|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gierz G., Hofmann K.H., Keimel K. — Continuous Lattices and Domains |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
Continuous lattice is embeddable in a product of chains 299 IV—3.20
Continuous lattice is quotient of an arithmetic lattice 123 I—4.18
Continuous lattice is quotient of an arithmetic lattice, of same weight 245 III—4.7
Continuous lattice, closure operator on 87 I—2.12
Continuous lattice, closure properties 86 I—2.11
Continuous lattice, congruences on 88 I—2.14 303
Continuous lattice, Continuous poset 54 I—1.6
Continuous lattice, Dedekind cuts in 301 IV—3.24
Continuous lattice, distributive see “Distributive continuous lattice”
Continuous lattice, equational characterization 83 I—2.7
Continuous lattice, free over a compact Hausdorff space 454 VI—3.8(ii)
Continuous lattice, free over a compact pospace 455 VI—3.10
Continuous lattice, free over a set 455 remarks following VI—3.9
Continuous lattice, homomorphic images 86 I—2.10
Continuous lattice, homomorphism of 86 I—2.10
Continuous lattice, interval topology is Hausdorff 510 VII—3.4
Continuous lattice, irreducible elements 400 V—2.1 401
Continuous lattice, is the upper topology 510 VII—3.4
Continuous lattice, kernel operator on 88 I—2.15 89
Continuous lattice, lattice of congruences 303 IV—3.29(i)
Continuous lattice, lattice of continuous closure operators 302 IV—3.26
Continuous lattice, lattice of continuous kernel operators 302 IV—3.26 303
Continuous lattice, lattice of ideals 402 V—2.6
Continuous lattice, Lawson closed subsemilattices 215 III—1.12
Continuous lattice, Lawson topology is the interval topology 510 VII—3.4 (see also “Lawson topology”)
Continuous lattice, order-generating sets in Id L 402 V—2.6
Continuous lattice, order-generating subsets 401 V—2.4(i)
Continuous lattice, primes order-generate 101 I—3.15
Continuous lattice, primes topologically generate 406 V—3.9
Continuous lattice, projection operator on 89 I—2.17
Continuous lattice, pseudoprimes are weak primes 405 V—3.5
Continuous lattice, quotient of 88 I—2.14
Continuous lattice, Scott topology is strongly sober 497 VII—1.10
Continuous lattice, smallest closed order-generating subset 400 V—2.1
Continuous lattice, smallest closed topologically generating subset 401 V—2.4(ii)
Continuous lattice, subalgebras 86 I—2.10
Continuous lattice, topologically generating sets in 400 V—2.3
Continuous lattice, topologically generating sets in Id L 402 V—2.6
Continuous lattice, weak irreducibles are closed 404 V—3.2
Continuous lattice, weak primes are closed 404 V—3.2
Continuous lattice, weak primes are closed, are weak irreducibles 405 V—3.6
Continuous lattice, weak primes are closed, equal weak irreducibles 407 V—3.11
Continuous lattice, weight of 326 IV—5.13
Continuous lattice, weight of projective limit 327 IV—5.14
Continuous lattice, when completely distributive 102 I—3.16
Continuous semilattice 54 I—1.6
Continuous semilattice, irreducible elements 97 I—3.7
Continuous semilattice, smallest approximating relation on 60 I—1.16
Continuous semilattice, with order-generating primes, but not distributive 109 I—3.33
Continuous valuation 379 IV—9.5
Converse relation 4 O—1.7
Countably based domain 242 III—4.4
Countably based domain is a Polish space 421 V—5.17
cube 15 O—2.7(9)
dcpo 9 O—2.1
dcpo is a quasicontinuous domain iff Scott topology is hypercontinuous 513 VII—3.9
dcpo of Scott-continuous functions 161 II—2.5 162
dcpo, Lawson topology on 211 III—1.5
dcpo, open filter determined 285 IV—2.11
dcpo, order consistent topology on 152 II—1.30
dcpo, Scott closed subsets 279 IV—1.25
dcpo, Scott topology is a continuous lattice 197 II—4.13
dcpo, Scott topology is a continuous lattice on 134 II—1.3
dcpo, when Lawson topology is productive 221 III—2.6
dcpo, with continuous Scott topology 221 III—2.6
dcpo, with nonsober Scott topology 155 II—1.36
dcpo-algebra 359 IV—8.1
dcpo-algebra, free over X 360 IV—8.2
dcpo-cone 388 IV—9.20
dcpo-semilattice 360 remarks following IV—8.2 364
Deflationary semilattice 363 IV—8.8
Dense element, in a lattice 113 I—3.5
Densely injective space 182 II—3.10
Densely injective space and bounded complete domains 182 II—3.11
Density, of a domain 248 III—4.13
Diagonal, of a space 88 I—2.13
Diagram, cone over 305 IV—4.1
Diagram, cone over, in a category 305 IV—4.1
Direct limit, in a category 308 remarks following IV—4.3
Direct system, in a category 308 remarks following IV—4.3
Directed complete poset 9 O—2.1 (see also “dcpo”)
Directed complete semilattice 9 O—2.1 40 40
Directed distributive law 83 I—2.7
Directed net 2 O—1.2
Directed set 1 O—1.1
Disjoint sum 73 I—1.31 321
Distributive algebraic lattice, compact open sets are a basis for the spectrum 423 V—5.21(i)
Distributive algebraic lattice, compact open sets are a basis for the spectrum, patch topology on primes is compact 420 V—5.13(ii)
Distributive arithmetic lattice, categorically equivalent to distributive lattices 423 V—5.22
Distributive arithmetic lattice, categorically equivalent to distributive lattices, Priestley duality 491 VI—7.10
Distributive arithmetic lattice, categorically equivalent to distributive lattices, primes are closed 406 iiV—3.7(ii)
Distributive arithmetic lattice, categorically equivalent to distributive lattices, spectrum is totally order disconnected 490 VI—7.9(i)
Distributive complete lattice is linked bicontinuous if bicontinuous 503 VII—2.10
Distributive complete lattice is linked bicontinuous if bicontinuous, way-below relation in 105 I—3.23
Distributive continuous lattice see also “Continuous frame”
Distributive continuous lattice and prime preserving maps 278 IV—1.23
Distributive continuous lattice is a continuous frame 101 I—3.15
Distributive continuous lattice is topological 501 VII—2.4
Distributive continuous lattice, dual to locally compact sober spaces 423 V—5.20 426
Distributive continuous lattice, is a frame 101 I—3.15
Distributive continuous lattice, is the Lawson topology 419 V—5.12
Distributive continuous lattice, patch topology on primes is compact 420 V—5.13
Distributive continuous lattice, prime element in 99 I—3.12
Distributive continuous lattice, primes are closed 406 V—3.7(i)
Distributive continuous lattice, pseudoprimes equal weak primes 405 V—3.5
Distributive continuous lattice, spectrum is sober locally compact 417 V—5.5
Distributive continuous lattice, when stably continuous 420 V—5.13
Distributive continuous lattice, when way-below relation is multiplicative 406 V—3.7(i)
Distributive lattice 12 O—2.6
Distributive lattice, algebraic see “Distributive algerabic lattice”
Distributive lattice, arithmetic see “Distributive arithmetic lattice”
Distributive lattice, continuous see “Distributive continuous lattice”
Distributive semilattice 98 I—3.11
Distributive semilattice, prime element in 99 I—3.12
Domain 54 I—1.6
Domain equation, construction of minimal solution 344 IV—7.1
Domain is a quotient of an algebraic domain 246 I—4.17
Domain is a quotient of an algebraic domain , of same weight 245 III—4.7
Domain is embeddable in a cube 291 IV—3.2
Domain not closed under quotients 262 III—5.22
Domain of formal balls 435 V—6.8 437
Domain, basis for 240 III—4.1
Domain, basis for the Scott topology 138 II—1.10
Domain, characterization in Scott topology 142 II—1.14 154
Domain, characterization in Scott topology, through S-convergence 138 II—1.9
Domain, countably based 242 III—4.4 244 250
Domain, density of 248 III—4.13
Domain, environment 433 V—6.1
Domain, is meet continuous 222 III—2.11
Domain, Lawson topology is productive 221 III—2.6
Domain, Lawson topology is productive, is separable metric 244 III—4.6
Domain, morphisms into the unit interval 291 IV—3.1
Domain, properties of weight on 247 III—4.12
Domain, quasicontinuous 226 III—3.2
Domain, relation between weight and density 248 III—4.14
Domain, Scott open subsets 136 II—1.6
Domain, Scott topology has basis of open filters 142 II—1.14
Domain, Scott topology has basis of open filters, is Baire 142 II—1.13
Domain, Scott topology has basis of open filters, is locally compact sober 142 II—1.13
Domain, topological characterization 184 II—3.16
Domain, way-below relation in 62 I—1.20
Domain, weight of 242 III—4.4 243
Dual of a dcpo 283 IV—2.7
Dual topology 479 VI—6.17
Duality of categories 266 IV—1
Duality of categories,  271 IV—1.10(iv) 271 IV—1.10(iv)
Duality of categories, 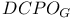 - - 271 IV—1.10(i) 271 IV—1.10(i)
Duality of categories,  271 IV—1.10(iii) 271 IV—1.10(iii)
Duality of categories, 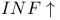 - - 271 IV—1.10(ii) 271 IV—1.10(ii)
Duality of categories,  - - 267 IV—1.3 267 IV—1.3
| Duality of categories, AL-SEM 274 IV—1.16
Duality of categories, ALGDOM-POID 274 IV—1.15
Duality of categories, algebraic lattices and completely distributive algebraic lattices 521 VII—4.10
Duality of categories, compact semilattices and distributive continuous lattices 519 VII—4.6
Duality of categories, continuous lattices and completely distributive lattices 521 VII—4.10
Duality of categories, DAR-CCSOB 423 V—5.22
Duality of categories, distributive algebraic lattices and sober spaces having a basis of compact open sets 423 V—5.21(ii)
Duality of categories, distributive arithmetic lattices and totally order disconnected pspaces 490 VI—7.9
Duality of categories, distributive continuous lattices and locally compact sober spaces 423 V—5.20 426
Duality of categories, distributive continuous resp., lattices with CL-maps preserving primes and distributive continuous resp., lattices with  -maps preserving finite infs 278 IV—1.24 -maps preserving finite infs 278 IV—1.24
Duality of categories, distributive lattices and totally order disconnected pospaces 491 VI—7.10
Duality of categories, DLat-CCSOB 423 V—5.22
Duality of categories, domains and completely distributive lattices 398 V—1.7
Duality of categories, frames with enough points and sober spaces 426 V—5.27
Duality of categories, INF-SUP 267 IV—1.3
Duality of categories, Lawson duality 286 IV—2.14 287
Duality of categories, stably continuous frames and stably locally compact spaces 489 VI—7.4
Duality open-compact 288 IV—2.18
Environment 433 V—6.1
Equivalence of categories,  -LAT 274 IV—1.18 -LAT 274 IV—1.18
Equivalence of categories,  -LAT, stably compact spaces and compact pospaces 482 VI—6.23 -LAT, stably compact spaces and compact pospaces 482 VI—6.23
Evaluation map is Scott-continuous 163 II—2.9
Evaluation map is Scott-continuous, on ![$[L \rightarrow A]$](/math_tex/3fcbba558c075659393a579fa3fe5d6782.gif) 340 IV—6.14 340 IV—6.14
Exponentiable space 196 II—4.11
Exponentiable space, characterization 196 II—4.12
Extremally disconnected space 17 O—2.9
F-algebra 333 IV—6.3 346
F-algebra isomorphisms, construction by a pro-continuous functor F 338 IV—6.9
F-algebra, endomorphism 346 IV—7.2
F-algebra, morphism 333 IV—6.3 346
F-algebra, quotient of 338 remarks preceding IV—6.9
F-coalgebra 346 IV—7.2
F-coalgebra, endomorphism 346 IV—7.2
F-coalgebra, morphism 346 IV—7.2
Family of finite character, in a power set 136 II—1.5(4)
Filter 3 O—1.3
Filter of sets 103 remarks precedingI—3.18
Filter, open see “Open filter”
Filter, prime see “Prime filter”
Filter, principal 3 O—1.3
Filter, Scott open 135 remarks following II—1.3
Filtered net 2 O—1.2
Filtered set 1 O—1.1
Final F-coalgebra 348 IV—7.5 349
Finite element 128 remarks preceding I—4.29
Finitely additive 375 remarks following IV—9.1
Finitely separating function 166 II—2.15
Fixed point theorem, for monotone self-maps 20 O—2.20
Fixed point theorem, for monotone self-maps, for Scott-continuous self-maps 160 II—2.4
Fixed point theorem, for monotone self-maps, Pataraia’s 20 O—2.21
Fixed point theorem, for monotone self-maps, Tarski’s 10 O—2.3
Formal ball 435 V—6.8
Formal union 360 remarks following IV—8.2
Frame 12 O—2.6 101
Frame as a function space 200 II—4.19
Frame is meet continuous 38 O—4.3
Frame, closure properties 34 O—3.25
Frame, dual to sober spaces 426 V—5.27
Frame, homomorphism 34 O—3.24
Frame, subalgebra 34 O—3.24
Free continuous lattice 123 I—4.19 455 460
Free continuous lattice, over a compact Hausdorff space 454 VI—3.8(ii)
Free continuous lattice, over a compact pospace 455 VI—3.10
Free deflationary semilattice, over a domain 363 IV—8.10
Free inflationary semilattice, over a dcpo 362 IV—8.6
Free semilattice, over a domain 367 IV—8.12
FS-domain 166 II—2.15
FS-domain is Lawson-compact 258 III—5.14
FS-domain, preservation properties 167 II—2.17
Function space 162 II—2.6
Function space functor 162 II—2.7 321
Function space functor, Funct 324 IV—5.10
Function space functor, Funct, preserves injective (surjective) maps 325 IV—5.10
Function space functor, Funct, preserves projective limits 325 IV—5.10
Function space is a continuous lattice 192 II—4.6 193
Function space is a domain 190 II—4.4
Function space, Isbell and Scott topology agree 192 II—4.6 260 261
Function, idempotent 25 remarks preceding O—3.6
Function, idempotent, lower semicontinuous see “Lower semicontinuous function”
Function, idempotent, monotone 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, open 269 remarks preceding VI—1.5
Function, idempotent, order preserving 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, partial 15 O—2.7(10)
Function, idempotent, preserving arbitrary infs 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, preserving arbitrary sups 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, preserving directed sups 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, preserving filtered infs 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, preserving finite infs 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, preserving finite sups 5 O—1.9
Function, idempotent, Scott-continuous see “Scott-continuous function”
Function, idempotent, semicontinuous 17 O—2.10
Function, idempotent, upper semicontinuous 17 O—2.10
Galois adjunction see “Galois connection”
Galois connection 22 O—3 22
Greatest lower bound 1 O—1.1
Hausdorff space is locally compact iff O(X) is continuous 417 V—5.7
Heyting algebra 30 O—3.16 (see also “Frame”)
Heyting algebra, complete 12 O—2.6
Heyting algebra, Continuous see “Distributive continuous lattice”
Hilbert space 15 O—2.7(8)
Hoare powerdomain 361 IV—8.3 362
Hoare powerdomain of an algebraic domain 372 IV—8.22
Hofmann — Mislove Theorem 146 II—1.20 288 417
Hofmann — Mislove Theorem, holds only for sober spaces 147 II—1.21
Homomorphism of L-domains 92 I—2.23
Homomorphism of L-domains, of continuous lattices and bounded complete domains 86 I—2.10
Homomorphism of L-domains, of frames 34 O—3.24
Homomorphism of L-domains, of semilattices 5 remarks following O—1.9
Homomorphism of L-domains, onto chains, separation of points in complete lattices 299 IV—3.19
Hull-kernel topology, on the spectrum 409 V—4.3
Hypercontinuous lattice 509 VII—3.2
Hypercontinuous lattice is continuous 509 VII—3.3
Hypercontinuous lattice, characterizations 510 VII—3.4
Hypercontinuous lattice, Scott topology is the upper topology 510 VII—3.4
Ideal 3 O—1.3
Ideal functor Id 325 IV—5.12
Ideal functor Id is locally order preserving 325 IV—5.12
Ideal functor Id is not locally continuous 325 IV—5.12
Ideal, prime see “Prime ideal”
Ideal, principal 3 O—1.3
Idempotent function 25 remarks preceding O—3.6
Infimum 1 O—1.1
Inflationary semilattice 361 IV—8.3
Initial F-algebra 348 IV—7.5
Initial F-algebra - final F-coalgebra coincidence 349 IV—7.6 350
Injective space 176 II—3 177
Injective space and algebraic lattices 186 II—3.18
Injective space is a continuous lattice 180 II—3.7
Injective space, characterization of 178 II—3.4
Injective space, closure properties of 177 II—3.2
Injective space, equivalent conditions for 185 II—3.17
Interpolation property 56 I—1.9 60
Interval domain 70 I—1.26.1
Interval topology 43 O—5.4 217 501
Interval topology is the Lawson topology 510 VII—3.4
Interval topology, when Hausdorff 239 III—3.31 506 510
Irreducible closed set 43 O—5.5 101 141
Irreducible element 95 I—3 97
Irreducible element in a continuous semilattice 97 I—3.7
Irreducible element in a function space 202 II—4.23 203
Irreducible element in a modular lattice 108 I—3.29
Irreducible element, order generate a continuous semilattice 98 I—3.10
Irreducible subset of a space 43 O—5.5 46
Isbell topology 188 II—4.1
Isolated element 49 I—1.1
Isomorphism 5 O—1.9
Join 1 O—1.1
Join continuous lattice 36 O—4.1
Join continuous semilattice 36 O—4.1
Join-compact space 485 VI—6.31
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå




 -
-

 -
-
 -
-
 -maps preserving finite infs
-maps preserving finite infs -LAT
-LAT ![$[L \rightarrow A]$](/math_tex/3fcbba558c075659393a579fa3fe5d6782.gif)