|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Young D.M., Gregory R.T. — A Survey of Numerical Mathematics, Volume 2 |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
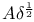 -norm 1021 1069 -norm 1021 1069
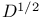 -norm 1009 -norm 1009
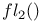 arithmetic 53 arithmetic 53
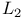 -norm 308—318 -norm 308—318
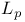 -norm 762 -norm 762
Absolute degree of approximation 981 1075 1089
Absolute degree of approximation of a linear discrete operator 606
Acceleration of convergence 95 159—160
Accumulated error 464—468
Accumulator 43
Accuracy of finite difference solutions 597—605
Accuracy of linear multistep methods 493 542—548
Accuracy of methods for solving ordinary differential equations 424
Adams — Moulton method 458—459 488—490 492
Addition of two linear mappings 693
Addition of two matrices 698
Addition of two vectors 672
Addition, modulo m 840
Addition, using a residue number system 846
Adjacent points 953
Adjoint matrix 712
Adjoint matrix, modulo m 856
Aitken 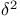 process 159—160 process 159—160
Aitken's method 264—265
Algebra of matrices 702—710
Algebraic compiler language 10
Algebraic eigenproblem 12 736—755 889—950 see
Algol 19
Algorithm, computational 7
Algorithm, computer aspects 5
Algorithm, computer-oriented 2
Algorithm, iteration 14
Algorithm, mathematical aspects 5
Algorithm, stable and unstable 7 9 804 808
Algorithmic language 19
Algorithmic methods 1
Allowable number ranges 71
Allowable numbers 72
Allowable numbers, complex 83
Almost triangular matrix 923
Alternating Direction Implicit method 1000 1039—1062 1075 1096—1097
Alternative discrete representations 590—594
Alternative stability theory 548
Analytic function of a complex variable A16
Analytic function of a real variable A11
Analytic function of two variables A14
Analytic methods for ordinary differential equations 431—435
Analytical solution 1
Approximation 246—248 308—340
Approximation by polynomials 308—317
Approximation by rational functions 248 326—329
Approximation with trigonometric functions 248 333—340
Approximation, best 11
Approximation, continued fraction 328
Approximation, least squares approximation by polynomials 318—325
Approximation, Pade rational approximation 326—329
Approximation, spline 296—301
Approximation, Weierstrass approximation theorem 308
Arithmetic operations, complex 83—91 A14—A15
Arithmetic, 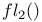 53 53
Arithmetic, binary 19 21
Arithmetic, complex 83—91 668 A14—A15
Arithmetic, floating-point 45—55
Arithmetic, residue 68 835—888
Arithmetic, rounded floating-point 52
Arithmetic, unnormalized floating-point 68
Arithmetic, variable-precision 68
Assembly language 10
Asymptotic equality A20
Asymptotic rate of convergence 1015 see
Attainable accuracy 96
Augmented matrix 784
Automatic digital computer 19
Automatic digital computer, characteristics of 19—69
Back-substitution method 794
Backward error analysis 9 46
Backward Euler method 480
Backward Gregory — Newton formula 283
Balancing 950 see
Base (radix), number representation for 19 20
Base for a residue number system 846
Basic derivative 981
Basis 685
Basis ordered 688 695 727
Basis, natural (standard) 689
Bernoulli numbers 375 380
Bernoulli's method 177 222
Bessel's functions 343
Bessel's interpolation formula 281—283
Best approximation 11
Bias of exponent 36 see
Biased characteristic 37
Bilinear form 731
Bilinear interpolation 342
Binary arithmetic 19 21
Binary arithmetic, computer 28
Binary arithmetic, digit (bit) 27
Binary arithmetic, number representation 20
Binary arithmetic, operations 21
Binary arithmetic, point 43
Binary computer 28
Binary digit (bit) 27
Binary number representation 20
Binary operations 21
Binary point 43
Bisection method of 95 105—112
Bit (binary digit) 27
Bit patterns 32
Block diagonal matrix 746 930
Block iteration 1063
Borrowingin binary subtraction 21
Boundary value problems 951—958
Boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations 576—657
CADD see "Subroutine CADD"
Cancellation 7 see loss
Cancellation law for integers modulo m 840
Cancellation law for scalar multiplication 854
carry bit 44
Carrying in binary addition and multiplication 21
Cauchy bounds 245
Cauchy bounds for roots of polynomial equations 209
Cauchy sequence A4
Cauchy — Riemann equations 134 164 168 A16 A17
Cauchy's method 142
Cauchy's method for polynomial equations 176
Cauchy's method for polynomials 195—196
CEDIT see "Subroutine CEDIT"
Central difference interpolation 280—288
Central difference interpolation, Bessel's formula 281—283
Central difference interpolation, Sterling's formula 281—283
Characteristic 37
Characteristic equation for a linear multistep method 549
Characteristic equation for a matrix 738
Characteristic polynomial 738 889
Characteristic value 738 see
Chebyshev polynomial 316 343 1066 1074
Chebyshev quadrature 345 401 412—419
Chebyshev quadrature, abscissas 414
Chebyshev quadrature, definiteness 418
Chebyshev — Gauss quadrature 421
Chinese remainder theorem 874—876
Choi, method of 790
Choleski decomposition 826
Chopping 43
Closed linear multistep method 494
Closed method based on numerical quadrature 453—459
Closed set A13
Closed-form solution of an equation 95
Closed-form solution of ordinary differential equations 422
CMOD see "Subroutine CMOD"
| Coefficient matrix 784
Coefficients in a linear combination 682
Coefficients of a polynomial 178
Coefficients, Lagrangian interpolation 271
Coefficients, method of undetermined 259—261
Cofactor 711
Cofactor, modulo m 856
Collatz procedure 960
Column of a matrix 696
Column, matrix 716
Column, vector 702
Commutative case 1047—1061
Commutative case, necessary conditions 1060
Commutative case, sufficient conditions 1055—1061
Companion matrix 219 227 889
Comparability theorem for matrix norms 774
Comparability theorem for vector norms 773
Compatible (consistent) norms 761
Complete pivoting for size 806
Complete set of vectors 753
Completely consistent iterative method 121 1064
Complex conjugate 717
complex numbers 668 717
Complex numbers, convergent sequence of A15
Complex numbers, elementary arithmetic operations 83—91 668 A14—A15
Complex numbers, field of 668
Component of a vector 671 688
Component, natural 689
Componentwise addition of vectors 672
Componentwise convergence 757 774
Componentwise equality of vectors 671
Componentwise multiplication of a vector by a scalar 673
Componentwise subtraction of vectors 678
Composite numerical quadrature formula 371 377
Computational algorithm 7
Computer see also "Automatic digital computer"
Computer arithmetic 68 see
Computer representable numbers 20 72 96
Computer representable numbers, complex 83
Computer representable numbers, range of 45
Computer, binary 28
Computer, fixed-word-length 28
Computer, negative number representation 29—40
Computer-allowable numbers 72
Computer-allowable numbers, complex 84
Computer-oriented algorithm 2
Concept of a number 22
Condition numbers for the eigenvalue-eigenvector problem 943—950
Condition numbers for the linear equations problem 811
Condition numbers, spectral 811 946—950
Condition of consistency 505 574
Condition of stability 506 574
Conditional stability 493 548—553 567
Conditional transfer 57
Conditional transfer statement 20
Conformable pair of matrices 706
Conformal mapping 952
Congruence for integers 836
Congruence for matrices 851
Conjugate gradient method 1071—1072
Connected component 1006
Connected set 1003
Consistency 1075
Consistency of a linear discrete operator 606
Consistent (compatible) norms 761
Consistent discrete representation 981
Consistent iterative method 121
Consistent linear discrete operator 606
Consistent system of equations 780
Consistently ordered matrix 1023
Constructive methods 1
Continued fraction 328
Continuity A7 A15
Continuity theorem for matrix norms 774
Continuity theorem for vector norms 772
Continuous function of a complex variable A15
Continuous function of a real variable A7
Contraction mapping 125 127
Control data 6600 38
Convergence for iterative methods 1000 1012
Convergence of a sequence of matrices 758
Convergence of a sequence of vectors 756 772
Convergence of a series A5 A16 757
Convergence of an infinite series of matrices 758
Convergence of an infinite series of vectors 757
Convergence of iterative improvement 832
Convergence of linear multistep methods 493 504—515
Convergence order of, an iterative method 145—159
Convergence order of, Muller's method 154—159
Convergence order of, Newton Method 146—150
Convergence order of, Secant method 150—154
Convergence rates 95
Convergence, acceleration of 159—160
Convergence, componentwise 774
Convergence, criteria for 771—778
Convergence, first order 145
Convergence, geometric 146 159
Convergence, linear 146
Convergence, matrix-norm 774
Convergence, second order 160
Convergence, vector-norm 772 774
Convergent sequence of complex numbers A15
Convergent sequence of matrices 758
Convergent sequence of real numbers A4
Convergent sequence of vectors 756 772
Conversion of number representations 22—28
Conversion, binary-to-octal 27 28
Conversion, octal-to-binary 28
Coordinate 676
Coordinate with respect to an ordered basis 696 727—729
Coordinate, mapping 689
Coordinate, vector 688
Corrected Heun method 452 471 487
Corrected value 458
CPOSTED see "Subroutine CPOSTED"
CQUAD see "Subroutine CQUAD"
Cramer's rule 2 17 263 787 790 A18
Crank — Nicolson method 1075 1078 1086—1088 1093 1095 1097
Criteria for convergence 771—778
CSQRT see "Subroutine CSQRT"
Cubic equation 95
Cubic spline function 296—301
Cubic splines 359
Cyclic Chebyshev semi-iterative method 1069
Data space 10
Decimal notation 20
Decomposable matrix 815
Defective matrix 741—743
Deferred approach to the limit 614
Definite formula or method 349 386
Definite methods for numerical quadrature 492
Definiteness, Chebyshev quadrature 416—418
Definiteness, definite formula 349 386
Definiteness, Gaussian quadrature 409
Definiteness, linear interpolation 395—396
Definiteness, Newton — Cotes formulas 392—393 421
Definiteness, Simpson's rule 396—397
Degree of a polynomial 178 A19
Degree of approximation of a linear discrete operator 606
Derogatory matrix 748—751
Descartes' Rule of Signs 197—201 245
Desk calculating machine 2
Determinant evaluation by Chio's method 790
Determinant evaluation by elimination 798
Determinant of a square matrix 711
Determinant of a square matrix, modulo m 855
Diagonal matrix 707
Diagonalizable matrices 742—743 890
Diagonally dominant matrix 826
Diagonally dominant matrix, strictly 298
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



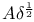 -norm
-norm 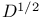 -norm
-norm 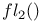 arithmetic
arithmetic 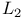 -norm
-norm 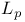 -norm
-norm 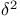 process
process