|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Burke E.K., Kendall G. — Search Methodologies: Introductory Tutorials in Optimization and Decision Support Techniques |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
P -dominated set 494
P, polynomial time 562
p-boundary 483
P-lower approximation 483 496
p-median 218 220 234
P-rough set 483 484
P-upper approximation 483 496
PAES see “Pareto archived evolution strategy”
parallel 318 353 376 530 545 571
Parallel, algorithm 264
Parallel, EMO methodologies 309
Parallel, search strategy 157 178
Parallel, VNS 230
Parallelization 65 111 206 309
Parameter, calibration 181
Parameter, control parameter 131 191 194 195 198—201 203 207 320
Parameter, optimization 320 321
Parental solutions 98
PARETO 491
Pareto archived evolution strategy 296
Pareto envelope based selection 296
Pareto-optima! solution 273 275 276 284 290 291 302 307 308 310 544
Pareto-optimal set 281 285 286 310
Partial order 284
Partial solutions 24—27 30 33 61 259
Particle swarm optimization 308 402 416—427
Particle swarm optimization, adaptive PSO 421
Particle swarm optimization, advanced features 421
Particle swarm optimization, controlling diversity 423
Particle swarm optimization, convergence enforcement 422
Particle swarm optimization, evolutionary algorithm 421
Particle swarm optimization, maximum velocity 422
Particle swarm optimization, neighborhood best velocity update 421
Particle swarm optimization, PSO algorithm 417
Particle swarm optimization, PSO for neural network training 417
Particle swarm optimization, queen particle 422
Partitioning 24 30 37 188 205 218 223 570 575
Path consistency 242
Pathogen 375 376
Pattern classification 342
PCPs see “Probabilistically checkable proofs”
Pearson correlation coefficient 383
Penalty function 9
Perceptron learning 353 354
Perfect graph 35
Permutation 32 36 85 166 189 321 410 576 594 599
Permutation, closure 327—333
Permutation, code 102
Permutation, matrix 596
Permutation, problem 415
Permutation, problems 404 407—409 418 419
Permutation, spaces 605
Personnel scheduling 239 538 545
PESA see “Pareto envelope based selection”
Phase transition 250
Phenotype 306 386
Pheromone 402—435
Pheromone, matrix 405—408 410 415
Pheromone, update 404 406 413
Pheromone, update, best-worst 413
Pheromone, update, elitist solution 413
Pheromone, update, moving average 414
Pheromone, update, online step-by-step 414
Pheromone, update, quality-dependent 413
Pheromone, update, rank-based 413
Pheromone, values 406
Plant location problem 165—167 169 170 172 175—177 216
Plug flow tubular reactor 456
Plug flow tubular reactor, case study 456
Polynomial time 318
Polynomial time, algorithm 563 574 575
Polynomial time, approximation scheme 333 559
Polynomial time, approximation scheme (PTAS) 569
Polynomial time, guarantee 24
Polynomial time, verifier 577
Population 14 97—100 127—129
Population, acceptance criterion 305
Population, matrix 408
Population, matrix update 408
Population, population-based ACO 407
Population, size 139
Positive dominance cone 494 496
Possibly 479—484 496 498—501
Post-optimality studies 306
Predictive system 344
Preference-based multi-objective optimization 279
Prefix notation 128
Primal 23 231 572
Primal simplex 90
Principle of optimality see “Bellman’s principle”
Principled efficiency enhancement technique 99
Prior knowledge 344 490—493 521
Probabilistic safety factor 108
Probabilistic tabu search see “Tabu search probabilistic”
Probabilistically checkable proofs 575 576
Probabilistically selected 131 137
probability distribution 194 342 406 572
Probability space 342
Problem-specific repair mechanism 102
Production planning problem 40 43 44
Production scheduling 241 261 466
Propagation 242 248 251—257 261 266 268 578
Proportional-differential-like fuzzy controller 456
Proportional-integral-like fuzzy controller 455
Protected division 139 142
Pruning 26 30 36 246
PSO see “Particle swarm optimization”
PTAS see “Polynomial time approximation scheme”
Q-learning 351 352
Quality measure 484
Quality of approximation 476 480 482 484 486 499 504 511 512 516 519
Queens problem 247
Random, 3-SAT 579
Random, binary template 102
Random, bouncing 424
Random, constants 129
Random, cut 572
Random, enumeration 322 332 335
Random, heuristic 540
Random, initial weights 362
Random, jump 234
Random, MAX-SAT solution 573
Random, number 99 192 232 233 323 421 423 547 549
Random, problem 540
Random, restart 246
Random, sampling 113 174 322
Random, search 141 325 336
Random, selection 102—104 137 219 221
Random, sequence 201
Random, solution 232 305 559 579
Random, value 418
Random, variable 191 342 559 573
Random, walk 98 105 168 601 606
Ranking selection 98
Real-time decision problem 178
Recombination 98 99 113 358 530 599 604
Recombination, landscapes 599—600
Recombination, mutation 357
Recombination, operators 100 109 112 304 552
Recombination, sexual 127 137 157
Recursion 146
Recursive relationship 37 39 43 54 55 63
Reduct 480 482 486 499 500 504 518 520
Redundant criteria 499
Reflexive 284 483 488 489 494 510 512
Regression 138 343
Regression tree 345
Reinforcement learning 342 351—352 357 360 368 369 530
Relaxation 35 70 72 73 79 113 176 178 231 568 578
Repair 53 244 246 257 549
| replacement 98 100 105 115 322
Reproduction 99 127 132 137—139 142 153 361
Resource allocation 240 321
Restart diversification 176
Robot learning 343
Robustness 181 329 366 369
Rough approximation 477 484 485 489 492 497 498 500 502 507 513
Rough sets 475—527
Rough sets, certain 487
Rough sets, certain knowledge 477 497 501
Rough sets, certain rules 476 482 490
Rough sets, classical rough set approach 476 477 482 507 519 520
Rough sets, dominance-based rough set approach 477
Rough sets, formal description 482
Rough sets, fundamentals 478—490
Rough sets, illustrative example 515—517
Rough sets, possibly 479
Rough sets, uncertain knowledge 477
Roulette wheel 98 99
Routing 38 44 63 178 229 230 261 415 543 544 553 578
Rule base design, heuristic, systematic 453
Running metrics 307
SALSA 258
Sarsa learning algorithm 352
Satisfiability, Boolean 319
Schema theorem 100 152 155
Search space 10—11 175—177
Selection 99—100 131
Selection-intensity models 107
Self-adaptive systems 357
Separation 86 187 239 257 259 366 477
Sequencing problems 64 79
Sequential algorithms 570
Sequential job scheduling 571
Sequential mode of training 355
Shaking 223 224 229 230 233 234
Short-term memory 168 171
Shortest path 27 30 32 38 45 54 60 402 405 564 593
SICStus 258
Similarity 276 380 392 439 488 490
Similarity, classes 488
Similarity, measure 381 382 449 465
simplex 90
Simplex, algorithm 45 46
Simplex, method 49
Simplex, type 24
Simulated annealing 187—210
Single machine total weighted tardiness problem 409
Skewed VNS 225
Ski-lodge problem 546—551
Slack variable 23
SMTWTP see “Single machine total weighted tardiness problem”
Social insect colonies 401
Soft constraint see “Constraint soft”
Solomon’s six problem sets 544
SPEA2 see “Strength Pareto-EA”
Staff planning 240
Staff scheduling 545 see
Stagnation recovery 424
Standard form 23
States 38
Steady state 98 105 457 552
Steepest descent 215 226
Stochastic 38 213 216 244 355 404
Stochastic element 246 247
Stochastic gradient ascent algorithm 416
Stochastic noise 109
Stochastic programming 178
Stochastic search 151
Stochastic search algorithm 323
Stochastic universal selection 98 99
Stochastic variable 152 193 194
Stopping criterion 404 407
Strategic oscillation 176
Strict partial order 284
strong typing 144
Subcomponent complexity 108
Subjective function 97
subroutines 146
Sum-of-squares clustering 218—229
Superfluous attribute 481 485
Supervised learning 342—357 367
Supply chain management 240 241
Surrogate objectives 177
Survival of the fittest 98
Swapping probability 101
Swarm intelligence 401—435
Symbolic regression 138
Synapse 353 354
Syntax 359 486 489 502 507 513 518
Syntax, tree see “Tree syntax”
Tabu, list 61
Tabu, list, fixed length 172
Tabu, list, random length 172
Tabu, list, variable length 172
Tabu, search 165—186
Tabu, search, multiple tabu lists 172
Tabu, search, probabilistic 174
Tabu, search, reactive 178
Tabu, search, recency memory 175
Tabu, tenure 171 172
Takeover time models 107
Task scheduling 240
Tchebycheff catastrophe 212
Temperature 190 320 377 442 446 456
Temporal difference learning 351
Terminal node 25 34 36 344
Terminal set 129 138 144 146
Termination criterion 129 131 137 140 143 151 173 174 304
Test function, Griewank 419
Test function, Rastrigin 419
Test function, Rosenbrock 419
Test function, Schaffer’s 16 419
Test function, sphere 419
Test problem design 309
Thrashing behavior 245
Threshold function 353
Threshold methods 168
Time continuation 113
Time-independent 194
Timetabling 30 59 112 261 538 542 543 552
Tools 258
Top-down learning 347
Tournament selection 98 100 107 142 153 293 358 552
Tractability 248 318 579
Transfer functions 354
Transformation operator 439 445 465
Transitive 284 483 489 510 512
transportation 240 241 254 255 261 466
Transportation, assignment 56
Transportation, cost 70 166
Transportation, problem 56 57 167 169 177
Traveling salesman problem 11—12 30 60 97 101 104 187 188 205 223 227 318 324 333 395 404 561 576 603
Traveling salesman problem, Euclidean 333
Traveling salesman problem, minimum traveling salesman 558 576
TREE 25—27
Tree, rooted point-labeled program 133
Tree, syntax 128 135
Truncation selection 100
TSP see “Traveling salesman problem”
Turing 127 156 352
Turing, machine 317—320 562
Turing, machine, deterministic 317
Turing, machine, nondeterministic 318
Two-dimensional cutting problems 43—44
Uncertain knowledge 369 477
Uniform probability 137 154
Unimodal landscapes 595
Unimodular 45
Union 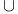 444 444
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте