|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Feller W. — Introduction to probability theory and its applications (volume 1) |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
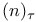 29 29
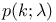 157 157
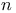 and and 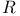 174 174
 , distribution of decimals 31 61 , distribution of decimals 31 61
 for recurrent events 303 308 for recurrent events 303 308
Absolute probabilities 116
Absolute probabilities in Markov chains 384
Absorbing barrier in random walks 342 368 369 376
Absorbing barrier in random walks in higher dimensions 361
Absorbing boundaries 477
Absorbing states (in Markov chains) 384
Absorption probabilities in birth and death processes 455 457
Absorption probabilities in diffusion 358 367
Absorption probabilities in Markov chains 399ff. 418 424 425 438ff.
Absorption probabilities in random walk 342ff. 362 367 “Extinction” “First “Ruin
Acceptance cf. “Inspection sampling”
Accidents as Bernoulli trials with variable probabilities 282
Accidents bomb hits 160
Accidents distribution of damages 288
Accidents occupancy model 10
Accidents Poisson distribution 158 292
Accidents urn models 119 121
Adler, H.A. and Miller, K.W. 467
Aftereffect urn models 119 122
Aftereffect, lack of 329 458
Age distribution in renewal theory 335 340
Age distribution in renewal theory, example involving ages of a couple 13 17
Aggregates, self-renewing 311 334 340
Alleles 133
Alphabets 129
Andersen cf. “Sparre Andersen E.”
Andre, D. 72 369
Animal populations recaptures 45
Animal populations trapping 170 239 288 301
Aperiodic cf. “Periodic”
Arc sine distributions 79
Arc sine law for first visits 93
Arc sine law for last visits 79
Arc sine law for maxima 93
Arc sine law for sojourn times 82
Arc sine law for sojourn times, Counterpart 94
Arrangements cf. “Ballot problem” “Occupancy”
Average of distribution “Expectation”
Averages, moving 422 426
Averaging, repeated 333 425
b(k; n, p) 148
Bachelier, L. 354
Backward equations 358 468 474 482
Bacteria counts 163
Bailey, N.T.J. 45
Ballot problem 69 73
Balls in cells cf. “Occupancy problems”
Banach’s match box problem 166 170 238
Barriers, classification of 343 376
Bartky, W. 363
Barton, D.E. and Mallows, C.L. 69
Bates, G.E. and Neyman, J. 285
Bayes’ rule 124
Bernoulli trials definition 146
Bernoulli trials interpretation in number theory 209
Bernoulli trials with variable probabilities 218 230 282
Bernoulli trials, infinite sequences of 196ff.
Bernoulli trials, multiple 168 171 238
Bernoulli trials, recurrent events connected with 313ff. 339 “Betting” “First “Random “Returns “Success etc.)
Bernoulli — Laplace model of diffusion 378 397
Bernoulli — Laplace model of diffusion generalized 424
Bernoulli, D. 251 378
Bernoulli, J. 146 251
Bernstein, S. 126
Bertrand, J. 69
beta function 173
Betting 256 344ff. 367
Betting in games with infinite expectation 246 251ff. 322
Betting on runs 196 210 327
betting systems 198 346
Betting three players taking turns 18 24 118 141 424 “Ruin
Bias in dice 149
Billiards 284
Binomial coefficients 34 50ff.
Binomial coefficients, identities for 63ff. 96 97 120
Binomial distribution 147ff.
Binomial distribution as conditional distr. in Poisson process 237
Binomial distribution central term 150 180 184
Binomial distribution combined with Poisson 171 287 301
Binomial distribution expectation 223
Binomial distribution expectation, absolute 241
Binomial distribution generating function 268
Binomial distribution in occupancy problems 35 109
Binomial distribution tail estimates 151—152 173 193ff.
Binomial distribution variance 228 230
Binomial distribution, as limit in Ehrenfest model 397
Binomial distribution, convolution of 173 268
Binomial distribution, for hypergeometric distr. 59 172
Binomial distribution, integrals for 118 368 370
Binomial distribution, normal approximation to 179ff.
Binomial distribution, Poisson approximation to 153ff. 171—172 190
Binomial distribution, Poisson approximation to numerical examples 109 154
Binomial distribution, the negative cf. “Negative binomial”
Binomial formula 51
Birth process 448ff. 478ff.
Birth process general 476
Birth process, backward equations for 468
Birth process, divergent 451ff. 476
Birth-and-death process 354ff.
Birth-and-death process in servicing problems 460 478ff.
Birth-and-death process, backward equations for 469
Birth-and-death process, inhomogeneous 472
Birthdays as occupancy problem 10 47 102
Birthdays duplications 33 105
Birthdays duplications table 487
Birthdays expected numbers 224
Birthdays, Poisson distribution for 106 155
Birthdays, Poisson distribution for, combinatorial problems involving 56 58 60 169 239
Bivariate generating functions 279 340
Bivariate negative binomial 285
Bivariate Poisson 172 279
Blackwell, D., Dewel, P. and Freedman, D. 78
Blood counts 163
Blood tests 239
Boltzmann — Maxwell statistics 5 21 39ff. 59
Boltzmann — Maxwell statistics as limit for Fermi — Dirac statistics 58 (cf. “Occupancy problems”)
Bomb hits (on London) 160
Bonferroni’s inequalities 110 142
Books produced at random 202
Boole’s inequality 23
Borel — Cantelli Lemmas 200ff.
Borel, E. 204 210
Bose — Einstein statistics 5 20 40 61 113
Bose — Einstein statistics negative binomial limit 62
Bottema, O. and Van Veen, S.C. 284.
Boundaries for Markov processes 414ff. 477
Branching processes 293ff. 373
Branching processes with two types 301.
Breakage of dishes 56
Breeding 144 380 424 441
Brelot, M. 419
Bridge ace distribution 11 57
Bridge definition 8
Bridge waiting times 57
Bridge waiting times, problems and examples 27 35 37 47 56 100 112 140 169 “Poker” “Shuffling”)
Brockmeyer, E., Halstroem, H.E. and Jensen, A. 460
Brother-sister mating 143 380 441
Brownian motion cf. “Diffusion”
busy hour 293
Busy period in queuing 299 300 315
Cantelli, Borel — Cantelli lemmas 200
Cantelli, F.P. 204
Cantor, G. 18 336
Car accidents 158 292
Cardano, G. 158
| cards cf. “Bridge” “Matching “Poker” “Shuffling”
Cartesian product 129
Cascade process cf. “Branching process”
Catcheside, D.J. 55 287
Catcheside, D.J., Lea, D.E. and Thoday, J.M. 112 161
Causes, probability of 124
Cell genetics, a problem in 379 400
Centenarians 156
Central force, diffusion under 378
Central limit theorem 244 254 261
Central limit theorem applications to combinatorial analysis 256
Central limit theorem to random walks 357
Central limit theorem to recurrent events 320 (cf. “DeMoivre — Laplace limit theorem” “Normal
Chain letters 56
Chain reaction cf. “Branching process”
Chains, length of random 240
Chandrasekhar, S. 425
Changes of sign in random walks 84ff. 97
Changing stakes 346
Channels cf. “Servers” “Trunking
Chapman — Kolmogorov equation for Markov chains 383 421
Chapman — Kolmogorov equation for non-Markovian processes 423
Chapman — Kolmogorov equation for stochastic processes 445 470ff. 482
Chapman, D.G. 45
Characteristic equation 365
Characteristic roots = eigenvalues 429
Chebyshev inequality 233 242
Chebyshev, P.L. 233
Chess 111
Chromosomes 133
Chromosomes, breaks and interchanges of 55 112
Chromosomes, Poisson distribution for 161 171 287
Chung, K.L. 82 242 312 409 413
Clarke, R.D. 160
Classification multiple 27
Closed sets in Markov chains 384ff.
Cochran, W.G. 43
Coin tossing as random walk 71 343
Coin tossing experiments 21 82 86
Coin tossing ties in multiple 316 338 “Bernoulli “Changes “First “Leads” “Random “Returns “Success etc.)
Coin tossing, simulation of 238
Coincidences = matches 100 107
Coincidences multiple 112
Collector’s problem 11 61 111
Collector’s problem waiting times 48 225 239 284
Colorblindness as sex-linked character 139
Colorblindness, Poisson distribution for 169
Combinatorial product 129
Combinatorial runs cf. “Runs combinatorial”
Competition problem 188
Complementary event 15
Composite Markov process (shuffling) 422
composition cf. “Convolution”
Compound Poisson distribution 288ff. 474
Conditional distribution 217ff. 237
Conditional expectation 223
Conditional probability 114ff. (cf. “Transition probabilities”)
Confidence level 189
Connection to a wrong number 161
Contagion 43 120 480
Contagion, spurious 121
Continuity equation 358
Continuity theorem 280
Convolutions 266ff.
Convolutions, special cases 173
Coordinates and coordinate spaces 130
Cornell professor 55
Correlation coefficient 236
Cosmic rays 11 289 451
Counters cf. “Geiger counter” “Queuing” “Trunking
Coupon collecting cf. “Collector’s problem”
Covariance 229ff. 236
Cox, D.R. 226
Cramer, H. 160
Crossing of the axis (in random walks) 84ff. 96
Cumulative distribution function 179
Cycles (in permutations) 257 270
Cyclical random walk 377 434
Cylindrical sets 130
Dahlberg, G. 140
Damage cf. “Accidents” “Irradiation”
Darwin, C. 70
de Mire’s paradox 56
Death process 478
Decimals, distribution of e and  32 61 32 61
Decimals, distribution of law of the iterated logarithm 208 (cf. “Random digits”)
Decomposition of Markov chains 390
Defective items, Poisson distribution for 155
Defective items, Poisson distribution for elementary problems 55 141
Defective random variables 273 309
Delayed recurrent events 316ff.
Delayed recurrent events in renewal theory 332 334
DeMoivre — Laplace limit theorem 182ff.
DeMoivre — Laplace limit theorem application to diffusion 357 (cf. “Central limit theorem” “Normal
Demoivre, A. 179 264 285
Density fluctuations 425 (cf. “Bernoulli — Laplace model” “Ehrenfest
Density function 179
Dependent cf. “Independent”
Derivatives partial, number of 39
Derman, C. 413
Determinants (number of terms containing diagonal elements) 111
Dewel, P. 78
Diagonal method 336
Dice ace runs 210 324
Dice ace runs as occupancy problem 11
Dice de Mere’s paradox 56
Dice equalization of ones, twos, ... 339
Dice Newton — Pepys problem 55
Dice Weldon’s data 148
Difference equations 344ff.
Difference equations method of images 369
Difference equations method of particular solutions 344 350 365
Difference equations passage to limit 354ff. 370
Difference equations several dimensions 362
Difference equations several dimensions for Polya distribution 142 480
Difference equations several dimensions in occupancy problems 59 284
Difference of events 16
Diffusion 354ff. 370
Diffusion with central force 378 (cf. “Bernoulli — Laplace model” “Ehrenfest
Dirac — Fermi statistics 5 41
Dirac — Fermi statistics for misprints 42 57
Discrete sample space 17ff.
Dishes, test involving breakage of 56
Dispersion = variance 228
Distinguishable cf. “Indistinguishable”
Distribution conditional 217ff. 237
Distribution function 179 213
Distribution function, empirical 71
Distribution joint 213
Distribution marginal 215
Doblin, W. 413
Domb, C. 301
Dominant gene 133
Domino 54
Doob, J.L. 199 419 477
Dorfman, R. 239
Doubly stochastic matrices 399
Drift 342
Drift to boundary 417
Duality 91
Dubbins, L.E. and Savage, L.J. 346
Duration of games in sequential sampling 368 (cf. “Absorption probabilities” “Extinction” “First “Waiting
Duration of games in the classical ruin problem 348ff.
e, distribution of decimals 32 61
Ecology 289
Efficiency, tests of 70 148 149
Eggenberger, F. 119
Ehrenfest model 121 377
Ehrenfest model density 425
Ehrenfest model reversibility 415
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



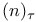
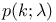
 and
and 
 , distribution of decimals
, distribution of decimals  for recurrent events
for recurrent events