|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Cody R.P., Smith J.K. Ч Applied Statistics and the SAS Programming Language |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
# (УpoundФ sign) 106Ч107 285
$ (dollar sign) 4
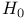 138Ч141 138Ч141
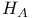 138Ч141 138Ч141
& (ampersand), format modifier 283
* (asterisk), comment indicator 15Ч18
*/ (asterisk slash), end of comment indicator 16Ч18
, (comma) data delimiter 281Ч282
- (dash), specifiying a like group of variables 62
-- (double dash), specifying a list of variables 62
. (period) 8
/ (slash) 14
/* (slash asterisk), begin comment indicator 16Ч18
: (colon), format modifier 282
; (semicolon) 4
? (question mark) 288Ч289
?, with INPUT 288Ч289
?? (double question mark) 288Ч289
??, with INPUT 288Ч289
@ (УatФ sign) 144 199 287Ч288
@@ (double УatФ sign) 153Ч154 287Ч288
Adding new observations see УSETФ УPROC
Adjusted r-square 225
age calculation 103Ч105 356
Alpha, coefficient 276Ч277 393Ч394
alphanumeric 476
Alternative hypothesis 138Ч139 145Ч146 151
Ampersand (&), format modifier 283
Analysis of covariance see УCovarianceФ
Analysis of variance, assumptions for 151Ч159
Analysis of variance, contrasts 158Ч159 169Ч170
Analysis of variance, n-way factorial design 170Ч171
Analysis of variance, one-way 150Ч159
Analysis of variance, repeated measures designs see УRepeated measures ANOVAФ
Analysis of variance, two-way 159Ч170
Analysis of variance, unbalanced designs 171Ч174
ANOVA procedure see УPROC ANOVAФ УAnalysis
APPEND procedure see УPROC APPENDФ
Arrays 329Ч351
ASCII 300Ч302 304Ч305 338
Average, moving 391Ч392
Balanced designs 151
Bar graph 35Ч41
batch 2 18 300
Block chart 41
Boxplot 27Ч32
BY variables 32Ч34 43 110 166 322Ч326
CARDS statement 4 299Ч300 373
Character arrays 332Ч333
Character functions, COMPBL 367
Character functions, COMPRESS 368
Character functions, Concatenation (II) 168 371Ч372 377
Character functions, INDEX 373Ч374
Character functions, INDEXC 373Ч374
Character functions, INPUT 358Ч360
Character functions, LENGTH 366Ч367
Character functions, LOWCASE 375
Character functions, PUT 358Ч360
Character functions, REPEAT 365Ч367
Character functions, SCAN 373
Character functions, SOUNDEX 378
Character functions, SUBSTR 369Ч371
Character functions, TRANSLATE 375Ч376
Character functions, TRANWRD 376Ч377
Character functions, TRIM 371Ч372
Character functions, UPCASE 374Ч375
Character functions, VERIFY 368Ч369
Character informats 102
Character-to-numeric conversion 358Ч360
Chart procedure see УPROC CHARTФ
Chi-square 76Ч78
Chi-square from cell frequencies 79Ч80
CLASS statement, with PROC MEANS 33Ч34 45Ч53
CLASS, with ANOVA 154Ч155
coefficient alpha 276Ч277 393Ч394
Coefficient of variation 25 27 225
Colon (:), format modifier 282
Comma delimited data 281Ч282
Comment statement 15Ч18
Communality 256Ч262
COMPBL function 367
COMPRESS function 368
Concatenation operation 168 371Ч372 377
Confidence interval, about the mean 25Ч26
Confidence interval, about the odds ratio 83Ч86
Confidence interval, about the slope 126Ч128
CONTENTS procedure see УPROC CONTENTSФ
CONTRAST statement 158Ч159 169Ч170
CORR procedure see УPROC CORRФ
Correction for continuity 78
Correlation 115Ч137
Covariance, analysis of 174Ч178
Covariance, homogeneity of slope assumption 176Ч177
CronbachТs coefficient alpha 276Ч277 393Ч394
Crossed designs 159Ч174
Crosstabulations 75Ч79
Cumulative frequencies 13 35
dash (-) 62
Data set 23Ч26 305Ч307 309Ч310
DATA step 13 23Ч24
Data vector see УProgram Data VectorФ
DATALINES 4 299Ч300 373
DATALINES4 4 299Ч300 373
DATASETS procedure see УPROC DATASETSФ
date functions 356Ч358
date functions, DAY 358
Date functions, INTCK 358
Date functions, INTNX 358
date functions, MONTH 356Ч358
Date functions, WEEKDAY 357
date functions, YEAR 356Ч358
dates, working with 356Ч358
Day function 358
DDNAME 300Ч302
default options 26
Degrees of freedom, with ANOVA 155
Degrees of freedom, with Chi-square 78
Degrees of freedom, with regression 224Ч225
DELETE statement 293Ч360
Descending option, with PROC LOGISTIC 238
Descending option, with PROC SORT 426
Descriptive statistics 22Ч57
Designed regression 222Ч226
DIF function 360Ч361
DIM function 331Ч362
DISCRETE, option with PROC CHART 35Ч39
Display Manager 2
Distribution-free tests see УNonparametric testsФ
Division 8
DLM=, INFILE option 281Ч282
DO loop 163Ч164 183Ч184 214Ч215
Dollar sign ($) 4
Double dash (--) 62
DROP statement 311Ч312
DROP, data set option 311Ч312
DSD, INFILE option 281Ч282
Dummy variables 234Ч235
Duncan multiple range test 155Ч158
Efficiency techniques 311Ч317
Eigenvalues 256Ч258
else statement 7Ч9 72Ч73
END=, INFILE option 302Ч303
EOF=, INFILE option 302
Error in ANOVA 152
error messages 5
Error messages, suppressing 288Ч289
exponentiation 9
F ratio, with ANOVA 152Ч153
F1LEDEF 300Ч302
Factor analysis 250Ч264
| FACTOR procedure see УPROC FACTORФ
Factorial designs 170Ч174
FILE, statement 394
Filename 300Ч302
files, reading and writing 298Ч318
FIRST. 110Ч111
FisherТs exact test 78
FMTSEARCH, system option 310
format library 309Ч310
Format list 286Ч287
FORMAT procedure see УPROC FORMATФ
FORMAT statement 67
FREQ procedure see УPROC FREQФ
Frequency bar chart 35Ч41
Frequency distributions 34Ч35
Functions see УCharacter functionsФ УDate УNumeric УTrigonometric
GLM procedure see УPROC GLMФ
GOTO statement 393
Grand mean 151
Greenhouse Ч Geisser-Epsilon 188
GROUP=, option with PROC CHART 39Ч41
GROUP=, option with PROC RANK 142
HBAR 36Ч40
HIGH, with PROC FORMAT 73
Homogeneity or variance assumption 151
Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness-of-fit 238
Hotelling Ч Lawley trace 191Ч193
Huynh Ч Feldt Epsilon 188
ID statement, with PROC MEANS 47Ч48
ID statement, with PROC PRINT 11Ч12
ID statement, with PROC UNIVARIATE 31
If statement 9
Implicitly subscripted arrays 339Ч340
IN statement 420
IN=, option with merge 322Ч324
INDEX function 373Ч374
INDEXC function 373Ч374
INFILE options 281Ч282 302Ч304
INFILE statement 300Ч302
INFORMAT 282Ч285
Input function 358Ч360
Input statement 3^4
INPUT, column form 383Ч384
INPUT, list 280Ч282
INT function 354
INTCK function 358
Interaction 162
intercept 123
Interquartile range 27 32
Interrater reliability 82 277Ч279
INTNX function 358
Invalid data, checking for 368Ч369
Invalid data, overriding LOG messages 288Ч289
Item analysis 273Ч276
JCL 301Ч302
JOB statement 301
justification 4
Kappa, coefficient 82 277Ч279
KEEP statement 95
KEEP, data set option 403
Kuder Ч Richardson 276Ч277 393
L95 126Ч128
L95M 126Ч128
LABEL statement 63Ч65
Labels for SAS statements 393
LAG function 391Ч392 360Ч361
Large data sets, working with 311Ч317
LAST. 109Ч111
Least significant difference 156
Least squares 122
left justified 4
length function 366
LENGTH statement 366
LEVELS= 37Ч38
libname 306Ч307
Likert scale 66Ч70
Linear regression 121Ч124
LINESIZE (LS), system option 271
List-directed input 280Ч281
Lists of variables 62
Log transformation 353Ч354
logical operators 9
LOGISTIC procedure see УPROC LOGISTICФ
Logistic regression 235Ч247
Longitudinal data 101Ч114
LOW, with PROC FORMAT 73
LOWCASE function 375
LRECL, INFILE option 304
LSD 156
Macro variable 269 386Ч387
Mann Ч Whitney U-test 143
Mantel Ч Haenszel Chi-square for stratified tables 90Ч92
MAXDEC=n 6 24Ч25
McNemarТs test 81Ч83
MDY function 356
Mean function 354Ч355
Means procedure see УPROC MEANSФ
Median 27 54
MERGE statement 321Ч324
Meta analysis see УMantel Ч Haenszel...Ф
MIDPOINTS=, option with PROC CHART 37Ч38
Missing value 8
Missing values, changing 999 to missing 329Ч332
Missing values, changing N/A to missing 332Ч333
MISSOVER, option with INFILE 303
Moments 30Ч31
Month format 356Ч358
Month function 356Ч358
Month/day/year 356Ч358
Morse code, conversion to 338Ч339
multidimensional arrays 347Ч348
Multilevel sort 10Ч11
Multiple comparisons 155Ч158
Multiple lines per subject 106Ч109 285Ч286
Multiple regression 221Ч249
Multiplication 8
N function 355
Named input 433
Nested DO loops 214Ч215
Nesting in ANOVA 194
NMISS function 355
Nonexperimental regression 226Ч228
Nonparametric tests, two-sample, paired (Wilcoxon signed rank test) 28 31
Nonparametric tests, two-sample, unparied (Wilcoxon ranksum test) 143Ч145
NOPRINT option, with PROC CORR 274
NOPRINT option, with PROC FREQ 387
NOPRINT option, with PROC MEANS 46Ч47
NOPRINT option, with PROC REG 134
Normal probability plot 32
NOUNI 187
NPAR1WAY procedure see УPROC NPAR1WAYФ
Null hypothesis 138Ч141
Numeric functions, INT 354
Numeric functions, LOG 353Ч354
Numeric functions, LOG10 354
Numeric functions, MAX 355
Numeric functions, MEAN 354Ч355
Numeric functions, MIN 355
Numeric functions, N 355
Numeric functions, NMISS 355
numeric functions, round 354
Numeric functions, SQRT 354
NWAY, option with PROC MEANS 46Ч48
Oblique rotations 258Ч259
OBS=, system option 316
Observation 3
Observation counter 266Ч267 337 369 383 391
Odds ratio 83Ч86
One-tailed test 138 145Ч146
one-way analysis of variance see УAnalysis of varianceФ
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте