јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Davis M., Sigal R., Weyuker E. Ч Computability, complexity, and languages: Fundamentals of theoretical computer science
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Computability, complexity, and languages: Fundamentals of theoretical computer scienceјвторы: Davis M., Sigal R., Weyuker E.јннотаци€: This introductory text covers the key areas of computer science, including recursive function theory, formal languages, and automata. It assumes a minimal background in formal mathematics. The book is divided into five parts: Computability, Grammars and Automata, Logic, Complexity, and Unsolvability. * Computability theory is introduced in a manner that makes maximum use of previous programming experience, including a "universal" program that takes up less than a page.* The number of exercises included has more than tripled.* Automata theory, computational logic, and complexity theory are presented in a flexible manner, and can be covered in a variety of different arrangements.
язык: –убрика: Computer science /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 2-nd edition√од издани€: 1994 оличество страниц: 628ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.03.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
273Ч274 278 278 215Ч230 215 217 215Ч230 215 217 1-completeness 209 226 Algorithms 3 68 79Ч80 95 411 Almost everywhere 421 Alphabets 4 113 347 375 505 Alphabets of linear bounded automata 330 Alphabets of pushdown automata 310 Alphabets of Turing machines 146 Approximation orderings 470Ч471 487 505 see "Partial Arithmetic hierarchy 215Ч230 Arithmetic predicates 223 Assignments, complete type 512 513 516 539 Assignments, continuous variable 514Ч515 539 Assignments, Herbrand ideal type 546 Assignments, on propositional atoms 348 406 455Ч456 Assignments, type 511Ч512 Assignments, variable 514Ч515 atoms 347 Automata theory 237 Axiom of Choice 474 Axiomatizable theories 407Ч410 415 Axiomatizable theories, 410 Axiomatizable theories, complete 410 Axiomatizable theories, consistent 410 Axiomatizable theories, nonrecursive 415 Balanced words 309Ч310 Bar-Hillel's pumping lemma 287Ч290 299 Base n notation 116 328 580 Binary relations 472 Binary relations, restrictions of 472 Blum axioms 419Ч425 Blum speedup theorem 437Ч438 Blum, Manuel 419 Boolean algebra 350 Bottom elements 477 Bracket languages 301Ч308 Cantor, Georg 406 Cartesian product 3 Case, John 103 Chains 477 499 Chang, C.L. 593 Chomsky hierarchy 327Ч330 Chomsky normal form grammars 285Ч287 287Ч290 297 303 306 308 313 316 319 Chomsky normal form grammars, separators of 303Ч308 313 319 Chomsky Ч Schuetzenberger representation theorem 306 Church's thesis 69 80 90 95 96 141 161 162 197 407 445 447 Church, Alonzo 411 clauses 355Ч356 Clauses, linked sets of 366Ч367 396 398 400 Clauses, minimally unsatisfiable sets of 366Ч367 392 395 Clauses, unit 361 362 363 Closure properties 4 Closure properties for context-free languages 291Ч297 Closure properties for context-sensitive languages 329 337Ч344 Closure properties for regular languages 249Ч256 CNF see "Conjunctive normal form" Co-NP 450 COBOL 323 Coding of 579Ч582 Coding of 579Ч582 Coding of 579Ч582 Coding of finite functions 203Ч204 580 Coding of pairs 59Ч60 see Coding of programs 65Ч67 Coding of sequences 60Ч63 see Coding of states of programs 71 Coding of strings 113Ч115 COF 227 Coincidence lemma 518 527 COMP 48 Compact elements of a cpo 486 Compactness theorem for predicate logic 390 404Ч406 Compactness theorem for propositional calculus 370Ч373 390 404 Compilers 323Ч326 Complete partial orders 475Ч486 516 see "Orderings" Complete partial orders, algebraic 486 494 Complete partial orders, compact elements of 486 Complete partial orders, flat 477 539 Complete partial orders, of continuous variable assignments 516Ч517 Complexity, abstract 419Ч438 Complexity, measures 419 composition 39Ч40 42 76 77 108 200 576 Computability theory 17 18 31 70 98 113 169 237 443 Computable real numbers 554 587 589Ч590 Computations, by 27 28 29 70Ч75 420 468 557 Computations, by linear bounded automata 339Ч343 Computations, by nondeterministic Turing machines 160 171 447Ч448 451Ч456 Computations, by pushdown automata 311Ч323 Computations, for W-terms 559Ч575 584Ч587 588 Computations, infinite 469Ч470 563 Configurations of linear bounded automata 330 331 Configurations of Post Ч Turing programs 130 Configurations of pushdown automata 311 Configurations of Turing machines 147 159Ч160 444 452Ч456 Conjunctive normal form 356Ч360 364 368 392 393 444 446 447Ч448 451Ч456 457Ч458 461 Constant symbols 375 506 Context-free grammars 269Ч280 326 327 497Ч499 see Context-free grammars, ambiguity of 300 303 307 319 Context-free grammars, branching 277 279 285 Context-free grammars, Chomsky normal form see "Chomsky normal form grammars" Context-free grammars, derivation trees in see "Derivation trees" Context-free grammars, derivations in 270 275 277 Context-free grammars, Greibach normal form 287 Context-free grammars, kernels of 271 Context-free grammars, languages generated by 270 Context-free grammars, left-linear 285 Context-free grammars, leftmost derivations in 275Ч277 Context-free grammars, positive 269 271 273 277 327 Context-free grammars, productions of 269 Context-free grammars, regular 280Ч285 327 Context-free grammars, right-linear 283 304 Context-free grammars, rightmost derivations in 275Ч277 Context-free grammars, self-embedding 284 Context-free grammars, unsolvable problems involving 297Ч301 Context-free languages 269Ч326 327Ч328 337 450 see Context-free languages, and compilers 323Ч326 Context-free languages, and pushdown automata 308Ч323 Context-free languages, closure properties for 291Ч297 Context-free languages, deterministic 323 Context-free languages, infinite 298Ч299 Context-free languages, inherently ambiguous 301 Context-free languages, nonregular 270 Context-free languages, regular 280Ч285 Context-sensitive grammars 189Ч190 327Ч330 Context-sensitive grammars, unsolvable problems involving 339 Context-sensitive languages 327Ч344 Context-sensitive languages, closure properties for 329 337Ч344 Context-sensitive languages, open questions concerning 343 Cook Ч Karp thesis 445 Cook's theorem 451Ч456 Corollaries 8 Correctness of operational semantics 557 Correctness of programs 536 Course-of-values recursion 62Ч63 CPO 477 see cpo, flat 477 Data structure systems 531 536 Data structure systems, infinitary 544Ч556 584Ч592 Data structure systems, simple 539Ч544 557Ч575 Davis Ч Putnam rules 360Ч366 368 391 393 396 444 Davis, Martin 593 de Morgan identities 2 6 7 50 251 291 350 354 371 380 Definition by cases 50Ч51 Degree of function symbols 375 Degree of polynomials 441 Degree of relation symbols 375 Derivation trees 274Ч279 298 498 Derivation trees, pruning and splicing of 279 289 DFA 243 see DFA, minimal 266 Diagonal Lemma 492 502 518 Diagonalization 88Ч90 94 106 328 406 429 Disjunctive normal form 356Ч360 444 DNF see "Disjunctive normal form" Dovetailing 80 81 408 DTIME 450 Duality, general principle of 350 356 358 380 Dyck languages 303 306 Empty program 26 Enderton, Herbert P. 593 Enumeration Principle 370 371 405 Enumeration theorem 81 Equivalence relations 263 Euclid 57 Exchange Lemma 490 491 503 EXPTIME 450 451 Extension Lemma 526Ч527 532 534 573 Fibonacci numbers 62 529 Finite automata 237Ч242 Finite automata, deterministic 243 280 292 Finite automata, nondeterministic 242Ч249 281 324 Finite automata, nonrestarting 250 316 Finite satisfiability 370Ч372 Finiteness theorem 204 First-order logic see "Quantification theory" Fixed point induction principle 499 see fixed Fixed point theorem 101 501 see Fixed point theorem for cpos 495Ч496 497 499 501 524 Fixed points 494Ч503 Fixed points as solutions to W-programs 523 Floyd, R.W. 181 Formulas, atomic 376 Formulas, ground 392 Formulas, Herbrand instances of 412Ч414 Formulas, in predicate logic 376 Formulas, propositional 347 496Ч500 Formulas, quasi-representing sets 409 Formulas, representing functions 410 Formulas, representing sets 408 409 Formulas, semantically equivalent 380 FORTRAN 279 323 324 Function symbols 375 506 Function symbols, arity of 506 Function symbols, built-in 509 Function symbols, constructor 509 Function symbols, degree of 375 Function symbols, discriminator 509 Function symbols, proper 506 Function symbols, selector 509 Functions 3 Functions, 574 575Ч584 Functions, binary 3 Functions, Boolean-valued 5 Functions, characteristic 6 78 see Functions, computable 28Ч32 41 42 77 112 116 121 469 567 Functions, computed by 19 22Ч25 30 Functions, computed by Post Ч Turing programs 134 135 140 141 147 149 150 Functions, computed by Turing machines 146Ч152 Functions, computed strictly 134 135 139 146 148 Functions, constructible 428 Functions, continuous 486Ч494 495 Functions, domain of 3 Functions, elementary 59 Functions, exponential 425 442 444 450 Functions, G-computable 198 Functions, G-partial recursive 198 Functions, G-recursive 198 Functions, higher order 470 481 520 Functions, intuitively computable see "Church's thesis" Functions, monotonic 487Ч494 Functions, n-ary 3 200 Functions, nowhere defined 3 31 Functions, on strings 116Ч117 Functions, one-one 4 84 Functions, onto 4 Functions, partial 3 24 Functions, partial recursive 30 84 Functions, partially computable 30 39 70 73 75 76 83 96 116 127 140 148 198 199 467 501 578Ч582 Functions, partially computable in 121 127 135 140 141 Functions, partially G-computable 198 Functions, polynomial time computable 445 Functions, primitive recursive 39Ч63 84 105Ч112 117 188 262 576Ч578 Functions, range of 3 82 83 84 functions, recursive 30 84 426 428 436 437 Functions, strict 487 539 564 Functions, strict extensions of 487 Functions, total 3 5 30 40 42 90 198 199 200 201 202 204 205 Functions, unary 3 G-r.e. sets 211Ч215 Gap theorem 425Ч428 Garey, Michael R. 593 Goedel numbers 60Ч63 66 67 71 74Ч75 79 84 108 200 204 217Ч218 222 232 435 580 Goedel's incompleteness theorem 407Ч410 Goedel, Kurt 60 Goldbach's conjecture 69 70 grammars 186Ч191 see "Context-sensitive "Regular Grammars, derivations in 188 270 Grammars, languages generated by 186 270 327Ч329 Grammars, left-linear 285 Grammars, null productions of 269 327 344 Grammars, phrase structure 186 327 Grammars, positive context-free 269 327 Grammars, productions of 186 269 Grammars, regular 280Ч285 327 Grammars, right-linear 283 304 Grammars, self-embedding 284 Grammars, start symbol of 186 269 Grammars, terminals of 186 269 Grammars, unsolvable problems concerning 191Ч192 300Ч301 322 339 Grammars, variables of 186 269 graphs 458Ч460 Graphs, cliques in 459 Graphs, complete 458Ч459 Greatest lower bounds 476 Greibach normal form grammars 287 Ground clauses 392 Ground resolution 369 see in Ground resolution theorem 369 Gunter, Carl A. 593 Halmos, Paul R. 593 Halting problem 68Ч70 78 82 89 97Ч98 99 197 467 488 523 554 see halting Halting problem for Post Ч Turing programs 144 Halting problem for Turing machines 157Ч158 Harrison, Michael 594 Herbrand instances of formulas 412Ч414 Herbrand universes 388 389 390 392 393 395 398 405 406 412 542 Herbrand's theorem 388Ч398 404 Hilbert, David 410 411 Homomorphisms 253 296 344 Horn clauses 403 Horn programs 404 Hrbacek, Karel 594 Ideals 482Ч483 546Ч556 Ideals, principal 482 552 Immerman, Neil 339 Index sets 95 103 230Ч231 Induction 9Ч13 Induction, complete 11Ч12 Induction, course-of-values 11Ч12 302 Induction, fixed point 499Ч500 536Ч537 Induction, hypothesis 10 Induction, loading 11 109 Induction, mathematical 9Ч13 52 86 206 215 245 256 264 271 293 304 305 433 495 540 571 576
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -trees
-trees 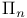
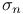
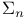 as a collection of sets
as a collection of sets 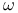 -consistent
-consistent 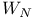 -programs
-programs 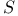 programs
programs  -computable
-computable