|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ghosh Sujit K., Mallick Bani K., Dey Dipak K. Ч Generalized Linear Models: A Bayesian Perspective |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, case-control study with deprivation 333Ч337 341Ч342 343fЧ344f
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, classic approaches 337Ч339
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, classic approaches, extensions and procedures 339
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, classic approaches, formulation 337Ч339
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, logistic regression estimate 91Ч93
Empirical Bayes (EB) approaches, small area inference 94
Equicorrelated multivariate probit (MVP), prior-posterior summary 126t
Ergodic means, Gibbs sampler for a 249 249f
Errors-in-variables modeling 331Ч344
EscobarТs Gibbs sampling algorithm 235
Estimates of appropriateness, model-based 211
Estimates of appropriateness, standard categorical 211
Evolution equation 59
Exchangeable random effects, GLMMs 392
Expected predictive deviance 402
Exponential dispersion models (EDM) 12Ч14
Exponential dispersion models (EDM), OGLMs 77
Exponential family 12Ч14
Exponential power distribution, binary regression model, data adaptive Bayesian analysis 246Ч248
Exponential power model 250t
Extended Gamma processes 10
Extended Gamma processes, prior 290
Extended Gamma processes, prior, posterior samples 302
Finite mixture model, binary response regression 233Ч234
Finite mixture model, University of Arkansas student retention 238
Finite mixture model, University of Arkansas student retention, vs. general mixture model 237Ч238
First order difference model 30
Fisher information matrix 5
Fisher information matrix, fitting OGLMs 78Ч79
Fisher scoring algorithm, DGLMs 61
Fitted values, male flour beetle data set 268t
Flour beetle data set, male 262t 267t 268t
Formal Bayesian model, determination 80
Founder nodes, prior distributions 390
Functionally compatible vs. compatible 29
Gamma distribution 390
Gamma process priors, cumulative baseline hazard 289Ч290
Gamma processes 10
Gamma residual effects 25
Gaussian distributions, gamma and inverse 5
Gaussian distributions, inverse, correlated ordinal data models 142
Gaussian models, state-space, DGLMs 61
Gaussian models, vs. Markov model, point-referenced binary spatial data 374
GelfandТs hierarchical centering reparameterization technique, time series count data 166Ч167
General F implementation, Gibbs sampler item response modeling 183
General mixture model, University of Arkansas student retention 238
General mixture model, University of Arkansas student retention, vs. finite mixture model 237Ч238
General mixtures, binary response regression 234Ч236
General regression, link function g modeling 219
Generalized estimating equation (GEE), correlated ordinal data models 133
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) 391Ч394
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), correlated random effects 392Ч393
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), definition 24Ч26
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), exchangeable random effects 392
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), hierarchical 31Ч36
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), models 43Ч44
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), normal linear random effects 43Ч48
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), prior distributions 44Ч46
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), prior elicitation and variable selection 41Ч52
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), random effects 23Ч37
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), WinBUGS 392Ч393
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), WinBUGS, covariate measurement error 397Ч400
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), WinBUGS, informative missing data 396Ч397
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), WinBUGS, missing data 396
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), WinBUGS, prediction 397
Generalized linear models (GLMs) 4Ч5
Generalized linear models (GLMs), Bayesian analysis 273Ч284
Generalized linear models (GLMs), Bayesian view 3Ч17
Generalized linear models (GLMs), Bayesian, small area inference 89Ч105
Generalized linear models (GLMs), BMARS 221Ч228
Generalized linear models (GLMs), categorical data 365
Generalized linear models (GLMs), components 274 389
Generalized linear models (GLMs), DAG 387 388f
Generalized linear models (GLMs), DAG extensions 393f
Generalized linear models (GLMs), DoodleBUGS 389Ч390
Generalized linear models (GLMs), dynamic 57Ч70
Generalized linear models (GLMs), non-canonical links 391
Generalized linear models (GLMs), overdispersion 12Ч14 73Ч85 391Ч392
Generalized linear models (GLMs), parametric Bayesian 10
Generalized linear models (GLMs), semiparametric 10Ч12
Generalized linear models (GLMs), variable selection 288
Generalized linear models (GLMs), WinBUGS 389Ч391
Generalized linear models (GLMs), WinBUGS, cavort measurement error 397Ч400
Generalized linear models (GLMs), WinBUGS, informative missing data 396Ч397
Generalized linear models (GLMs), WinBUGS, missing data 396
Generalized linear models (GLMs), WinBUGS, prediction 397
Generalized Liouville distributions (GLD) model 350
Generalized Liouville distributions (GLD) model, compositional data 354Ч361
Gibbs sampler 7 36Ч37 219
Gibbs sampler, analysis of survival data 259Ч260
Gibbs sampler, correlated ordinal data models 138Ч142
Gibbs sampler, cumulative baseline hazard 289Ч290
Gibbs sampler, DGLMs 62 63Ч64
Gibbs sampler, fitting OGLMs 79
Gibbs sampler, for a ergodic means 249 249f
Gibbs sampler, for a ergodic means, posterior distribution 249 249f
Gibbs sampler, General F implementation, item response modeling 183
Gibbs sampler, GLMMs 48
Gibbs sampler, method, Monte Carlo posterior estimates 232Ч235
Gibbs sampler, mixture-model approach example 263Ч265
Gibbs sampler, post AMI practice guideline development 199 203 204
Gibbs sampler, probit link data augmentation, item response modeling 184Ч185
Gibbs sampler, small area inference 97
Gibbs sampler, two-parameter exponential family model, item response modeling 181Ч182
Gibbs sampler, variable selection 273Ч284
Gibbs variable selection, Gibbs sampler variable selection strategies 277Ч278
Gibbs variable selection, graphical model representation 279f
Gibbs variable selection, posterior model probabilities 280t 281t
Gilks Ч Wild algorithm, small area inference 97
Graphical model representation, variable selection 279f
Grayscale plot, residential properties dataset 384f
Health service areas (HSAs), small area inference 100
Hessian matrix, correlated ordinal data models 140
Hierarchical Bayes (HB) 4
Hierarchical Bayes (HB), approaches 90
Hierarchical Bayes (HB), approaches, logistic regression estimate 91Ч93
Hierarchical Bayes (HB), model 6
Hierarchical Bayes (HB), point estimator, small area inference 93
Hierarchical Bayes (HB), small area inference 94
Hierarchical generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) 31Ч36
Hierarchical generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs), Bayesian inferences 36Ч37
Hierarchical generalized linear models (GLMs), overdispersion 84Ч85
Hierarchical Poisson regression model, small area inference 94
Hierarchical, centering, reparameterization technique Gelfand, time series count data 166Ч167
Highest posterior density (HPD), correlated ordinal data models 150Ч155
Histogram, posterior predictive distributions 192f
Historical data, time series count data 159
Hybrid sampler 223
Hyperparameters 59
Hyperparameters, small area inference 96Ч97
Hyperparameters, specifications 47Ч48
Hyperparameters, specifications, time series count data 164Ч165
Identity link 390
Importance sampling density (ISD), point-referenced binary spatial data 378Ч379
Importance weighted marginal, posterior density estimation (IWMDE), Chen method 50
Improper priors, theorems, item response modeling 178Ч179
Incidence probabilities 255
Incidence probabilities, posterior densities plot 266 266f
Independent random effects 26
Independent variable, small area inference 92
Indicator kriging, point-referenced binary spatial data 374
Indicator variograms, point-referenced binary spatial data 374
Inference, correlated binary data 120
Inference, finite population proportion small area 92
Inference, item response modeling 185Ч186
Inference, point-referenced binary spatial data 373Ч385
Inference, small area, Bayesian generalized linear models 89Ч105
Informative prior elicitation, Bayesian analysis 44Ч46
Informative prior elicitation, item response modeling 180
Inverse Gaussian distribution, correlated ordinal data models 142
| Inverse link function 231
IsConstant method, graphical model 403
Item parameters, conditional distribution, item response modeling 185
Item response curve 175Ч176
Item response modeling 173Ч193
Item response modeling, Bayesian fitting 181Ч185
Item response modeling, checking 186Ч188
Item response modeling, exam administration 176Ч178
Item response modeling, example 188Ч191
Item response modeling, inferences 185Ч186
Item response modeling, item response curve 175Ч176
Item response modeling, prior distributions 178Ч180
JefferysТ prior 8 13
JefferysТ prior, fitting OGLMs 78Ч79
Joint posterior distribution 48
Joint posterior distribution, small area inference 98
Joint prior, time series count data 163
Joint probability mass function, correlated binary data 120
Kalman filter 59 60
Kalman Filter, DGLMs 62
Kepler node 404
Kernel smoothing, correlated binary data 125Ч126
Kriging, indicator, point-referenced binary spatial data 374
Kuo and Mallick sampler, graphical model representation 279f
Kuo and MallickТs Unconditional Priors, posterior model probabilities 280t 281t
Kyphosis dataset 224
Kyphosis dataset, boxplot 226f
LaplaceТs method 8
LaplaceТs method, small area inference 94 97
LaplaceТs prior 8
Latent Bayesian residual 248 249Ч250
Latent detrended variogram plot, residential properties dataset 383f
Latent variables, conditional distribution, item response modeling 184
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis 6
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, Bayesian models 5
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, contribution, computation 124Ч125
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, equations 5
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, functions 5 6
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, functions, Cox variable selection 292Ч293
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, functions, item response modeling 178
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, functions, time series count data 160Ч162
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, mixture-model approach, analysis of survival data 257
Likelihood analysis, Bayesian analysis, ordinate, correlated binary data 124Ч125
LindleyТs paradox 223
Linear approximation, piecewise 61
Linear Bayes approach, DGLMs 60Ч61
Linear predictor 274 389
Link 218 274
Link function 6 10 25 60 243 389
Link function h 239
Link function, g modeling 218Ч219
Link function, g modeling, binary response regression 218Ч219
Link function, g modeling, general regression 219
Link function, g modeling, mixture models 219
Link function, inverse 231
Log deviance loss 16
Log link 390
Log marginal likelihood 126t
Log scoring loss 16
Log Value method, graphical model 403
Log-concave, posterior 5
Log-linear models 280 280t
Log-linear models, for 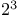 contingency table BUGS codes 282Ч283 contingency table BUGS codes 282Ч283
Logical nodes 403Ч404
Logistic distribution 25
Logistic models 2
Logistic models, binary explanatory factors, BUGS codes 283Ч284
Logistic models, item response modeling 175Ч176
Logistic regression estimate, small area inference 91Ч93 98
Logistic regression estimate, small area inference, example 91
Logistic regression estimate, vs. classical logistic regression model 224Ч225 225f
Logistic regression models 225Ч226 280Ч281 281t
Logit link 25 390
Logit link, functions 243
Logit normal model see УProbit normal modelФ
Logit normal model, correlated binary data 119
Logit regression model, Bayesian analysis 243
LogitLogQ method, graphical model 403
Longitudinal binary data, correlated binary data 119Ч123
Longitudinal binary data, drop-outs 127
Longitudinal binary responses, scale mixture of multivariate, normal (SMMVN) link functions 133
Low birth weight in infants dataset 248Ч250
Male flour beetle data set 262t
Male flour beetle data set, absolute residuals 268t
Male flour beetle data set, fitted values 268t
Male flour beetle data set, model comparisons 267t
Map method, graphical model 403
Marginal likelihood, ChibТs method 127
Marginal likelihood, correlated binary data 124
Marginal likelihood, multivariate models 155
Marginal likelihood, time series count data 161
Marginal posterior distribution, Bayesian graphical models 388
Marginal posterior distribution, time series count data 166Ч167
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) 5 8 27 28 31 36Ч37 50
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), based approaches, complex Bayesian inference problems 62Ч65
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), correlated binary data 124
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), implementation, Bayesian procedure 12
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods 218 256 287Ч288 313
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, Bayesian graphical models 388Ч389
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, classification trees 368
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, compositional data 350Ч351
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, errors-in-variables models 340
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, point-referenced binary spatial data 378
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), methods, WinBUGS 390Ч391
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), posterior distribution sample algorithm 117 127Ч128
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), small area inference 94
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), small area inference, BUGS software 96
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), technique, DGLMs 64
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), time series count data 166Ч167
Markov random field models 29Ч30
Markov transition model 123
Matrix inversion, point-referenced binary spatial data 375
Maximized log-likelihood 126t
Maximum likelihood estimators, (MLE) 5
Maximum likelihood logistic regression analysis, University of Arkansas student retention 238
Mean survival time, posterior densities plot 266Ч267 267f
Measurement error problem 331
Medical care, quality assessment 196Ч197
Meningococcic meningitis, DGLMs application 66Ч68
Metropolis algorithm, correlated ordinal data models 142
Metropolis sampling scheme, correlated ordinal data models 141
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm 5 7 36Ч37
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, correlated ordinal data models 138 140Ч141
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, DGLMs 64Ч65
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, fitting OGLMs 79
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, small area inference 97 99Ч100
Metropolis-Hastings step 275
Missing at random (MAR) 396Ч397
Missing completely at random (MCAR) 396Ч397
Mixture models 10
Mixture models, analysis of survival data 255Ч268
Mixture models, analysis of survival data, likelihood 257
Mixture models, correlated binary data diagnostics 314
Mixture models, link function g modeling 219
Mixture models, posterior computations, correlated binary data diagnostics 317
Model adequacy 14Ч15
Model adequacy, OGLMs 81
Model and notation, Cox variable selection 289
Model checking 232 236
Model checking, WinBUGS 402
Model choice, Bayesian approach 15Ч16
Model comparisons, male flour beetle data set 267t
Model determination, analysis of survival data 260Ч261
Model determination, approaches 14Ч17
Model determination, compositional data 352Ч354
Model diagnostic, binary response regression 236Ч237
Model diagnostic, computational methods 237
Model diagnostic, diagnostic tools 237
Model diagnostic, diagnostic tools, goal 236
Model elaboration 14
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



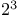 contingency table BUGS codes
contingency table BUGS codes