|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| David H., Nagaraja H. Ч Order Statistics (Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
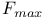 256Ч258 365 256Ч258 365
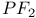 , Polya frequency function of order 2 78 , Polya frequency function of order 2 78
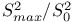 132Ч133 362 132Ч133 362
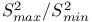 256Ч258 365 256Ч258 365
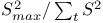 153 258 362 153 258 362
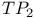 (totally positive of order 2) 25 (totally positive of order 2) 25
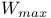 / /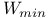 365 365
Adaptive estimators 216Ч218
Analysis of variance, by range methods 253Ч256 261 364Ч365
Applications general 1Ч3
Applications of extremes 284Ч285
Applications of range 239Ч240
Approximations for moments of Order statistics 70Ч74 83Ч86
Approximations to upper percentage points of statistics expressible as maxima 125Ч133
Asymptotic distribution for dependent variates 309Ч311
Asymptotic distribution for multivariate samples 313Ч315
Asymptotic distribution of concomitants of Order statistics 345Ч350
Asymptotic distribution of extremes 296Ч309
Asymptotic distribution of intermediate Order statistics 311Ч313
Asymptotic distribution of linear functions of Order statistics 331Ч335
Asymptotic distribution of midrange 326Ч327
Asymptotic distribution of quantiles 285Ч290
Asymptotic distribution of range 324Ч326
Asymptotic distribution of sample spacings 327Ч328
Asymptotic distribution of trimmed mean 329Ч331
Asymptotic estimation 335Ч341
Bahadur representation of sample quantile 285 288 311
BasuТs theorem 174 209
Bayesian methods 236
Bernoulli distribution 32 54Ч55 88
Best linear estimates see УLinear estimatorsФ
Best linear unbiased (BLU) predictor 209Ч210
Beta distribution 6
Beta distribution bounds for 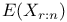 92 92
Binomial distribution, moments of Order statistics in 44 360
Binomial distribution, range in 261Ч262 356
Bioequivalence 255
Bivariate distributions, estimation in 250Ч253 279
Bivariate distributions, Order statistics in 13 25 278
Bivariate exponential 102 117 321
Bivariate extremal distributions 313Ч315 321
Bivariate normal distribution, circular 250Ч251
Bivariate normal distribution, linear function of Order statistics in 114
Bivariate normal distribution, moments of Order statistics in 54
BlomТs estimates 191
blue 185Ч189 see
BLUE, tables of coefficients of 363Ч364
Bonferroni inequalities 126 133 152
Boole formula 125
Bootstrap estimation 183Ч185 227Ч228
Bounds for linear functions of Order statistics and their expectations 106Ч112 118
Bounds for moments of Order statistics 60Ч74
Bounds for upper percentage points of statistics expressible as maxima 125Ч133
c-comparison; c-ordering; c-precedence 79Ч82
Cauchy distribution 357
Cauchy distribution, median in 54
Cauchy distribution, moments of Order statistics in 57 357
Cauchy distribution, trimmed mean in 237
CauchyТs functional equation 142
CauchyТs functional equation, integrated 142
CauchyТs inequality 107 111
Censoring 191
Censoring, BLUE in presence of 363Ч364
Censoring, estimation in presence of 191Ч208 229Ч231 335Ч341
Censoring, in exponential distribution 204Ч208 232Ч235
Censoring, of multivariate normal 203
Censoring, progressive 200Ч201
Censoring, Type I 191Ч195
Censoring, Type II 191Ч208
Characterizations 142Ч144 156Ч158
Chi (1 DF) distribution 357
Chi (1 DF) distribution, estimation for 363
Chi (1 DF) distribution, moments of Order statistics in 357
Chi (1 DF) distribution, percentage points of Order statistics in 355
Chi-squared distribution see УGamma distributionФ
Circular normal distribution 250Ч251
Closest two out of three observations 237
Clusters 137
Combinatorial extreme-value distributions 129
Completeness 173Ч175
Computer simulation, Order statistics in 15 355
Computing distribution of functions of Order statistics 355
Computing distribution of Order statistics in inid case 105Ч106
Concave-convex functions 82
Concomitants of Order statistics 144Ч148 158 251Ч253
Concomitants of Order statistics in double sampling 267Ч268
Concomitants of Order statistics in ranked-set sampling 263Ч264
Concomitants of Order statistics, asymptotic theory of 345Ч350 353
Conditional distribution of Order statistics 17
Confidence intervals for  in normal samples 257 365 in normal samples 257 365
Confidence intervals, distribution-free 159Ч164 169Ч170
Contamination see УOutliersФ
control charts 274Ч276
Convex function 66 107
Correlation coefficient, quick estimate of 252
Covariances of Order statistics 34Ч35 50
Covariances of Order statistics, tables of 356Ч359
Covering circle 251
Data analysis 2 239
Data compression 3 290Ч296
Density-quantile function 84
Density-quantile function in asymptotic distribution of Order statistics 285Ч291 311Ч312 336Ч340
Dependent variates, asymptotic distribution of Order statistics 309Ч311
Dependent variates, bounds for expectations of L-statistics 106Ч112 118Ч119
Dependent variates, Order statistics in 99Ч102 114Ч117
Dependent variates, quantile-theory for 288
DFR, Decreasing failure rate 75 89
Differences of order statistics 13Ч14 26Ч29
Differences of order statistics in uniform distribution 14 133Ч137
Differences of order statistics, successive (spacings) 18 133Ч137 153Ч154 327Ч328
Dirichlet distribution 21 134
Discrete populations see also under specific distributions
Discrete populations, distribution of Order statistics 16 19Ч20 29 31
Discrete populations, distribution of range 30
Discrete populations, quick tests in 261Ч262
Dispersion, measures of 243Ч250 278Ч279
Dispersion, smaller in 77Ч78
Distribution of Order statistics 9Ч32 see
Distribution of Order statistics for dependent variates 99Ч102 114Ч117
Distribution of Order statistics for discrete parent 16 29
Distribution of Order statistics for independent non-iid variates 96Ч99
Distribution of Order statistics, unimodality of 23
Distribution-free bounds for moments of Order statistics and range 59Ч74 86Ч89
Distribution-free confidence intervals for quantiles 159Ч164 169Ч170
Distribution-free prediction intervals 167Ч169
Distribution-free tolerance intervals 164Ч167 169
Domain of attraction (for extreme) 296Ч300 303 305
Domain of attraction (for extreme) in tail index estimation 341Ч344
Domain of attraction (for extreme), convergence of moments 305
Domain of attraction (for extreme), discrete parent 304
Double exponential (Laplace) 358 364
Double sampling 267Ч268
Duality principle 46Ч47
EDA (exploratory data analysis) 239
Efficiency see relevant statistic
Elementary coverages 134 167
entropy 91
Equality of variances, tables for test of 362 365
Equality of variances, tests of 136 153 257Ч258
Equicorrelated normal variates 100Ч102 114Ч115
Equicorrelated normal variates, asymptotic distribution of maximum for 311
Equicorrelated normal variates, linear functions of 101 114Ч115
Equicorrelated normal variates, maximum in modulus of 360
Equicorrelated normal variates, maximum of 360
Equicorrelated normal variates, range of 101
Equicorrelated normal variates, studentized maximum of 361
Estimation by Order statistics 171Ч237
Estimation by Order statistics for censored data 191Ч208 230Ч234 363Ч364
Estimation by Order statistics for distributions with end-point(s) depending on unknown parameters 173Ч177 224Ч225
Estimation by Order statistics of extreme quantiles 342
| Estimation by Order statistics, simplified 189Ч190 200
Exchangeable variates 47 102Ч103
Expected values see УMoments of Order statisticsФ
Exponential distribution 17Ч18 22 26 52 142 157
Exponential distribution in life testing 204Ч208 232Ч234
Exponential distribution, asymptotic distribution of maximum in 22
Exponential distribution, bivariate (Marshall Ч Olkin) 102 117 207 321
Exponential distribution, characterization of 142Ч143 157Ч158
Exponential distribution, estimation of parameters of 204Ч208 232Ч235
Exponential distribution, L-statistics in 137Ч138
Exponential distribution, moments of Order statistics in 52
Exponential distribution, optimal spacing of Order statistics in 290Ч291 295
Exponential distribution, recurrence relation for 117
Exponential distribution, test of 273
Exponential distribution, tests in 205Ч206 232
Exponential distribution, truncated 57Ч58 359
Extremal 60
Extremal pdf 61Ч64
Extremal process 306
Extremal quotient 15 326
Extreme deviate 1 124Ч125
Extreme multivariate 131 362
Extreme studentized 149 324 361
Extreme, tables of cdf of 361
Extreme-value distribution(s) in asymptotic theory 283Ч285
Extreme-value distribution(s), bivariate 314Ч315 321
Extreme-value distribution(s), estimation of parameters of 204 297
Extreme-value distribution(s), generalized 297 357
Extreme-value distribution(s), moments of Order statistics in 357
Extreme-value distribution(s), multivariate 314Ч315
Extreme-value distribution(s), optimal spacing of Order statistics in 295
Extreme-value distribution(s), probability plotting for 271
Extreme-value distribution(s), three types of 296 303
Extreme-value theory 283Ч285 311 323
Extremes 1 see
Extremes, applications of 284Ч285
Extremes, asymptotic distribution of 296Ч309 317Ч321
Extremes, kth 306Ч307 319Ч320
Failure rate 75 204 see
Failure rate, increasing (IFR) 75 89Ч90
Finite population, Order statistics in 23 25 111 151 170 280
Fisher information (FI) 180Ч183 225Ч227
Folded normal distribution 363
Force of mortality 204 see
Fractional Order statistics 21 162
Gamma distribution 91
Gamma distribution, bounds for 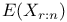 92 92
Gamma distribution, L-statistics in 139
Gamma distribution, moments of Order statistics in 357
Gamma distribution, optimal spacing of Order statistics in 295
Gamma distribution, percentage points of Order statistics in 355
Gaps of order m 136Ч137
Gauss Ч Markov theorem 186
Generalized distance 96 292
Generalized Order statistics 21Ч22
Geometric distribution 22 32 235
Geometric range 326
GiniТs coefficient of concentration 140
GiniТs mean difference 249Ч250 253 269 273 279
GiniТs mean difference, asymptotic normality of 331 334
Goodness-of-fit tests, based on spacings 136Ч137 316Ч317
Goodness-of-fit tests, based on spacings and probability plotting 272Ч273 281Ч282
Goodness-of-fit tests, tables for 365
Graphical methods, half-normal plotting 273
Graphical methods, hazard plotting 274
Graphical methods, probability plotting 270Ч272
Greatest convex minorant 66
Greenwood statistic 136
Grouped data 201Ч202
GuptaТs simplified estimators 189Ч191
Half-normal distribution see УChi (1 DF) distributionФ
Half-normal plotting 273Ч274
Harmonic analysis 135 362
Hazard plotting 274
Hazard rate 75 204
Hazard rate, ordering 75 90
Historical references, L-statistics 331
Historical references, method of inclusion and exclusion 130
Historical references, outliers 107
Historical references, robustness 212
HoelderТs inequality 109
Homogeneity of variances see УEquality of variancesФ
Hypothesis testing by Order statistics in exponential distribution 206
Hypothesis testing by Order statistics in normal distribution 257Ч261
Hypothesis testing by Order statistics in uniform distribution 177Ч179
IFR, Increasng failure rate 75 89Ч90
IFRA, Increasing failure rate average 76 89Ч90
Inclusion and exclusion, principle of 46 125Ч133
Independence results 18Ч19
Independence results for studentized statistics 123Ч124 148
Independence results, asymptotic 289Ч290 309 313 315
Inequalities for moments of Order statistics see УBoundsФ
Inequalities for ordered sums 109Ч110
Inequality, Bonferroni 126
Inequality, Cauchy 107 111
Inequality, Hoelder 109
Inequality, Jensen 79
Inequality, Schwarz 61 85
Information in Order statistics 180Ч183
Inid (independent nonidentrically distributed) Order statistics in inid case 26 96Ч99 112Ч114
Intensity function 204 see
Intermediate Order statistics 311Ч313
Interquartile distance 163
Interval analysis 205
Interval hypothesis 255Ч256 364Ч365
Inverse cdf, approximations to moments of Order statistics by 80 see
Inverse Gaussian 358 363
JensenТs Inequality 79
k-out-of-n systems 2 97
kth extreme 306Ч307 319Ч320
Kurtosis, coefficient of 217 247
L-estimators see УLinear estimatorsФ
L-moments 269 281
L-statistics see УLinear functions of Order statisticsФ
Laplace distribution 358 364
Least-squares (LS) estimation of location and scale parameters 185Ч191
Legendre polynomials 51 71Ч73
Life testing 204Ч208
Likelihood ratio order 76 90
Linear estimators 171Ч172 see
Linear estimators by Gauss Ч Markov theorem 185Ч191 228Ч230
Linear estimators for censored data 191Ч204 230Ч231 363Ч364
Linear estimators for grouped data 201Ч202
Linear estimators for symmetric parent 188Ч189
Linear estimators in presence of outliers 218Ч223
Linear estimators, asymptotic theory of 331
Linear estimators, BlomТs 191
Linear estimators, miscellaneous 191
Linear estimators, robust 211Ч223 235Ч237
Linear estimators, simplified (Gupta) 189Ч190 200
Linear functions of Order statistics 33 see
Linear functions of Order statistics as estimators of scale and location parameters 185Ч208 228Ч234
Linear functions of Order statistics for equicorrelated normal variates 100Ч102 114Ч115
Linear functions of Order statistics in bivariate normal 114 140
Linear functions of Order statistics, asymptotic distribution of 331Ч335
Linear functions of Order statistics, bounds for 106Ч109 117Ч118
Linear functions of Order statistics, distribution of 137Ч140
Linear functions of Order statistics, optimal asymptotic estimation by 335
Linear functions of Order statistics, studentized 148Ч150
Linear programming 128
Lipschitz condition 333
LloydТs method of estimation by Order statistics 185Ч189 228Ч230
Location and scale parameters see also УLinear estimatorsФ
Location and scale parameters for censored data 191Ч208 363Ч364
Location and scale parameters in uniform distribution 173Ч177 224
Location and scale parameters, estimation of 185Ч208
Location and scale parameters, quick measures of 241Ч243
Location and scale parameters, robust estimation of 211Ч223 235Ч237
Log-gamma distribution 364
Log-logistic distribution 364
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 , Polya frequency function of order
, Polya frequency function of order 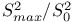
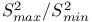
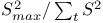
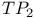 (totally positive of order 2)
(totally positive of order 2) 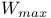 /
/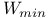
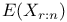
 in normal samples
in normal samples