јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Mukamel S. Ч Principles of Nonlinear Optical Spectroscopy
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Principles of Nonlinear Optical Spectroscopyјвтор: Mukamel S. јннотаци€: This textbook presents a systematic and unifying viewpoint for a wide class of nonlinear spectroscopic techniques in time domain and frequency domain. It is directed towards active researchers in physics, optics, chemistry, and materials science, as well as graduate students who enter this complex and rapidly developing field.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1995 оличество страниц: 576ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.03.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Operators, Heisenberg 417 Operators, Hermitian 21 117 Operators, product of, normally ordered 485 Operators, product of, trace of 46 Operators, projection See Projection operators Operators, tetradic 57 190 Operators, time evolution See Time evolution operators Operators, window 376 Optical Bloch equations 144 181Ч185 Optical coherence 191 196Ч197 375Ч376 Optical coherence Green function 443 Optical Kerr effect 445 446 447f Optical measurements 116 Optical measurements, interpretation of 111 Optical measurements, polarization and 93Ч103 Optical polarization 3 111 129 151 Optical polarization in macroscopic system 128 Optical polarization, anharmonic oscillator picture 163Ч167 Optical polarization, calculation of 111 113 Optical polarization, dispersive in-phase contribution See Birefringence Optical processes, classification, by power-law dependence 3Ч5 4f Optical processes, classification, by resonant mode 7 9Ч10 10fЧ12f 12Ч13 Optical processes, classification, by temporal profile 5fЧ7f 5Ч7 Optical processes, frequency-domain 127 Optical response functions of extended systems, nonlocal expressions for 123Ч124 Optical response functions of homogeneous medium of noninteracting particles 127Ч128 Optical response functions of multilevel system with relaxation 143Ч144 149Ч151 152fЧ158f 153Ч159 Optical response functions of multilevel system with relaxation, Kramers Ч Kronig relations and 144Ч146 147f Optical response functions of multilevel system with relaxation, linear response in Liouville space and 147Ч149 Optical response functions, semiclassical simulation 187Ч188 Optical response functions, simulations, coherence Green function and 203 204Ч205 Optical response functions, simulations, equation derivation for 206Ч207 Optical response functions, simulations, moments of linear absorption and 193Ч196 195f Optical response functions, simulations, phase averaging and 189f 189Ч192 199Ч201 Optical response functions, simulations, static limit of 201Ч203 Optical spectroscopy, vs. nuclear magnetic resonance 12 Optical Stark effect 446 514 Optical susceptibilities 124 127 150 171 244 245 445 466 Optical susceptibilities of multilevel system interacting with medium in arbitrary timescale 244Ч247 Optical susceptibilities of periodic structures in k space 496Ч498 Optical susceptibilities, linear 95 128 145 Optical susceptibilities, linear, real and imaginary parts 152f Optical susceptibilities, local field expressions, of homogeneous systems 475Ч477 Optical susceptibilities, nonlinear 12 151 157 462 479 Optical susceptibilities, nonlinear, enhanced, in molecular aggregates 498Ч504 503fЧ506f 506Ч507 Optical susceptibilities, nonlinear, exciton-population variables and 507Ч512 511fЧ512f Optical susceptibilities, second-order 128 Optical susceptibilities, third-order 128 162 Ordinary rate equation 184 Orthogonality in Hilbert space vs. Liouville space 58f Orthogonality, scalar product rule for 42 Orthonormality 50 56 Oscillator strength sum rule 165 Oscillators, anharmonic See Anharmonic oscillators Oscillators, Brownian oscillator model See Brownian oscillator model Oscillators, continuous distribution of 221Ч226 225f 226f Oscillators, Drude See Drude oscillator Oscillators, harmonic 17 163 164 233 Out-of-phase polarization 446 Outer product of vectors in Hilbert space 41 56 Outer product of vectors in Liouville space 57 Overdamped motions, strongly 333 Pade approximant 225 Particle dynamics 386Ч387 Particle velocity 88 Path integral in Liouville space 349 Path integral techniques 227 Pauli anticommutation rule 470 Pauli exclusion principle, Bloch equations and 491 Pauli exclusion principle, definition of 471 Pauli exclusion principle, enhanced nonlinear susceptibilities in molecular aggregates and 513Ч514 Pauli exclusion principle, Frenkel exciton model and 499 502 Pauli exclusion principle, Green function expression and 487 Pauli exclusion principle, pure state factorization and 489 PE (two-pulse photon echo) 295 Pentacene, fluorescence excitation spectrum 291f Pentacene, spectral diffusion 389f Permutations over fields 124 125 Perturbation series, partial resummation of 30 Perturbation theory 27 Perturbative expansion 116 Perturber, effect on linear absorption 238 Phase conjugation 175 Phase matching condition 98 98f Phase relaxation See Dephasing Phase shift, in binary collision 238 Phase space 69 71Ч72 75 Phase space, filling 491 Phase-averaging 349Ч351 Phase-averaging in Liouville space 199Ч201 Phase-locked pump-probe absorption, three-pulse 338Ч339 Phase-locked spontaneous light emission spectroscopy (PLSLE) 295 310Ч312 340 341 Phase-locked transient gratings 324 324f 325f 326 Phase-sensitive detection 99 Phonons 514 Photon echo spectroscopy 4 99 133 295 432 474 Photon echo spectroscopy, accumulated, unified theory for 295 314Ч315 Photon echo spectroscopy, accumulated, unified theory for, with incoherent light sources 316Ч317 Photon echo spectroscopy, impulsive 301Ч304 302f Photon echo spectroscopy, impulsive, Brownian oscillator analysis of 304Ч306 307fЧ310f 308 310 Photon echo spectroscopy, term, use of 304 Photon echo spectroscopy, three-pulse 295 Photon echo spectroscopy, three-pulse, with homodyne or heterodyne detection 299Ч301 300f Photon echo spectroscopy, two-pulse 301 Photon emission rate 265 266 Physical 129 PIC (pseudoisocyanine bromide) 491 504f 505f Picosecond pulse shaping techniques 423 Picosecond Raman spectroscopy 413 417Ч418 430Ч431 PIER 4 (pressure-induced extra resonance in four-wave mixing) 282 Planck's constant 16 PLSLE (phase locked spontaneous light emission spectroscopy) 295 310Ч312 340 341 Poisson bracket 70 257 Poisson distribution 220 Polar medium, dielectric fluctuations, cumulant expansion and 234 236Ч237 Polariton 515f515Ч515 Polarizability 122 124 Polarizability of molecular assemblies, linear 495 Polarizability of molecular assemblies, third-order 492 496 Polarizability operator 416 Polarizability, autocorrelation function 199 Polarization 79 83 92 113 164 445Ч446 Polarization operator 82 84 123 160 Polarization operator, microscopic definition of 82Ч83 111 Polarization, density 87 87f 93 112 127 Polarization, linear 3 Polarization, multipolar expansion of 83 106Ч107 Polarization, nonlinear See Nonlinear polarization Polarization, nonlinear response functions, rotational contribution to 447Ч450 Polarization, optical See Optical polarization Polarization, optical measurements and 93Ч103 Polarization, optical measurements and, absorption of weak probe 100Ч103 Polarization, optical measurements and, heterodyne detection of wave mixing 99Ч100 Polarization, optical measurements and, linear absorption 94Ч96 Polarization, optical measurements and, multiwave mixing 96Ч99 98f Polarization, polarization-dependent grating signal 451Ч455 454f 455f Polarization, scalar product 87 Polarization, second-order 159 Polarization, third-order 4 116 159 433 446 496 Polarization, third-order, nonlinear techniques See Off-resonance spectroscopy Polarization, time-dependent 115 Polarization, vector field 85 Polarization, vector, third-order 447Ч448 Polarization, vibrational contribution to heterodyne-detected transient grating 450Ч451 Polarization-sensitive techniques 445 Population relaxation 176 181 Population relaxation and pure dephasing 516Ч517 Population relaxation, matrix 144 Population relaxation, matrix, realistic, 167Ч169 168f Populations 47 134 Populations, damping of 134 Populations, time-dependent 52Ч53 Positive time ordered exponential 24 Power law, dependence, optical measurements and 3Ч5 Power Ч Zienau transformation 84Ч88 87f Poynting vector 90 Pressure broadening (collisional broadening) 238 Pressure-induced extra resonance in four-wave mixing (PIER 4) 282 Principal part of integral 38 Probability, conservation of 178 182 Probe absorption for snapshot spectrum 377Ч382 Probe absorption, field and matter perspective 101Ч102 Probe difference absorption 327 Probe field amplitude 103 Product of operators, normally ordered 485 Product of operators, trace of 46 Projection operators 177 Projection operators in Liouville space 67Ч68 Projection operators, definition of 34Ч35 Projection operators, idempotent 35 Propagation 144 Pseudoisocyanine bromide (PIC) 491 504f 505f PTCDA (3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride) 480f Pulse shaping 414 Pump-probe spectroscopy 360 369 376 445 Pump-probe spectroscopy in three-electronic-level system 393Ч394 394f Pump-probe spectroscopy in three-electronic-level system, coherent vs. sequential components of 395Ч396 Pump-probe spectroscopy in three-electronic-level system, interplay of field and matter coherence 399Ч403 Pump-probe spectroscopy in three-electronic-level system, snapshot limit for 396Ч399 398fЧ401f Pump-probe spectroscopy of GaAs quantum well 370f Pump-probe spectroscopy with frequency dispersed detection, wavepacket representation of 407 Pump-probe spectroscopy, absorption 7 8f 100 Pump-probe spectroscopy, classical limit 385 Pump-probe spectroscopy, detuning 9f Pump-probe spectroscopy, doorway-window picture 133 Pump-probe spectroscopy, doorway-window picture, time variables for 375f Pump-probe spectroscopy, formal expression 373 Pump-probe spectroscopy, Fourier transform relationship with hole-burning 340Ч343 342f Pump-probe spectroscopy, impulsive 414 Pump-probe spectroscopy, impulsive, homogeneous broadening limit 335 Pump-probe spectroscopy, impulsive, inhomogeneous broadening and 294 333 335 Pump-probe spectroscopy, impulsive, quantum beats and 328Ч333 329fЧ331f 334f 335 335f Pump-probe spectroscopy, long pulses, vs. electronic dephasing 382Ч383 Pump-probe spectroscopy, off-resonance 384Ч385 Pump-probe spectroscopy, phase locking in 312 Pump-probe spectroscopy, phase-locked transient grating and 324 Pump-probe spectroscopy, quantum beats 294Ч295 305 Pump-probe spectroscopy, resonant impulsive pump 383Ч384 Pump-probe spectroscopy, sequential 322 326Ч328 327f 336 Pump-probe spectroscopy, short pulses, vs. nuclear dynamics 382 Pump-probe spectroscopy, short pulses, vs. nuclear dynamics and long vs. electronic dephasing 377Ч382 Pump-probe spectroscopy, signal generation 4Ч5 Pump-probe spectroscopy, snapshot spectrum 377Ч382 Pump-probe spectroscopy, third-order polarization and 116 Pump-probe spectroscopy, time-domain 380 Pump-probe spectroscopy, two-photon absorption 173 Pure dephasing 516Ч517 Pure dephasing and population relaxation 516Ч517 Pure dephasing processes 161 179Ч180 Pure dephasing rate 149 169 179 187 310 310f Pure dephasing relaxation times 181 Pure dephasing, Green function for 519 Pure state 47 49t 52 136 159 Quadratic detection See Homodyne detection Quantized transverse electromagnetic field 81 Quantum beats 5 305 333 369 420 Quantum beats, impulsive pump limit and 369 Quantum beats, impulsive pump-probe spectroscopy and 328Ч333 329fЧ331f 334f 335 335f Quantum dynamics in Hilbert space See Hilbert space Quantum dynamics in Liouville space See Liouville space Quantum electrodynamics, coupled Maxwell Ч Liouville equations 92Ч93 Quantum electrodynamics, electrostatic intermolecular interaction and 86Ч88 87f Quantum electrodynamics, equations of motion for field 89Ч90 Quantum electrodynamics, minimal (p.A.) coupling Hamiltonian and 79Ч84 Quantum electrodynamics, multipolar Hamiltonian and 85Ч86 Quantum electrodynamics, power-Zienau transformation and 84Ч85 Quantum electrodynamics, radiation-matter interaction and 79Ч83 Quantum electrodynamics, semiclassical material equations 90Ч92 Quantum field, absorption of 262Ч264 263f Quantum harmonic oscillator, Hamiltonian for, in Wigner representation 73 74f Quantum Liouville equation 51 Quantum mechanical average 494 Quantum theory of relaxation 53 Quantum wells 479Ч480 Quantum wires 479Ч480 Rabi formula 20 Rabi frequency 20 Rabi oscillations 20Ч21 183 Radiation fields 114 Radiation fields, degrees of freedom 23 Radiation fields, perturbative expansion 112 Radiation fields, retardation effects 112 Radiation fields, vacuum fluctuations of 261 Radiation fields, weak field approach 112 Radiation-matter interaction 264 Radiation-matter interaction, minimal coupling Hamiltonian and 79Ч83 Radiation-matter interaction, quantum description of 112 155Ч156 Radiation-matter interaction, time-dependent 29 Radiative decay 513 Raman excitation, filtering effect using pulse shaping 428 Raman polarization 413 Raman resonance 411 Raman spectroscopy 170 261Ч262 262f 263f 361 Raman spectroscopy, coherent See Coherent Raman spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy, femtosecond 294 417Ч418 428 Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence and 271Ч279 272f 274fЧ279f Raman spectroscopy, inhomogeneous broadening and 294 Raman spectroscopy, off-resonant conditions 10 Raman spectroscopy, picosecond 413 417Ч418 430Ч431 Raman spectroscopy, probe field in 453 Raman spectroscopy, spontaneous See Spontaneous Raman spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy, stationary 294 Raman spectroscopy, timescales for 412 Raman spectroscopy, two-dimensional 435Ч436 Reduced density operator 134 356 Reduced description 132 Reduced doorway wavepacket 429 Reduced equations of motion, for Liouville space wavepackets 357Ч359 Reference frequency for spectral moments 193 194 Reference nuclear configuration 210 Reflection 3 144 Refraction 3 144 Relaxation 12 131 481 Relaxation of population 177Ч178 Relaxation, homogeneous broadening 169 Relaxation, inhomogeneous broadening 169 Relaxation, matrix, conservation of probability and 178 Relaxation, matrix, criteria for 178 Relaxation, model 168 Relaxation, rates 38 143 230 Relaxation, superoperator 68 163 179 Relaxation, superoperator, calculation 144 176Ч180 Relaxed fluorescence 250 Relaxed fluorescence, lineshapes 233f Relaxed fluorescence, spectrum 220 220f Relevant polarization 130 Renormalized perturbation theory 162 Resonance frequency 151 Resonant coherent Raman spectroscopy 279Ч285 280f 284f Resonant fluorescence anisotropy 446 Resonant gratings 321Ч322 Resonant impulsive pump 383Ч384 Resonant techniques See also specific resonant techniques Resonant techniques vs. off-resonant techniques 7 9Ч10 10fЧ12f 12Ч13 Resorufin, absorption and emission spectra 308 308f Resorufin, photon echo signal 308 309f Response functions 112 Response functions of multilevel manifold with relaxation 149Ч151 152fЧ158f 153Ч159 Response functions, calculation methods 209 Response functions, classical correlation functions and 242 257Ч258
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 function
function 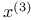 with
with