|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Agresti A. Ч An introduction to categorical data analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
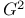 statistic 29 34 89 194.See statistic 29 34 89 194.See
 96 114 156 185 194 197 96 114 156 185 194 197
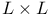 See Linear-by-linear association See Linear-by-linear association
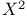 statistic 28 89.See statistic 28 89.See
 197 197
Abortion, opinion on legalization 11Ч12
Accident rates 87 100
Adjacent categories logit 216Ч218 276
Adjusted residual 31
Adjusted residual and Pearson statistic 51Ч52 155 235
Adjusted residual for independence 31 181 242Ч243
Adjusted residual for Poisson GLMs 91 155Ч156 262 271
Adjusted residual for symmetry 235
Adjusted residual, binomial GLMs 118 274
Admissions into graduate school 168Ч169 202
Afterlife, belief in 17Ч20 46 146Ч149 209Ч211
Agreement 242Ч246
AIDS, opinion items 167Ч168 249
Alcohol and infant malformation 35Ч38 98
Alcohol, cigarette, and marijuana use 152Ч157 172 178Ч180
Alligator food choice 207Ч209 220
Arrests and soccer attendance 100Ч101
ASE 24
Aspirin and heart attacks 20Ч25 45
Association graphs 174Ч180
Astrology, belief in 46
Automobile accident rates for elderly men and women 87 100
Automobile accidents in Florida 169Ч170
Automobile accidents in Maine 158Ч162 164 225
AZT and AIDS 119Ч122 138
Backward elimination 127Ч129 179Ч180 273
Baseball and complete games 136
Baseline-category logits 206Ч211
Bayesian methods 13 51 192
Bernoulli variable 7 74
Binary data 19
Binary data, dependent proportions 227Ч229
Binary data, independent proportions 19Ч22
Binary data, matched pairs 227Ч229
Binary data, models 74Ч80 103Ч135 229Ч233
Binomial distribution 7
Binomial distribution and GLMs 74
Binomial distribution and logistic regression 77Ч78
Binomial distribution, comparing proportions 19Ч27 227Ч229
Binomial distribution, independent binomial/multinomial sampling 19
Binomial distribution, likelihood function 8Ч10 144
Binomial distribution, mean and standard deviation 7
Binomial distribution, overdispersion 219Ч220
Binomial distribution, Poisson, connection to 99
Binomial distribution, proportion, inference for 8Ч12 15
Binomial distribution, residual 115 118
Birth control and premarital sex 170Ч171 181
Birth control and religious attendance 200Ч201
Birth control opinion and political, religious, sex items 170Ч171
Bradley Ч Terry model 246Ч249 256 278
Breast cancer 48 50 138
Breast examination and age 221
Breslow Ч Day statistic 63Ч64 66 122 269
British rail accidents 101
Busing, opinion, and other racial items 169
Cancer of larynx and radiation therapy 50
Canonical link 73 132
Carcinoma, diagnoses 242Ч246
Case-control study 26 108 231Ч233 264
Cataracts and head covering 253Ч254
Categorical data analysis 1Ч279
Challenger space shuttle and O-rings 135
Chemotherapy and lung cancer 222Ч223
Chi-squared distribution: df 28 32 111 154 259
Chi-squared distribution: mean and standard deviation 28
Chi-squared distribution: reproductive property 32 52
Chi-squared distribution: table of percentage points 279
Chi-squared statistics: and sparse data 34 194
Chi-squared statistics: independence 30 52 267Ч269
Chi-squared statistics: invariance to category ordering 34
Chi-squared statistics: likelihood-ratio 28Ч30.See also Likelihood-ratio statistic
Chi-squared statistics: linear trend 35 188
Chi-squared statistics: normal components 52
Chi-squared statistics: partitioning 32Ч33 52 261
Chi-squared statistics: Pearson 28. See also Pearson chi-squared statistic
Cholesterol and cereal 224 254
Cholesterol and heart disease 131 132
Cholesterol and psyllium 224 254
Cigarettes, marijuana, and alcohol 152Ч157 172 178Ч180
Clinical trial 27 58 192Ч193
Cochran Ч Armitage trend test 39
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test 61
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test and logit models 122 186 233Ч234
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test and marginal homogeneity 229Ч230 233Ч234
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test and McNemar test 229Ч230
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test, computer software 190 269 274Ч275
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test, nominal variables 189Ч190 274
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test, odds ratio estimate 62 122 231 251
Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test, ordinal variables 188Ч189 274Ч275
Cochran'sQ 233 251 261
Coding factor levels: logit models 120Ч121
Coding factor levels: loglinear models 148Ч149
Coffee and myocardial infarction 140
Coffee market share 235Ч237 239Ч240
Cohen's kappa 246 276 278
Cohort study 27
Cola taste testing 255
Collapsibility 176Ч180
Colon cancer and diet 250
Comparing models 124Ч129 156 194 196Ч198
Computer chip defects 98Ч99
Conditional association 54 57 152 176
Conditional distribution 17
Conditional independence 58
Conditional independence, Cochran Ч Mantel Ч Haenszel test 61 122 186 269 274Ч275
Conditional independence, exact test 64Ч65 269
Conditional independence, generalized CMH tests 188Ч190 274Ч275
Conditional independence, logit models 120Ч122 185Ч186
Conditional independence, loglinear models 151 156 173 185Ч187
Conditional independence, model-based tests 156 185Ч190
Conditional ML estimate 132 231 233 264
Conditional symmetry 253
Condoms and education 139Ч140
Confounding 53 177
Contingency table 16Ч17 258
Continuation-ratio logit 218Ч220 276
contrast 273
Controlling for a variable 53 55
Correlation 35 129 188 268
Correspondence analysis 261
Court assignment and juvenile rearrest 249
Credit cards and income 98
Cross-over experiment 250
Cross-product ratio 23
Cross-sectional study 27
Crossover experiment 250
Cumulative distribution function 78 211Ч212
Cumulative logit models 211Ч215 223 276
Death penalty, and racial items 54Ч58 67 167
Degrees of freedom: chi-squared 23 259
Degrees of freedom: comparing models 197
Degrees of freedom: independence 30 259
Degrees of freedom: logistic regression 111
Degrees of freedom: loglinear models 154 196
Degrees of freedom: Poisson GLM 89
Design matrix 198
Developmental toxicity 219Ч220
Deviance 96 114 127 196
Dfbeta 117
Diabetes and MI for Navajo Indians 232Ч233
Diagnoses of carcinoma 242Ч246
Diagnostics 89Ч92 112Ч118 155Ч156 272
Diarrhea and Cephalexin 134Ч135
Diet and colon cancer 250
Dissimilarity index 162 180
| Drug use (Dayton) 152Ч157 172 178Ч180
Dummy variables 87 118Ч121 273
Educational aspirations and income 49
Efficient score test see Score test
EL50 104Ч105
Elderly drivers and accidents 87 100
Empty cells 190Ч193
Environment and city spending 253
Esophageal cancer 141
Estimated expected frequencies 30
Exact inference: 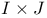 tables 44Ч45 268 tables 44Ч45 268
Exact inference: computer software 44 133 268Ч269
Exact inference: conditional independence 64Ч65 269
Exact inference: conservativeness 43Ч44 50
Exact inference: Fisher's exact test 39Ч44 268
Exact inference: logistic regression 132Ч135 272
Exact inference: LogXact 133 267 272
Exact inference: odds ratios 44 66 269
Exact inference: ordinal data 45 268
Exact inference: StatXact 44 65 267 268 269
Exact inference: trend in proportions 45
Expected frequency 27 30
Explanatory variable 2
Exponential family 97
Exponential function (exp) 4 103
Extramarital sex and premarital sex 238Ч239 241Ч242
Factor 118 120Ч121 272
Fisher scoring 94 260 264
Fisher's Exact Test 39Ч44 268Ч269
Fisher, R.A. 40 259Ч261 265
Fitted values 76 84
Four-way tables 158Ч162 164Ч166 175 178Ч180
Gender gap and party identification 30Ч33
General estimating equations 264
General Social Survey 11
Generalized additive model 106
Generalized CMH tests 188Ч190 274Ч275
Generalized linear model 72Ч73
Generalized linear model, binomial (binary) data 74Ч80 103Ч135
Generalized linear model, computer software 269Ч271
Generalized linear model, link functions 73 269
Generalized linear model, normal data 73Ч74 97
Generalized linear model, Poisson (count) data 80Ч93 145Ч167
Geometric distribution 14
Ghosts, belief in 46
GLM See Generalized linear model
Goodman, Leo 262
Goodness-of-fit statistics: continuous predictors 89Ч90 112Ч114
Goodness-of-fit statistics: deviance 96 114 127
Goodness-of-fit statistics: likelihood-ratio chi-squared 89 114Ч115 196
Goodness-of-fit statistics: logistic regression 112Ч115 142
Goodness-of-fit statistics: loglinear models 154Ч157 196
Goodness-of-fit statistics: Pearson chi-squared 89 196 260
Goodness-of-fit statistics: Poisson GLMs 89Ч92 196
Government spending 171Ч172 199Ч200 253
Graduate admissions and gender 168Ч169 202
Graduation rates for athletes 138
Graphical association 174Ч180 264
Guns in home 14
Hat matrix 117
Health and law enforcement spending 253
Heart attacks and aspirin 20Ч25 45
Heart attacks and smoking 25Ч27
Heart disease and snoring 75Ч80
Heterogeneous linear-by-linear association 203
Hierarchical models 150
history 257Ч265
HIV and early AZT 119Ч122 138
HIV diagnostic test 51
Homogeneity of odds ratios 59 63Ч64 66 122 269
Homogeneous association 59Ч60 63 66 260 269
Homogeneous association, logit models 120Ч122 163 177
Homogeneous association, loglinear models 151Ч152 158 163 185
Homogeneous linear-by-linear association 187Ч188 203 224
Horseshoe crabs and satellites 81Ч93 99Ч100 105Ч107 112Ч118 122Ч129 137Ч138 142Ч144
Hosmer Ч Lemeshow test 113Ч114 273
Human suffering by region 222
Hypergeometric distribution 39Ч40
Identity link 73
Identity link, binary data 74Ч76
Identity link, count data 85 101 102
Incomplete table 191
Independence 18 30
Independence, chi-squared test 30 267Ч268
Independence, conditional independence 58 151 185Ч190 269
Independence, exact tests 39Ч45 268
Independence, logit models 109Ч110 214Ч215 217
Independence, loglinear model 145Ч148 184Ч185
Independence, nominal test 188Ч190
Independence, ordinal tests 34Ч39 184Ч185 188Ч189 215 217
Infant malformation and alcohol 35Ч38 98
Infinite parameter estimate: logistic regression 133Ч135 191Ч193 204
Infinite parameter estimate: loglinear model 191Ч193 203
Influence 92 117 272
Information matrix 94 198
Interaction 59 128Ч129 141 151 262
Iterative model fitting 93Ч94 195Ч196
Job discrimination 65Ч66 69 70
Job satisfaction and income 49 186Ч190 202 218 223
Joint distribution 17
Journal prestige rankings 255
Juveniles, court assignment, and rearrest 249
Kappa 246 276 278
Kruskal Ч Wallis test 189
Kyphosis and age 136
Leverage 91 117
Likelihood equations 14Ч15 195
Likelihood function 8Ч9 88 94Ч95
Likelihood-ratio statistic 28Ч29 88Ч89
Likelihood-ratio statistic and sample size 194
Likelihood-ratio statistic, chi-squared distribution 28 196
Likelihood-ratio statistic, comparing models 114Ч115 156 185 194 196Ч198
Likelihood-ratio statistic, degrees of freedom 28
Likelihood-ratio statistic, deviance 96Ч114
Likelihood-ratio statistic, generalized linear model 96
Likelihood-ratio statistic, goodness of fit 89 113Ч115 196
Likelihood-ratio statistic, logistic regression 109
Likelihood-ratio statistic, loglinear models 154
Likelihood-ratio statistic, partitioning 32Ч33 198
Linear predictor 72
Linear probability model 74Ч76 270
Linear trend in proportions 34Ч39 74Ч76
Linear-by-linear association 182Ч185 187Ч188 201 217 274
Link function 72Ч73 269
Link function, canonical 73 132
Link function, identity 73
Link function, log 73 80
Link function, logit 73
Link function, probit 79Ч80
Local odds ratio 183
LOG function 4
Log link 73 80
Logistic distribution 78 144
Logistic regression 77Ч79 103Ч135 229Ч234
Logistic regression and case-control studies 108 231Ч233
Logistic regression and normal distributions 108
Logistic regression, comparing models 124Ч129 144 196Ч198
Logistic regression, computer software 269Ч273
Logistic regression, degrees of freedom 111
Logistic regression, diagnostics 117Ч118
Logistic regression, exact 132Ч135
Logistic regression, GLM with binomial data 77Ч79
Logistic regression, goodness of fit 111Ч118 142
Logistic regression, inference 109Ч111 185Ч186 195Ч199
Logistic regression, infinite ML estimates 133Ч135 191Ч193 204
Logistic regression, interpretation 103Ч108
Logistic regression, linear approximation 104 109
Logistic regression, matched pairs 229Ч233
Logistic regression, median effective level 104Ч105
Logistic regression, model selection 126Ч129 165Ч167
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



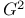 statistic
statistic 
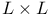
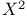 statistic
statistic 
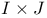 tables
tables