|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Held A. (ed.) Ч General Relativity and Gravitation: One Hundred Years After the Birth of Albert Einstein, Vol. 2 |

ќбсудите книгу на
Ќашли опечатку?
¬ыделите ее мышкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter
|
Ќазвание: General Relativity and Gravitation: One Hundred Years After the Birth of Albert Einstein, Vol. 2
јвтор: Held A. (ed.)
язык: 
–убрика: ‘изика/
—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц
ed2k:
√од издани€: 1980
оличество страниц: 558
ƒобавлена в каталог: 26.01.2009
ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
# 109
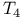 space-time 341 345 346 space-time 341 345 346
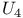 space-time 335 341 347 space-time 335 341 347
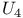 space-time, field equations of 338 space-time, field equations of 338
Acausal propagation anomaly 385
action see УLagrangianФ УHamiltonianФ
Action for a triplet of free Maxwell fields 360
Action for Brans Ч Dicke Theory 575
Action for Brans Ч Dicke Theory, supersymmetric extension 575
Action for Dirac theory 559
Action for ECSK theory in 3 + 1 form 60
Action for Einstein theory 45 470 549 563
Action for Einstein theory, coupled to Bosonic matter 379
Action for Einstein theory, coupled to Bosonic matter, tensor field 49
Action for Einstein theory, coupled to Bosonic matter, Yang Ч Mills field 63
Action for Einstein theory, linearized 361
Action for five-dimensional theory 542
Action for general field 32 235
Action for general field in 3 + 1 form 33
Action for GL(4R) gauge theory 315
Action for gravitation as Yang Ч Mills theory 63
Action for Klein Ч Gordon field 559
Action for Maxwell field 32 235
Action for Maxwell field in 3 + 1 form 33
Action for reduced phase space 43
Action for scalar, pseudoscalar, and Majorana fields 367
Action for spin-1 and spin-1/2 fields (free) 367
Action for supergravity 62 371 564
Action for supergravity in forms 570
Action for supergravity, conformal 572
Action for supergravity, coupled to a spin-(3/2,1) multiplet 375
Action for supergravity, coupled to matter 374 376
Action for supergravity, linearized 368
Action for supergravity, with cosmological constant 373
Action for Yang Ч Mills field 63
Action in terms of a conformal TT decomposition 69
Action, Rarita Ч Schwinger (spin-3/2 field) 369 562
Adiabatic regularization 282
Adjoint of an operator 127
ADM (Arnowitt, Deser, Misner) energy 482
ADM variables 46 (see also УCanonical analysisФ)
Affine (nonmetric) geometry 579
Affine collineations 461
AGCT (anholonomized general coordinate transformation) 312
Algebra see УGraded algebraФ УLie УPoincare
Algebra of symmetries of supergravity 565Ч568
Algebra, gauge, closure of 566 574
Algorithm 495
Algorithm for deciding the equivalence problem 533
Algorithm for performing multiple covariant differentiation 532
Almost-canonical structure 43 163
Almost-canonical transformation 68 70
Angular momentum, conserved by NoetherТs theorem 334
Annihilation operator 257
Ashtekar Ч Hansen energy 486
Asymptotically flat initial data 156 185
Asymptotically flat slices 165
Asymptotically flat space-time 81 174 481 УMomentumФ)
Atiyah Ч Singer index theorem 284
BabbageТs analytic machine 491
Bandors 314
Bare constant 276
Bel Ч Robinson tensor 388
Belifante Ч Rosenfeld procedure 322
Berger Ч Eben canonical splitting 141
Bergmann Ч Dirac canonical analysis 32Ч44
Bianchi identity 293 373
Bianchi types 87Ч89 (including footnote) 436
Bit 498
Black hole, evaporation of 267Ч270
Black hole, particle flux of 268
Black hole, temperature of 268
Blackbody radiation, PlanckТs formula for 19
Blow up see УGarbage collectorФ
BMS (Bondi Ч Metzner Ч Sachs) group 482
Bogolubov transformation 260 262 266 267
Bondi mass 176 477 482 529
Bose variables 217
Brill Ч Hartle, averaging of tensors 551
BrouwerТs theorem 289
Bubble time canonical formalism 69
Bundle see УPrincipal bundleФ
Bundle of affine frames 306
Bundle of linear frames 295
Bundle of orthonormal frames 291
Bundle of projective frames 306
Bundle, associated 294
Bundle, cotangent 396
Bundle, infinitesimal connection on 291Ч296
Bundle, section of 289
Bundle, Stiefel 299
Bundle, tangent 445
Bundle, vector 294
BYTE 498
Canonical analysis and degrees of freedom 38
Canonical analysis for source-fields in first-order form 53Ч54
Canonical analysis of ECSK (Einstein Ч Cartan Ч Sciama Ч Kibble) theory 59Ч61
Canonical analysis of Yang Ч Mills type field 207
Canonical analysis, Bergmann Ч Dirac procedure 32Ч44
Canonical analysis, boundary terms in 79
Canonical analysis, evolution equations for general field 37
Canonical analysis, gauge freedom in 39
Canonical analysis, Maxwell field as example 33Ч41
Canonical analysis, symmetries in 83 207
Canonical quantization 92 227Ч254
Canonical quantization, free particle as example 246
Canonical stress-energy tensor 541 550
Cartan Ч Maurer equation 318 322
CarterТs separable space-times 417Ч422
Casimir effect 259Ч261 265
Cauchy data see УCauchy problemФ УInitial
Cauchy data for general relativity 234
Cauchy data of a free Maxwell field 145 232
Cauchy data, constraints in general relativity 238
Cauchy data, propagation of 240
Cauchy problem 100Ч114 444 УInitial УInitial
Cauchy stability 115
Cauchy surface 102 256
Cauchy surface, existence of, global 241
Causal path 101
Centrifugal force 5
Characteristic surface, data on 104
Charge, central 366
Charge, electric 147 147
Chern number 281
Chern Ч Weil construction 298
Chiral charge 572
Chiral gauge field 573
Chiral generator 378 571
Chiral rotations (generator) 571
Chiral superfields 578
Chirality-duality, constraints 573
Chirality-duality, invariance 379 576
Christensen Ч DeWitt series 280
Class number 449
Commutator see УLie algebraФ
Commutator of canonical variables 244
Commutator of two Lie algebra valued forms 293
Commutator, covariant 256 564
Compact slices 164
Compatible charts 397
Computer and the 3 + 1 formulation 108
Computer languages, ALAM 492 511 529 531
Computer languages, ALBERT 492 531
Computer languages, ALGOL 499
Computer languages, ASSEMBLY 499
Computer languages, CAMAL 493 500 501 527 531 542 551Ч555
Computer languages, CLAM 492 513 515 527
Computer languages, FORMAC 507 510 531
Computer languages, FORMAC, packages 525Ч527
| Computer languages, FORTRAN 499 509Ч510 514
Computer languages, GRAD 492
Computer languages, GRAD ASSISTANT 507 511 531
Computer languages, ILAM 513
Computer languages, LAM 507 511Ч515
Computer languages, LISP 503 507Ч510 515
Computer languages, MACSYMA 506 527 531 532 551
Computer languages, REDUCE 506 514 515Ч517 527
Computer languages, SCRATCHPAD 501 527
Computer languages, SHEEP 493 495 514Ч515 516 527 531 533
Computer, central processor 496
Computer, peripheral equipment 497
Computer, storage 498
Computing and Bondi metric 517Ч520
Computing and factoring of polynomials 506
Computing and Harrison metrics 528 531
Computing on line 502
Computing, algebraic 502Ч507
Confinement potential 305
Confinement potential in the weak-field approximation of a Poincare gauge theory 347Ч350
Conformal anomaly 265 269 283 284
Conformal equivalence class of initial data 144 150
Conformal flat electrovac solutions 458
Conformal group 5 71
Conformal Killing tensor 422 432
Conformal rigidity 413
Conformal separability 456
Conformal supergravity 265 269 283 284 571Ч576
Conjugate momentum 33
Conjugate momentum of the metric 47
Connection on bundle of linear frames 300
Connection on tangent bundle 445
Connection, 1-form 55
Connection, holonomic, in a 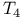 346 346
Conservation laws see УEnergyФ УMomentumФ УNoetherТs УConserved
Conservation laws in the two-timing formalism 541
Conservation laws, strong 475
Conservation laws, weak 474
Conserved quantities see УConservation lawsФ УEnergy-momentumФ УNoetherТs
Conserved quantities of Taub 131
Conserved quantities, current 331
Conserved quantities, current, axial 379
Conserved quantities, energy-momentum 302
Conserved quantities, generalized laws 302
Constant of the motion 471 747 УConserved УNoetherТs
Constraints 108 137 176
Constraints for ECSK theory 61
Constraints of EinsteinТs theory 48 238
Constraints of the gravitational super-Hamiltonian 67
Constraints, chirality-duality 573
Constraints, first class 36 239 241
Constraints, Hamiltonian 100 112 147 159 241
Constraints, hypersurface of a free particle 247
Constraints, kinetic, in supergravity 573
Constraints, linearized stability of 126Ч136
Constraints, momentum 100 112 142 159
Constraints, primary 34 35
Constraints, second class 37 241
Constraints, secondary 36 40
Coordinate, canonically separable 396
Coordinate, first class 401
Coordinate, harmonic (deDonder) 104 461
Coordinate, normal separable 406
Coordinate, quasinormal separable 398
Coordinate, second class 401
Coordinate, separable 397
Coriolis force 5
Cosmic censor hypothesis 189
Cosmology see УMetrics and cosmologiesФ УSpace-timesФ
Counterterms 362 363 385 387 УRenormalizationФ)
Creation of particles by curvature 261
Creation operator 257
Curvature see УRiemann tensorФ
Curvature in superspace 578
Curvature, 2-form 56
Curvature, mean 449
Curvature, particle production by 261
Cutoff 259 282
Cyclic field component 40
De Rham Ч Lichnerowicz Laplacian 123
de Sitter space, stress-energy tensor 271 (see also УMetrics and cosmologiesФ)
Debever isotropic forms formalism 421
Deformation of surface 197Ч201
Deformation, compensating 199
Deformation, normal 200 203
Degrees of freedom and canonical analysis 32Ч44
Degrees of freedom in EinsteinТs theory 49
Degrees of freedom, phase-space of gravitational 64
Degrees of freedom, space of 41
Degrees of freedom, topological 461Ч462
Derivative see УLie derivativeФ
Derivative, coupled source 51
Derivative, covariant exterior 293
Derivative, directional, of Kuchar 29
Derivative, G(roup) covariant 318
Derivative, space-covariant 29
Derivative, supercovariant 564
Derivative, using computers 505 529
Dirac bracket 41
Disk, rigidly rotating 1Ч14
Divergence see УLoopsФ
Divergence of the gravitational field 362Ч365
Divergence, ultraviolet 258 279
Domain of dependence 230 (see also УCauchy surfaceФ)
Dominance of energy hypothesis 146
Dominance of energy hypothesis, deDonder condition 344
Duality 365 375 378
Dynamical equations 108 112
ECSK (Einstein Ч Cartan Ч Sciama Ч Kibble) theory 78 (see also УEinstein Ч Cartan theoryФ)
ECSK (Einstein Ч Cartan Ч Sciama Ч Kibble) theory, canonical analysis of 59Ч51
Ehrenfest paradox 2
Ehrenfest principle 246Ч251
Einstein and the laser 17Ч21
Einstein energy 480 481 487
Einstein pseudotensor 476
Einstein superpotential 477 478
Einstein Ч Cartan theory 302 310 317
Einstein Ч Cartan theory, energy-momentum tensor of 304
Einstein Ч Cartan theory, Lagrangian 301
EinsteinТs theory and local isometric embedding 458Ч463
EinsteinТs theory as gauge theory 291
EinsteinТs theory, 3 + 1 decomposition 45 47
EinsteinТs theory, Cauchy data constraints 238
EinsteinТs theory, coupled to Yang Ч Mills field 214
EinsteinТs theory, degrees of freedom 49
EinsteinТs theory, linearized 122
EinsteinТs theory, linearized, and truncated 124
EinsteinТs theory, phase space formulation of 227Ч254
EinsteinТs theory, reduced 66 116
EinsteinТs theory, the square root of 216Ч221 381Ч382
EinsteinТs theory, waveless approximation 91
Electric charge, scale of 146 147
Electrovac solutions, conformally flat 458
Embedding 442
Embedding and stress-energy tensor 458
Embedding of Riemannian manifold 441Ч468
Embedding, class of 449 450Ч456 458
Embedding, energetically rigid 460
Embedding, explicit 447
Embedding, extremal point 459
Embedding, globally isometric 493Ч494
Embedding, implicit 447
Embedding, intrinsically rigid 460
Embedding, isolated point 459
Embedding, isometric 442Ч474
Embedding, minimal 449
Embedding, type number 465
Energy of an asymptotically flat space-time 81
Energy of intrinsic and extrinsic curvature 177
Energy of the vacuum 258
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



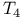 space-time
space-time 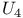 space-time
space-time