|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Burke E.K., Kendall G. — Search Methodologies: Introductory Tutorials in Optimization and Decision Support Techniques |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Exchangeable, attributes 481
Exchangeable, criteria 499 504
Exhaustive search 10—11
Expanded formulation 80
Facility location 70 78 80 83 91
Fail first 245
Fast Light Toolkit 547
Feasible solution 8
Financial decision support system 241
Finite-state machines 358
FireWall 380
First descent heuristic 215
First improvement strategy 590
First-fit-decreasing algorithm 533
Fish schooling 401 416
Fitness 9
Fitness, endogenous function 113
Fitness, exogenous function 113
Fitness, inheritance 113
Fitness, landscapes 587—610
Fitness, landscapes, an example 589
Fitness, landscapes, empirical studies 603
Fitness, landscapes, mathematical characterization 593
Fitness, landscapes, practical applications 603
Fitness, measure 98 129 131 134 139
Fitness, of a neural network 361
Fitness, proportionate selection 99 142
Fixed charge 77 170
Flow augmenting chains 46 47 50 57
Floyd’s shortest path algorithm 55
Ford — Fulkerson algorithm 46 47 53
Forward recursion 38
FPTAS see “Fully polynomial time approximation scheme”
Frequency assignment problem 546
Full initialization method 133
Fully polynomial time approximation scheme 559 574
Fuzzy, adaptive control schemes 461—463
Fuzzy, CSP 250
Fuzzy, implication 447
Fuzzy, inference system 449—454
Fuzzy, inference system, defuzzification unit 450
Fuzzy, inference system, fuzzification unit 449
Fuzzy, inference system, fuzzy logic reasoning unit 449
Fuzzy, inference system, knowledge base 449
Fuzzy, inference system, max-min fuzzy inference method 451
Fuzzy, inference system, max-product fuzzy inference method 451
Fuzzy, logic 369 439 442
Fuzzy, measures 500
Fuzzy, reasoning 437—474
Fuzzy, relation 446
Fuzzy, set composition 447
Fuzzy, set operations 443
Fuzzy, sets 437—467
Fuzzy, similarity measures 448
Fuzzy, similarity measures, L-fuzzy similarity 449
Fuzzy, similarity measures, M-fuzzy similarity 449
Fuzzy, similarity measures, P-fuzzy similarity 449
Fuzzy, similarity measures, S-fuzzy similarity 449
Fuzzy, similarity measures, W-fuzzy similarity 449
Fuzzy, systems, modeling 463
Fuzzy, systems, stability 464
GA see “Genetic algorithm”
Gene, deletion 127
Gene, duplication 127
Generalization test 344 357
Generation probability 193 195
Genes 97 102 103 156 549 550 603
Genetic algorithm 97—125 127 168 178 247 308 357 358 381 383 385 386 389 395 421 426 535 537 545 547 549 550 552 589 590
Genetic programming 127—164
Genotype 306 361 362 386
Global constraints 254—258
Global optimum 10
Gomory — Chvatal procedure 81
GP see “Genetic programming”
Gradient descent algorithm 355
Granulation 476
Granules of knowledge 479
Graph, algorithm 56
Graph, bipartite 58
Graph, coloring 30—35 84—89 204 224 239 558
Graph, complete 33—35
Graph, complete bipartite 565
Graph, eigensystem 597—599
Graph, partitioning 188 205 603
Graph, problem 45
Graph, representation 595—596
Graph, theory 19 30 62 178 231 321 437 605
Gray code 591
Greedy, approximation algorithms 563
Greedy, heuristic 218 224
Greedy, knapsack 568
Greedy, MAX-CUT 566
Greedy, MAX-SAT 565
Greedy, vertex cover 564
Grow initialization method 134
H-means 218
HAL 258
Hamiltonian path problem 563
Hamming, distance 217 226 231 382 594
Hamming, landscape 594 598
Hard constraints see “Constraint hard”
Headless chicken crossover 137
Heaviside function 353
Hebbian learning rule 354
Hedge see “Transformation operator”
Heuristics 11—12
Heuristics to choose heuristics see “Hyper-heuristics”
Hill climbing 12—13
Homogeneous 45 54 194 202 206
Hopfield networks 356
Human-competitive 147—149 156
Hyper-heuristics 14 529—556
Hyper-planes 20
Idiotypic networks 386—390
Inclusion property 484 496
Incomplete search technique 269
Independent variables 129
Indicator function 594
Indirect encoding of neural networks 362
Indisceraibility relation 483 493
Indiscernibility 476 477 488
Indispensable 438
Indispensable, attribute 480 482 485
Indispensable, criteria 499 504
Inductive learning 344—348 487
Inductive logic programming 342 346—348
Inertia weight 418
Infeasible solutions 8
Inference methods 242 243
Inference rules 439 448
Infix-notation 128
Information, gain 345
Information, theory 341 345
Information, transfer 408
Inhomogeneous algorithm 195 206
Initial random population 136 138 142 144
Initial solution 12
Initialization 98 133 134 156 229 360 383 425 550
Innovation 99 106 302
Integer programming 69—95
Integer quantities 76
Intensification 175 179 180 234 404 413
Interchangeability 243
Interior point 24 90
Intermediate vectors 604
Intermediate-term memory 175
Interpolation 343
Intersection 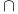 252 439 444 476 479 480 486 496 498 510 512 252 439 444 476 479 480 486 496 498 510 512
Intractable 110 248 557
intrusion detection systems see “Artificial immune systems”
| Invariant 109 231 257
Inverse consistency 243
Inverse problem 448
Irreducible 194
Iterative improvement 188 189 192 205
Job shop scheduling 165 169—171 175 188 207 395 410 537 545 571
K-means 219
Kilter, diagram 49
Kilter, line 49 57
Knapsack, binary knapsack problem 58
Knapsack, bounded knapsack problem 58
Knapsack, maximum fraction 568
Knapsack, maximum integer 568
Knapsack, problem 30 42—44 63 86 561 568 570 604
Knapsack, unbounded knapsack problem 38 58
Kruskal’s greedy algorithm 540
KUR problem 296
Lagrangian relaxation 36
Laplacian matrix 597
Learning 344—346
Learning, algorithms 333
Learning, Bayesian 351
Learning, bottom-up 246 347
Learning, chess play learning 343
Learning, classifier systems 357 358 396
Learning, decision-tree 347
Learning, element 341
Learning, inductive 348
Learning, reinforcement 351
Learning, robot learning 343
Learning, sample 490
Learning, sequence of actions 343
Learning, top-down 347
Level of confidence 487
Limited discrepancy search 246
Linear programming 20—24
Linear propagation 256
Linear relaxation 72 79—93
Linearly separable 354
Lisp S-expressions 128
Local optimum 10
Local search 12—13 112 115
Logic programming 258
Logical constraints 78
Long-term memory 175
Look ahead 246
Lower approximations 476 477 480 512 516
Lower bound 27 28 30 32 35 36 44 48—50 53 57 58
Machine learning 341—373
Makespan 166 537 604
Management science 8
Markov chains 193 195 202 203 206
Matching function 381 384 388
Matching problems 58
Mating pool 99 100
MAX-Ak-SAT 573
Max-closure 250
Max-CSP problem 250
Max-cut problem 567
MAX-SAT 565 573 575
Maximum flow problem 45—48
Maximum weighted independent set 89
McCulloch — Pitts neurons 353
Mean square error 354 361
Membership function 439 440 446 450 452 458 462 465 485
Membership function, Gaussian 442
Membership function, monotonically decreasing linear 441
Membership function, monotonically decreasing sigmoidal 442
Membership function, monotonically increasing linear 441
Membership function, monotonically increasing sigmoidal 441
Membership function, n-membership function 442
Membership function, trapezoid 440
Membership function, triangular 440
Memetic algorithm 112 115 116 395
Messy evolutionary search 551 552
Metaheuristics 13—14
Metropolis algorithm 190 191 608
Min-conflicts heuristic 247
Minimal domain size 245
Minimum, cost flow problem 48—53
Minimum, job scheduling 571
Minimum, spanning trees 541
Minimum, vertex cover 561 564 565
Mixed integer programming 178
Modern heuristics see “Metaheuristics”
Modifier see “Transformation operator”
MOEA see “Evolutionary algorithm multiobjective”
Monte Carlo 190 233 351
MOOP see “Multi-objective optimization problem”
Multi-attribute 475 519 521
Multi-modal optimization 274 275
Multi-objective optimization 273—316
Multicriteria 475 476 491 503—507 518 519 521
Multigraded dominance 510—512 516
Multilayer feedforward neural networks 355
Multimodal landscapes 595
Multiple function sets 144
Multiple terminal sets 144
Multistage programming 37
Mutation 61 98 99 104 113 127 132 133 137—139 144 151 157 304 358 359 361 363 379 381 385
Mutation, probability 105 115
Nadir objective vector 281
Negative dominance cones 494
Negative selection 378 383—385 393
Neighbor 188 589
Neighborhood 188 589
Neighborhood, graph 189
Neighborhood, relations 425
Neighborhood, search 211
Neighborhood, search, variable 238
Neighborhood, structure 169—171 589 593—594
Network flow programming 20
Network, flow 20 24 53 57 60 261
Network, flow programming 19 45—54 62 64
Network, management 240
Network, simplex algorithm 53
Neural networks 353—357 360—365
Niching operator 305
No free lunch 317—339
Node potentials 49
Non-dominated set 285 304
Non-dominated solutions 280—289 292 296 304 306
Non-dominated sorting algorithm 288 293 295 299
Non-evolutionary multi-objective optimization 308
Non-linear programming problems 273
Non-parametric estimates 602
Nondeterministic polynomial 318 562
Nonself cells 375
NP-complete 54 319
NP-hard 167 187 248 319 557
NPO 563
Nurse rostering 9
Objective function 9
Objective space 275 276 306 308
Off-policy 351
On-line 134 352 462 570
On-policy 351 352
Open-shop 537
Operations research 7—8
Operations Research library 545
OPL 92 258
Optimal solutions 10
Optimality 10 273
Optimization 54 87 90 97 115 201 261 273 306 308 357 386 395 415 416 425 428 565 598
Optimization, algorithm 110 187 279 282 303 329 333
Order see “O notation”
Ordinal selection 100
Out of kilter 49—53 56 60
Outranking 477 493 508 511 516
P 317
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте