Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Trefethen L.N., Bau D. — Numerical Linear Algebra
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Numerical Linear AlgebraАвторы: Trefethen L.N., Bau D. Аннотация: Numerical Linear Algebra is a concise, insightful, and elegant introduction to the field of numerical linear algebra. Designed for use as a stand-alone textbook in a one-semester, graduate-level course in the topic, it has already been class-tested by MIT and Cornell graduate students from all fields of mathematics, engineering, and the physical sciences. The authors' clear, inviting style and evident love of the field, along with their eloquent presentation of the most fundamental ideas in numerical linear algebra, make it popular with teachers and students alike.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2002Количество страниц: 361Добавлена в каталог: 07.04.2008Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
"Fast matrix inverse" 248 7 52 285 100 240 18 20 21 327 1-norm 18 20 2-norm 18 20 34 2-norm, computation of 36 4-norm 18 A-conjugate vectors 295 A-norm 294 Abel, Niels 192 324 326 Accuracy 103 111 ADI (alternating direction implicit) splitting 318 Algorithm, formal definition 102 Angle between vectors or subspaces 12 214 332 Arnoldi, approximation problem 259 Arnoldi, eigenvalue estimates see "Ritz values" Arnoldi, iteration 245 250—265 340 Arnoldi, lemniscate 262—263 340 Arnoldi, polynomial 262 Arnoldi, shift-and-invert 319 342 Augmented matrix 139 141 Back substitution 121—128 Backward, error 116 Backward, error analysis 108 111—112 334—335 Backward, stability 104 334 Banded matrix 154 161 337 Base 98 Basis, change of 8 15 32—33 182 Bauer — Fike theorem 201 BCG (biconjugate gradients) 245 303—312 341 Bi-CGSTAB 311 341 Biconjugate gradients see "BCG" Bidiagonal matrix 265 Bidiagonal reduction 236—240 Bilinear function 12 Biorthogonal vectors 305—306 Biorthogonalization methods 303—312 Bisection 227—229 233 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subroutines) 330 Block, matrix 143 154 230 235 249 317 330 Block, power iteration see "Simultaneous iteration" Boundary elements 245 248 317 Breakdown of Arnoldi iteration 256 C 63 Cancellation error 73 91 138 Cauchy — Schwarz inequality 21 Cayley transform 16 Cayley — Hamilton theorem 260 Cayuga, Lake 136 CG see "Conjugate gradients" CGN or CGNR 245 303—305 CGS (conjugate gradients squared) 311 Chaos 335 Characteristic polynomial 110 183 184 190 Chebyshev points 79 279 292 Chebyshev polynomial of a matrix 265 340 Chebyshev polynomials 287 292 300 Cholesky factorization 82 141 172—178 301 337 Circulant matrix 187 305 318 342 Column, pivoting 139—140 143 Column, rank 7 Column, space 7 Column, spaces, sequence of 48 169 245 Communication 59 66 Compact operator 265 331 Companion matrix 192 338 Complementary subspaces 43 332 Complete pivoting 161 336 Complex, arithmetic 59 100 Complex, conjugate 11 Complex, sign 29 72 Complex, symmetric matrix 312 Componentwise analysis 127 227 334 339 Computers, speed of 243—244 339 Condition number of a matrix 94 333 Condition number of an eigenvalue 258 Condition number, absolute 90 Condition number, computation of 94 Condition number, relative 90 Condition number, squaring of 142 235 305 Conditioning 89—96 333 Conjugate, complex 11 Conjugate, gradients 245 293—302 303 341 Conjugate, hermitian 11 Conjugate, residuals iteration 293 Convergence, cubic 195 208 212 221—222 Convergence, linear or geometric 195 262—264 Convergence, quadratic 195 226 Convergence, superlinear 195 337 Coppersmith and Winograd, algorithm of 247 340 Covariance matrix 234 CS decomposition 332 Cuppen, J.J.M. 229 Data-fitting see "Least squares problem" Davidson method 319 Defective eigenvalue 185 Defective matrix 185 Deflation 212 223 232 Deletion matrix 9 24 Demmel, James W., book by 329 Dense, matrix 244 Dense, subset 37 Determinant 8 10 34 97 161 330 Determinant, computation of 161 Diagonal matrix 15 18 20 32 Diagonalizable matrix see "Nondefective matrix" Diagonalization 188 Diagonally dominant matrix 162 Dimensions, physical 10 107 Direct algorithm 190 243 247 Divide-and-conquer algorithm 212 229—233 239 Domain decomposition 317 342 Dual norm 24 95 331 Eigenspace 181 183 Eigenvalue decomposition 33 182 Eigenvalue-revealing factorization 188 191 Eigenvalues 8 15 24 181—189 Eigenvalues, algebraic multiplicity of 183—184 Eigenvalues, computation of 110 190—233 257—265 Eigenvalues, defective 185 Eigenvalues, geometric multiplicity of 183—184 Eigenvalues, perturbation of 188 201 258 333 Eigenvalues, simple 184 Eigenvectors 15 43 181 Eigenvectors, computation of 202 218 227 Eigenvectors, localization of 232 233 EISPACK 257 330 337 338 Electric charge 279 283—284 Error, absolute 103 Error, relative 99 103 Euclidean length 12 17 78 ev and ew (abbreviations for eigenvector and eigenvalue) 188 337 EXPONENT 98 Exponential of a matrix 33 182 189 201 Fast Fourier Transform 63 Fast Poisson solver 317 Feynman, Richard 91 334 Field of values see "Numerical range" Finite differences 244 317 Finite elements 254 317 Finite sections 333 Fixed point arithmetic 98 fl 99 Floating point, arithmetic 66 97—101 334 Floating point, axioms 99 Floating point, numbers 98 Flop (floating point operation) 58 Forsythe and Moler, book by 243 331 FORTRAN 63 324 Forward error analysis 108 112 177 FRACTION 98 Frobenius norm 22 34 Full rank, matrix of 7 Fundamental law of computer science 246 325 340 Galois, Evariste 192 324 326 Gamma function 85 Gauss quadrature 285—292 341 Gauss — Seidel iteration 318 339 Gaussian elimination x 35 54 61 106 147—171 325 Gaussian elimination, stability 152—154 163—171 325 336 Generalized minimal residuals see "GMRES" Geometric interpretations 12 25 36 55 59 133 201 233 332 335 Gerschgorin's theorem 189 337 Ghost eigenvalues 282—283 Givens rotation 76 195 218 226 268 275 gmres 245 266—275 293 303 340 GMRES, approximation problem 269 GMRES, restarted 275 Golub and Van Loan, book by ix 329 Golub — Kahan bidiagonalization 236—237 Golub, Gene H. 236 330 331 339 Gradient 203 302 Gram — Schmidt orthogonalization 50—51 56—62 70 148 250—253 332 Gram — Schmidt orthogonalization, classical vs. modified 51 57 65—66 140 332 Graphics 63 Green's function 284 Growth factor 163—171 312 336 Guard digit 100 Hadamard inequality 55 Hadamard matrix 16 Hahn — Banach theorem 331 Hein, Piet 18 Henrici, Peter 327 Hermitian conjugate 11 Hermitian matrix 11 15 34 44 162 172 187 Hermitian positive definite matrix 172 294 Hessenberg matrix 193 198 252 Hessenberg orthogonalization 305—306 Hessenberg reduction 193 196—201 250—251 337—338 Hestenes, Magnus 293 341 Higham, Nicholas J. xii 335 Higham, Nicholas J., book by ix 329 Hilbert space 330 331 Hilbert — Schmidt norm see "Frobenius norm" Hoelder inequality 21 Horn and Johnson, books by 330 Horner's rule 265 Householder, Alston 70 330 332 Householder, reflector 70—73 Householder, Symposia 333 Householder, triangularization 64 69—76 114—120 147 251 332 Householder, tridiagonalization 196—201 251 Hydrodynamic stability 258 Hyperellipse 20 25 36 95 Hyperplane 71 ICCG (incomplete Cholesky factorization) 316 Ideal Arnoldi polynomial see "Chebyshev polynomial of a matrix" Idempotent matrix 41 Identity 8 IEEE arithmetic 97 334 Ill-conditioned matrix 94 Ill-conditioned problem 89 91 Ill-posed problem 334 ILU (incomplete LU factorization) 316 Image processing 36 68 Incomplete factorization 316 342 Infinitesimal perturbation 90 133 135 Inner product 12 52 109 285 Integral, equation 245 331 Integral, operator 6 53 286 Interlacing eigenvalues 227—228 Interpolation 10 see Intersection of subspaces 36 55 Invariant subspace 183 Inverse 8 Inverse, computation of 161 Invertible matrix see "Nonsingular matrix" Irreducible matrix 227 Iteration 206—207 210 219 338 Iterative methods x 69 192 243—249 326 339—340 Jacobi — Davidson methods 319 342 Jacobi, algorithm 225—227 233 338—339 Jacobi, Carl Gustav Jacob 225 Jacobi, iteration 318 Jacobi, matrix 287—292 Jacobi, polynomial 287 Jacobi, preconditioner 316 Jacobi, rotation 226 Jacobian 90 132—133 258 Jordan form 337 Kahan, William M. 236 334 339 Karmarkar algorithm 326 Kronecker delta function 14 Krylov matrix 253 Krylov sequence 245 Krylov subspace iteration 241—327 Krylov subspaces 245 253 Lanczos iteration 245 250 276—284 298 303 340 Lanczos lemniscate 284 Lanczos polynomial 280 LAPACK 166 205 232 243 257 338 Least squares problem 36 77—85 129—144 305 333 Least squares problem, rank-deficient 143 335 Lebesgue constants 96 334 341 Legendre points 292 Legendre polynomial 53 54 64 68 285— Lemniscate 262—263 LHC (Lawson — Hanson — Chan) bidiagonaiization 237—239 LINPACK 166 243 Look-ahead Lanczos 311 341 Low-rank approximation 35—36 331 Low-rank approximation, computation of 36 LU factorization 147 154 160 Machine epsilon 66 98 100 Mantissa 98 Mass-spring system 9 MathWorks, Inc., The 63 330 332 MATLAB 31 62 63—68 166 205 257 324 332 Matrix, augmented 139 141 Matrix, banded 154 161 337 Matrix, bidiagonal 265 Matrix, block 143 154 230 235 249 317 330 Matrix, circulant 187 305 318 342 Matrix, companion 192 338 Matrix, complex symmetric 312 Matrix, covariance 234 Matrix, defective 185 Matrix, deletion 9 24 Matrix, dense 244 Matrix, diagonal 15 18 20 32 Matrix, diagonalizable see "Nondefective matrix" Matrix, diagonally dominant 162 Matrix, Hadamard 16 Matrix, hermitian 11 15 34 44 162 172 187 Matrix, hermitian positive definite 172 294 Matrix, Hessenberg 193 198 252 Matrix, idempotent 41 Matrix, identity 8 Matrix, ill-conditioned 94 Matrix, irreducible 227 Matrix, nondefective 185—186 Matrix, nonnormal 186 258 Matrix, nonsingular 7 Matrix, normal 92 173 187 201 Matrix, orthogonal 14 218 Matrix, permutation 34 157 220
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



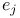
![$L^{2}[-1,1]$](/math_tex/e301642492ef20ee59e906f6f79cf25282.gif)
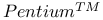 microprocessor
microprocessor 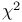 (Chi-squared) distribution
(Chi-squared) distribution  -norm
-norm  , calculation of
, calculation of