|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Young D.M., Gregory R.T. — A Survey of Numerical Mathematics, Volume 2 |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
RADIX see "Base"
Range of a linear mapping 694
Range of computer representable numbers 45
Range, dimension 694
Rank of a linear mapping 694
Rank of a matrix 730
Rate of convergence 1015
Rate of convergence for an iterative method 14 1000
Rational approximation 326—329 see
Rational fraction 20
Rational fraction, non-uniqueness of representation 20
Rational numbers, field of 668
Rayleigh quotient 221
RDIV see "Subroutine RDIV"
Real coordinate space, 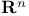 671 676 671 676
Real numbers, convergent sequence of A4
Real numbers, field of 668
Real numbers, interval A3
Real numbers, maximum A3
Real numbers, minimum A3
Real numbers, neighborhood A4
Real numbers, sequences A4
Real numbers, series A5
Real numbers, sets A3
Reciprocally consistent iterative method 121
Rectangle rule 362 450
Rectangle rule forward 362 368
Rectangle rule, backward 362 368
Recurrence procedure for 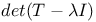 909 909
Red-black ordering 1024 1068
REDIT see "Subroutine REDIT"
Reduced polynomial 176 179
Reduction to Hessenberg form 924—929
Redundant vector 684—685
Reference deviation 310
Reference set 310
Reference-polynomial 310
Refined higher-order methods 624—642
Regular points 953
Related equation 121 1064
Relative degree of approximation 627 981 1075 1089
Relaxation factor 173 1027
Relaxation factor, optimum 1031—1034
Remes algorithm 309 316
Remes algorithm, second 317
Renormalization 43
Representable numbers 72
Representable numbers, complex 83
Representation modulo 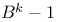 29 29
Representation modulo 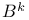 29 29
Representation of a number 22 see
Representation of Integers see "Integer"
Representative root 549 567
Residual 1027
Residue 837
Residue arithmetic 68 835—888
Residue arithmetic for matrices, single modulus 853
Residue arithmetic with a single modulus 837
Residue arithmetic with more than one modulus 846
Residue arithmetic, addition 840 846 853
Residue arithmetic, division 843 849
Residue arithmetic, multiplication 840 847 853
Residue class 837—839
Residue matrix 852
Residue number systems 845
Residue number systems, addition 846
Residue number systems, base for a 846
Residue number systems, division 849
Residue number systems, multiplication 847
Residue representation in a residue number system 845
Residue system of equations 858—860
Resultant procedure 178 242
Reversed sign convention 36 see
Richardson's method 1067
Richardson's method for initial value problems 1075 1077 1084—1086
Right eigenvectors 944
RMULT see "Subroutine RMULT"
Rolle's theorem A9
Romberg integration 265 345 381—385
Root separation property 912
Root-squaring method 178 242
Roots of an equation 94
Roots of polynomial equations 176—245
Roots of polynomial equations, bounds 203—212
Rotation matrix 725 893—894
Rounded floating-point operations 52
Rounding 43
Rounding, error 2
Rounding, error, accumulation 2
Row interchanges 800 805
Row of a matrix 696
Row, matrix 716
Row, vector 702
RSCAL2 see "Subroutine RSCAL2"
RSYNTH see "Subroutine RSYNTH"
Runge phenomenon 296
Runge — Kutta method 473—478 487—490 540
Runge — Kutta method, fourth order 477
scalar 669
Scaling see also "Balancing"
Scaling for the eigenvalue problem 950
Scaling for the linear equations problem 813—819
Schur (Frobenius, Euclidean) matrix norm 767—768
Scientific computer 19
Secant method 95 118—119 578
Secant method for inverse interpolation 302
Secant method for polynomials 189
Secant method order of convergence 150—154
Second algorithm of Remes 317
Second-order convergence 160
Self-adjoint differential equation 579 957—960 1003
Self-adjoint operator 589
Self-starting methods for ordinary differential equation 474
Semi-discretization 1075—1078
Semi-iterative methods 1064—1068
Sequence of complex numbers A15
Sequence of functions (for a real variable) A11
Sequence of functions (for a real variable), convergence A11
Sequence of functions (for a real variable), uniform convergence A12
Sequence of matrices 757
Sequence of real numbers A4
Sequence of vectors 756 772
Series of complex numbers, convergence A15
Series of complex numbers, power series A16
Series of complex numbers, radius of convergence A17
Series of functions A11
Series of real numbers A4
Series of real numbers, Cauchy, sequence A4
Series of real numbers, convergence A4
Series of real numbers, limit A4
Series of real numbers, power series A12
Series of real numbers, radius of convergence A12
Series of real numbers, Taylor series A11
Set, closed A13
Set, greatest lower bound (infimum) A3
Set, least upper bound (supremum) A3
Set, limit point A13
Set, neighborhood A15
Set, open A13
Sheldon's method see "Sheldon's parameter choice"
Sheldon's parameter choice 1069 1073
Shift of origin for polynomials 187
Shooting method for two-point boundary value problems 576—579
Sign and absolute value representation 29 31
Signed absolute value representation 31
Significant digits 2 6
Significant digits, loss of due to subtraction or cancellation 3 7
Similar matrices 741 890
Similarity class 745
Similarity transformation 741 890 925
| Simpson's rule 365 368
Simpson's rule, definiteness 396—397
Simpson's second rule 369 373
Single infinity of solutions 8
Single-length accumulator 52
Single-step (one-step) iterative method, stationary 119
Single-step error 461—469
Singular value of a matrix 755
Skew-symmetric matrix 892
Slide rule 2
Small quantities 5
Small quantities, replaced by zero 5
Smith canonical form 743—744
Smooth interpolation 247 295—301 see
Solution (linear algebraic equations) 779
Solution (linear algebraic equations), computational methods for 790—833
Solution (linear algebraic equations), Cramer's rule 787 790
Solution (linear algebraic equations), existence of 785
Solution (linear algebraic equations), iterative improvement 831
Solution (linear algebraic equations), nontrivial solution (homogeneous system) 788
Solution (linear algebraic equations), one-parameter family of solutions 784
Solution (linear algebraic equations), trivial solution (homogeneous system) 788
Solution (linear algebraic equations), unique 785—787
Solution of equations by graphical methods 95 103—105
Solution of equations by iterative methods 95 105—160
Solution of equations, Cauchy's method 142
Solution of equations, closed-form 95
Solution of equations, method of bisection 95 105—112
Solution of equations, method of false position 95 112—118
Solution of equations, Muller's method 95 136—145
Solution of equations, secant method 95 118—119
Solution of equations, the Newton method 95 131—135
Solution space 10
SOR method 1095—1097 see
Space variable 1075
Spanning set 684 693
Sparse matrix 999—1001
Spectral norm 767
Spectral radius 172 739 767 1011
Spline Function 389
Spline function, cubic 296—301 359
Splines 666
Splitting 1039
Square-root 61
Square-root by the Newton method 14
Square-root of a matrix 755
SSOR method see "Symmetric SOR method"
Stability for methods for solving ordinary differential equations 424
Stability of an algorithm 7 9
Stability of linear multistep methods 493 504—525
Stabilized elementary matrices 924
Stable method 1081
Standard (natural) basis 689
Stationary iterative method 119
Stationary one-step method 119
Stieltjes matrix 1073
Stirling's interpolation formula 281—283 610
Strictly diagonally dominant matrix 298
Strong instability 493 532 548—553 567
Strong stability 493 548—553 567
Structure of a matrix 743
Sturm sequences 201—202 245 911
Sturm's theorem 202
Subordinate (natural) matrix norm 761 769—770
subroutines 57—91 143 235
Subroutines, ANALYZE 57—61
Subroutines, CADD 87
Subroutines, CEDID 84
Subroutines, CMOD 88
Subroutines, CPOSTED 84—86
Subroutines, CQUAD 143
Subroutines, INT 57—61
Subroutines, POLLIF 235
Subroutines, POLLIN 235
Subroutines, POLYHOOK 235
Subroutines, POWER 66
Subroutines, RADD 75
Subroutines, RDIV 76
Subroutines, REDIT 73
Subroutines, RMULT 75
Subroutines, RSCAL2 77
Subroutines, RSYNTH 77
Subroutines, SCQRT 89—91
Subspace of 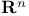 680 680
Subspace, under a linear mapping 693
Subspace, zero (null) 680
Subtraction on a binary computer 33
Successive overrelaxation method 161 173 1000 1026—1038
Sum norm 762
Sum of two linear mappings 693
Sum of two matrices 698
Sum of two vectors 672
Supremum (least upper bound) A3
Surveillance of number ranges 70—92
Surveillance programs 71
Symmetric functions of the zeros of a polynomial 185
Symmetric matrix 720 957
Symmetric SOR method 1068
Synthetic division 183
Systems of linear algebraic equations see also "Linear algebraic equations"
Systems of linear algebraic equations, homogeneous 788 A18
Systems of linear algebraic equations, nonhomogeneous 779 A18
Systems of linear algebraic equations, nontrivial solution A19
Systems of linear algebraic equations, trivial solution A18
Systems of ordinary differential equations 482—488
Taylor's series A11 A13
Taylor's series method 487
Taylor's series method for ordinary differential equations 432—435
Taylor's series, expansion 11
Taylor's theorem 94 A13
Taylor's theorem in two variables A13
Taylor's Theorem, integral form of remainder A11
Taylor's theorem, Lagrange form of remainder A10
Theorem of Frobenius 1047
Three-point difference equation 584 614
time variable 1075
Trace of a matrix 739
Transpose of a matrix 712
Trapezoidal rule 363 427 480
Triangle inequality for matrix norms 760
Triangle inequality for vector norms 759
Triangular decomposition 820
Triangular decomposition with partial pivoting 827
Triangular iterpolation 340 343
Tridiagonal matrix 298 901 909
Trigonometric approximation see "Approximation with trigonometric functions"
Trigonometric interpolation see "Interpolation with trigonometric functions"
Trigonometric polynomial 329
Trigonometric series 330
Trivial solution A18 577 737
Two-line SOR 1064
Two-parameter family of solutions of ordinary differential equation 423
Two-point boundary value problems 576—657 665 951 981
Two-point boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations 424
Two-point eigenvalue problem 658—666
Two-point numerical differentiation 352
Two-step method, stationary 119
Twos complement representation 30
Underflow (exponent) 45 55 70
Undetermined coefficients, method of 259—261
Undetermined weights, method of 262—264
Uniform convergence A12
Uniform norm 308 see
Uniformly consistent linear discrete operator 606
Uniformly continuous function A7
Uniformly continuous function of a real variable A7
Uniqueness theorems for ordinary differential equations 425—431
Unit matrix 701
Unit vector 682
Unitary matrix 724
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте