|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hubbard B. Ч The World According to Wavelets: The Story of a Mathematical Technique in the Making |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Hat" notation 96 103
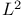 (space) 133 168 176Ч177 185 (space) 133 168 176Ч177 185
Adaptive time segmentation 78Ч80
Adaptive windowed Fourier analysis see "Malvar wavelets"
Adelson, Edward 42 45 47 62Ч63 139 162 187 188 192Ч193
Alessandro see "d'Alessandro Christophe"
Amplitude 99
Analog 18
Analytical Theory of Heat 7Ч8 14Ч15
Apery, Roger, and zeta function 184
Argoul, F. 54
Arneodo, Alain 54 55 59
Arnold, Vladimir, and KAM theorem 113
Artifacts 141 197
Artifacts, danger of, with wavelets 55Ч56 61
Artifacts, motion, reduction of, using wavelets 53Ч54
Astronomy 54 125
Atomic decompositions 26
Balian, Roger 29 36 78
Banach, Stefan 182
Barlaud, Michel 69Ч70
Basis 56 127Ч128 232Ч233 see
Battle Ч Lemarie spline functions 45 164
Battle, Guy 36 45
Benzi, Roberto 56
Berger, Jonathan 84
Best basis 81Ч86 88 136 194 201 202 205Ч207
Beylkin, Gregory 61 70
Bijaoui, Albert 54
Biorthogonal wavelets 69 80 196Ч197
Biot, Jean-Baptiste 109
Birkhoff, George 113
Bishop, Peter 187
Bit 64
Brahms 3 83Ч84
Burt, Peter 42 45 47 139 162
BYTE 64
Calderon, A.P. 186
Cayley, Arthur 122
Chameleon effect 55
Chaos 11 46
Ciliberto, S. 56
Coefficients 30 see "Wavelet
Coefficients, computing in non-orthogonal basis 133Ч135
Coefficients, computing in orthonormal basis 126 129Ч133
Coefficients, computing with integrals 30Ч33 98 114Ч116 126 131Ч133
Coefficients, filter coefficients 159
Cohen, Albert 78
Coherent structures 72
Coifman, Ronald 3 36 75 77Ч78 85
Coifman, Ronald, Best Basis (including Brahms) 81 83Ч84
Coifman, Ronald, fast algorithms 40
Coifman, Ronald, matrix compression 70Ч71
Compact support 45 47 48 140 161
Compact transforms 189 190
Complex conjugate 136 226 232
Complex exponential 102
complex numbers 101Ч102 214Ч215
Complex-valued vectors, scalar product of 136
Complex-valued wavelets 75
Compression 64Ч65 67Ч68 78 162 188Ч189 198 203 see
Compression, comparing methods difficult 70
Compression, matrices 70Ч71
Compression, most signals not compressible 67
Compression, random signal incompressible 65Ч67
Compression, wavelets and 33 63 68Ч71 83
Computers 18 20 26 29 46 72 74Ч75 117 123 192Ч193
Constant Q filtering 62
Continuous wavelet transform 34Ч36 61 74Ч75 80 81 124Ч125 126 196
Continuous wavelet transform, aesthetics of 74
Continuous wavelet transform, formula and fast algorithms 124Ч125
Convergence 104Ч113
Convergence, easier proof of convergence of Fourier series 106 232Ч235
Convergence, pointwise 106
Convergence, Siegel, Carl, and small divisor problem 109
Convergence, small divisors and stability of solar system 107Ч113
Convergence, uniform 106
Convergence, weak 229
Convolutions, definition 157Ч158
Convolutions, wavelet transform and 158Ч161
Cooley, J.W. 117
Correlation 32 81Ч82
Cosine 212
Cousin, V. 5 6
Critical sampling 34 193
Crossword puzzles 82
D'Alembert 11
d'Alessandro, Christophe 80 203
Daubechies wavelets 45Ч48 149 163 194 195 203
Daubechies, Ingrid, compression and wavelets 63 68Ч69 196
Daubechies, Ingrid, early involvement with wavelets 45 47
Daubechies, Ingrid, fast wavelet transform 155
Daubechies, Ingrid, matrix compression 71
Daubechies, Ingrid, multiresolution 39
Daubechies, Ingrid, noise 52
Daubechies, Ingrid, notation 142
Daubechies, Ingrid, pure mathematics and wavelets 52
Daubechies, Ingrid, quantization 69 134Ч135
Daubechies, Ingrid, redundance 36
Daubechies, Ingrid, time-frequency decompositions with wavelets 48Ч49
Daubechies, Ingrid, vanishing moments 161 198
Daugman, John 188
DCT see "Discrete cosine transform"
de Moivre formula 101 119 214 215 235
De Moivre, Abraham 101
Decoupling 12Ч13
Delambre, Jean-Baptiste 11
Delprat, Nathalie 125
Delta function see "Dirac  -function" -function"
Denoising, Best Basis and Brahms recording 83Ч85
Denoising, defining noise 56
Denoising, new questions 85
Denoising, restoring singularities 52
Denoising, skeletons and 125
Denoising, wavelet maxima 59Ч61
Denoising, wavelet thresholding, Donoho and Johnstone 56-59
Denoising, wavelet thresholding, other 59Ч61
DeVore, Ronald 59
Differential equations 7Ч8 11Ч15 22 46 73 107
Digital technology 18Ч20
Dilation 41
Dimensionality reduction 189
Dirac  -function (delta function) 168 230 233 -function (delta function) 168 230 233
Dirac basis 168
Dirichlet, Gustave Lejeune 8 106 230
Discrete cosine transform 161
Discrete transforms 74Ч75 80 125 126 136
Distributions 107 182 184 229Ч230
Divergence 105 107
Donoho, David 56Ч59 61 85 89
Donovan, George 163
Dot product see "Scalar product"
Dyadic 125
Dynamical systems 46 113
e (number) 101Ч102
Edison, Thomas 83
Egypt (and Fourier) 6
Einstein, Albert (speaking of Newton) 7
El Nino ocean current 53
Energy (of error) 135
Energy (of signal) 29Ч30 57 191 192 196
entropy 81 82
Epperson, Jay 70
Escudie, Bernard 124
Esteban, D. (and quadrature mirror filters) 147 162
Euler, Leonhard (and zeta function) 183
Event 172
Expectation 172
Exponential 102
Extended Self Similarity 56
| Faraday, Michael (on mathematical writing) xiii
Farge, Marie, choice of transform 76 200
Farge, Marie, choice of wavelet 74Ч75 194
Farge, Marie, interpreting coefficients 62 74
Farge, Marie, multiresolution analysis, importance of 39
Farge, Marie, wavelets and turbulence 71Ч72 78 189
Fast Fourier transform (FFT) 117Ч123
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), abuse of 21
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), alternative description 118
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), comparison with fast wavelet transform 161
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), discrete form of Fourier transform 118
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), history of 117 121
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), importance of 20 40 45 117
Fast Fourier transform (FFT), matrix form 119Ч123
Fast wavelet transform (FWT) 42Ч45 86 154Ч161
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), comparison with fast Fourier transform 161
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), concise 156
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), example with Haar scaling function and wavelet 156Ч157 159Ч161
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), importance of 40 45 139
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), scaling function in 42Ч44 154
Fast wavelet transform (FWT), speed of 45 139 155 161
Father function 41 see
FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigations) 83
Field, David J. 25 62 64 187Ч192
Filter coefficients 159
Filters 39 138 152 161
Filters, digital, frequencies of 147 151 230
Filters, high-pass filter 139 150 159
Filters, low-pass filter 138Ч139 147 159
Filters, shiftable filters 193
Filters, steerable filters 193
fingerprints 83
Fourier analysis see also "Fourier series" "Fourier "Fourier
Fourier analysis, quantum mechanics and 15 17 51
Fourier analysis, significance of 7Ч8 11Ч19 51
Fourier analysis, solving differential equations 12Ч15
Fourier analysis, time information hidden 22Ч23 53
Fourier analysis, unsuited to nonlinear problems 73Ч74
Fourier coefficients 9 12Ч13 17Ч18 97Ч100 104 114Ч116 185
Fourier series of function that decreases at infinity 231
Fourier series, convergence of 104Ч113
Fourier series, formulas for 97Ч98
Fourier series, formulas for, using complex exponentials 102
Fourier transform 9 15 29 82 96Ч103 192 200 see "Fourier "Windowed "Fourier
Fourier transform of periodic function 227Ч230
Fourier transform of sequence of numbers 147 227Ч230
Fourier transform, "hat" notation 96 103
Fourier transform, amplitude 99
Fourier transform, computing 118Ч119
Fourier transform, formulas for: 101
Fourier transform, formulas for:, using complex exponentials 102 220
Fourier transform, phase 99Ч100
Fourier transform, physical reality of 15 62
Fourier, Joseph 5Ч9 11 14Ч15 17 117 181
Fractal wavelets 163Ч164
Fractals 11 54Ч56 59
frames 196
Frazier, Michael 3 20 70 219
Freeman, William T. 193
Frequency of digital filter 151
Frequency of wavelets, not precise 31 198Ч199
Frequency, doubles, with octaves 19
Frequency, measured: in hertz 96
Frequency, measured: in radians 212Ч213
Frequency, spatial 16 96Ч97
Frequency, variables representing 97Ч98 118
Frisch, Uriel 54Ч56
Function spaces 127 129 181Ч182 184Ч185 see
Function spaces, access to: with Fourier analysis 185Ч186
Function spaces, access to: with wavelets 26 186
Functions 9Ч10
Functions as point or vector in infinite-dimensional space 103 127Ч129 183Ч185
Functions, analyzing functions 15 126
Functions, history (changing definition) 10Ч11 181Ч186
Functions, length of 129 133
Functions, notation: f or f(x) 102Ч103
Functions, zeta function 183Ч184
FWT see "Fast wavelet transform"
Gabor transforms 26Ч28 187 188
Gabor, Dennis, holography 22
Gabor, Dennis, importance of uncertainty principle in acoustics 49
Gabor, Dennis, limit of information transmissible 64
Gabor, Dennis, reservations about Fourier analysis 22Ч23
Gabor, Dennis, windowed Fourier analysis 23Ч24 26 31 187 203
Galand, C. (and quadrature mirror filters) 147 162
Gauss, Carl Friedrich (and fast Fourier transform) 20 117 121Ч122
Gelfand, Israel 107 182 184
Geronimo, Jeffrey S. 163Ч164
Gibbs' phenomenon 106
Gonnet, Caroline 125
Granlund, Goesta 187
Grasseau, G. 54
Gravitational waves, detection of 125
Grossmann, Alex, continuous wavelet transform 35
Grossmann, Alex, Daubechies 47
Grossmann, Alex, definition of wavelet a scholastic question 80
Grossmann, Alex, denoising 57
Grossmann, Alex, early involvement with wavelets 24Ч25 29Ч30 34 71
Grossmann, Alex, hearing and wavelets 62
Grossmann, Alex, influence of wavelets on interdisciplinary work 25
Grossmann, Alex, matrix compression 71
Grossmann, Alex, speed of computations 45
Guillemain, Philippe 125
H see "Planck's constant"
h bar 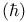 179 179
Haar function see "Haar wavelet"
Haar scaling function 141Ч143 145 148 149 156Ч157 159Ч161
Haar wavelet 36 141 152 156Ч157 159Ч161 163 196
Hardin, Douglas P. 163
Hausdorff, Felix 182
Healy, Dennis Jr. 53 70 78
Hearing 62Ч63
Heat diffusion 7Ч8 11Ч15 17
Heaviside, Oliver (and distributions) 184
Heisenberg boxes 168 205Ч207
Heisenberg cells see "Heisenberg boxes"
Heisenberg uncertainty principle in communication theory and signal processing 48Ч51 165Ч170 171 199
Heisenberg uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics 49 51 171 176 178 180
Heisenberg uncertainty principle, proof 136 224Ч226
Hermite, Charles 181
Hertz 18 96
High-pass filter see "Filters"
Hugo, Victor (on Fourier) 7
Hwang, Wen Liang (and wavelet maxima) 59 125
Hybrids see "Malvar wavelets" "Wavelet
Image processing 38 68Ч70 78 125 137 138 139 140 162
Infinite product 149
Information, Kolmogorov information content 65 67
Information, not to be confused with meaning 67
Information, quantifying 64Ч65
Inner product 126 see
Innocent, Jean-Michel 125
Integrals see also "Lebesgue integral" "Riemann
Integrals, comparison of Lebesgue and Riemann integrals 216Ч219
Integrals, computing coefficients with 30Ч33 98 114Ч116 131Ч133
Integrals, measuring continuous probability spaces 173Ч174
Integrals, relationship with scalar products 131Ч133
Integrals, zero, of wavelet 32 36
Integration 118
Isometry 225
Iterated Function Systems 146
iterations 46Ч47 86
Jacobi, Carl (on Fourier) 11
Jaffard, Stephane 55 186
Johnstone, Iain 56 59 61
Kam theorem 113
Kerkyacharian, Gerard 57
Koerner, T.W. 8 11 20 21
Kolmogorov, Andrei, compressibility of information 65Ч68
Kolmogorov, Andrei, definition of random 65
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 (space)
(space)  -function"
-function"