model
Random walk in random environment, one-dimensional master equation See randomized master equation
Random walk in random environment, variations 496
Random walk in random scenery 495
Random walk, additional references for Volume 1 505—507
Random walk, continuous-time 386 405. Chapter
Random walk, Polya type 437. See also Volume 1 Chapters
Random walk, self-avoiding See Self-avoiding walk
Random-random directed walk 420
Randomized master equation, asymmetric one-dimensional 419—421
Randomized master equation, dimension greater than 1 428—430
Randomized master equation, multistate 421—428
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, defined 410—411
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, disorder slows exploration 412—413
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, formalism of Alexander et al. 411—412
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, non-universal case 416—419
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, scaling arguments 413—414
Randomized master equation, symmetric one-dimensional, various treatments 415—416
Rayleigh's monotonicity law stated, and proved 324
Rayleigh's monotonicity law stated, used 327 328 349 472 473 478 479 493
Rayleigh, Lord 318
Realization of a percolation process 5
Realization of a random environment in Temkin's problem 387
Recurrent random walk in random environment 388
Renormalization, approximate for square lattice 254—258
Renormalization, exact for Sierpinski lattice 260—261
Renormalization, for percolation conduction problem 350
Renormalization, for Temkin's model 405—406
Renormalization, position-space 252
Renormalization, real-space 252
Renormalization, transformation 252
Renormalized effective medium, approximation 356
Replica method 348 415
Resistance 319
Resistance dimension 469 477
Resistive susceptibility 361
Right excursion, defined 388
Right recurrent, defined 388
Right recurrent, necessary and sufficient conditions 388
Russo — Seymour — Welsh theorem, cf. Cardy's conjecture on crossing probabilities 263
Russo — Seymour — Welsh theorem, stated 159
Russo — Seymour — Welsh theorem, used 240 249
Russo's formula, corollary to 101
Russo's formula, special case of 294
Russo's formula, stated and proved 99
Russo's formula, used 102 106 119
Scalar models 317
Scaling relation of Stauffer for 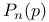 , implications for exponents 210 , implications for exponents 210
Scaling relation of Stauffer for 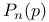 , rigorous for Bethe lattice 210 , rigorous for Bethe lattice 210
Scaling relation of Stauffer for 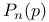 , stated 209 , stated 209
Scaling relations for percolation, heuristic discussion 2Q7—211
Scaling relations for percolation, rigorous results 215—216 248—251
Schwarz inequality, used 206 212 233 413.
Self-avoiding walk See also Volume 1 Chapter
Self-avoiding walk, additional references for Volume 1 507—510
Self-avoiding walk, bounds for percolation probability 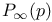 17 17
Self-avoiding walk, prior knowledge assumed 1—2
Self-avoiding walk, used 16 21 23 24 40 58 90 93 102 123
Series expansion, high-density for 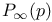 27 27
Series expansion, low-density for 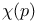 40 40
Series, resistors arranged in 319
Seymour — Welsh theorem 153
Shape of percolation clusters 51
Sierpinski lattice 260
Simon's inequality, stated and proved 94
Simon's inequality, used 98
Simple plane lattice 168
Sinai's problem 406—410
Sinai's theorem, non-rigorous derivation 407
Sinai's theorem, stated 407
Site percolation, clusters in 11
Site percolation, defined 11—12
Site percolation, exact thresholds for d=2, history 160
Site percolation, exact thresholds for d=2, summarized 160
Site percolation, includes bond percolation 13
Site percolation, picture of, backbone 293
Site percolation, picture of, hull 179
Site percolation, picture of, just above 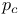 292 292
Site percolation, wet set, cardinality of 11
Site percolation, wet set, defined 11
Site, empty or vacant 11
Site, p-occupied 107 137
Site, present or occupied 11
Site-bond percolation 52 265
Slowly-varying 36 198 205 401
Smooth lattice 479
Solomon's theorem, on first-passage times in Temkin's model 403
Solomon's theorem, on recurrence of Temkin's model 388
Specific conductivity 326
Specific heat exponents in percolation 204
Spectral dimension 444 445 458 459 462 464 467 481 495
Spineless infinite cluster 104
Sponge 123
Sponge-crossing critical probability 124
Square lattice, 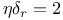 239 239
Square lattice, 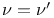 243 243
| Square lattice, 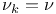 235 235
Square lattice, exact bond threshold 142
Star-triangle relation 69 156 264
Stepping distance, defined 86
Stepping distance, used 89 91 97 230 294 476 480 481
Stokes — Einstein relation 451—457 461 470
Stokes — Einstein relation, misleading use of term 453
Stokes — Einstein relation, standard use of term 452
Strong law of large numbers, applied to Temkin's problem 389 390 396
Strong law of large numbers, one-dimensional resistor networks 319 332
Susceptibility 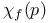 in percolation 37 107 201 in percolation 37 107 201
Susceptibility 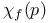 in percolation, exact for Bethe lattice 37 in percolation, exact for Bethe lattice 37
Swendsen — Wang distribution 279
Swiss-cheese model 339
Symmetric difference 128
Tauberian Theorem, discrete See Discrete Tauberian
Temkin's model, definition and formulation 387—388
Temkin's model, diffusion constant for 397
Temkin's model, excursions and recurrence 388—390
Temkin's model, first-passage times and excursion times 397—405
Temkin's model, mean duration of a left excursion, averaged over environments 397
Temkin's model, mean duration of a left excursion, distribution over environments 399
Temkin's model, possible behaviours 390—392
Temkin's model, renormalization 405—406
Temkin's model, treatment of Derrida and Pomeau 392—397
Temkin's model, variants 406
Theorem for Laplace transform, stated 413
Theorem for Laplace transform, strong See Tauberian Theorem for Laplace transform
Theorem for Laplace transform, used 413 414 417
Theorem of Aizenman and Newman on divergence of the mean cluster size 102
Theorem of Aizenman and Newman on the decay of connectivity function 97
Theorem of Aizenman and Newman on the decay of the cluster-size distribution 111
Theorem of Burton and Keane 135
Theorem of Grimmett and Marstrand, stated 125
Theorem of Grimmett and Marstrand, used 482 486
Theorem of Grimmett, Kesten, and Zhang 481
Theorem of Hammersley, van den Berg, and Kesten 95
Theorem of Kesten, Kozlov, and Spitzer 404
Theorem of Men'shikov See Men'shikov's theorem
Theorem of Newman and Schulman 133
Theorem of Nguyen 234
Theorem of Solomon, on first-passage times in Temkin's model 403
Theorem of Solomon, on recurrence of Temkin's model 388
Theorem of van den Berg and Keane 137
Theorem, Bond-site comparison 20
Theorem, infinite cluster uniqueness 135
Theorem, on recurrence for nested lattices 472
Theorem, on slices and quadrants of slices stated 482
Theorem, used 483—484
Thomson's Principle, stated and proved 323
Thomson's Principle, used 325 327 329 338
Trace operator 275
Transformation, ergodic 129
Transformation, measure-preserving 128
Transition matrix 423
Tree conductance 343
Tree graph 108
Trial current distribution 323
Trial potential distribution 321
Triangle condition, holds for large enough dimension 200
Triangle condition, implications for scaling theory 212
Triangle condition, introduced 200
Triangle condition, significance of 245
Triangle inequality, for real numbers 129 130
Triangle inequality, for stepping distance, stated 89
Triangle inequality, for stepping distance, used 91 98
Triangular lattice, admits Seymour — Welsh Theorem 153
Triangular lattice, exact bond threshold 142
Triangular lattice, exponents same as for honeycomb 200
Triangular lattice, site threshold 160
Triple point 136
Turnstile models 419
Uniqueness of infinite cluster, implications of 126
Uniqueness of infinite cluster, proved 132—136
Uniqueness principle, proof set as exercise 325
Uniqueness principle, used 472 474
Universality 50
Upper critical dimensionality, and hyperscaling 282—283
Upper critical dimensionality, and triangle condition 200—201
Upper critical dimensionality, apparent fractal dimensions above 298
Upper critical dimensionality, believed to be  50 50
Upper critical dimensionality, different for directed percolation 291
Upper critical dimensionality, evidence in favour of  201 272—274 201 272—274
Upper semicontinuous functions 137
Van den Berg-Kesten inequality, stated and proved 93
Van den Berg-Kesten inequality, used 93—95 102 105 110 115 116 244
Variational method 328
Vector models 317
Voronoi algorithm 59 339
Weak convergence 407 418 429
Weak Law of Large Numbers, for one-dimensional resistor networks 319
Wet set, bond percolation, defined 11
Wet set, radius of 94
Wet set, site percolation, defined 11
Wet set, span of 242
Whitney dual of two-dimensional lattice 143
Wigner — Seitz construction 59
“bow-tie” lattice 158 175 200
“dice” lattice 170
“incipient infinite cluster” 248 249 301—303 444—448 466 467
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



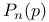 , implications for exponents
, implications for exponents 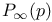
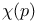
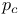
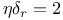
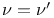
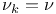
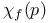 in percolation
in percolation