Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Davis M., Sigal R., Weyuker E. — Computability, complexity, and languages: Fundamentals of theoretical computer science
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Computability, complexity, and languages: Fundamentals of theoretical computer scienceАвторы: Davis M., Sigal R., Weyuker E.Аннотация: This introductory text covers the key areas of computer science, including recursive function theory, formal languages, and automata. It assumes a minimal background in formal mathematics. The book is divided into five parts: Computability, Grammars and Automata, Logic, Complexity, and Unsolvability. * Computability theory is introduced in a manner that makes maximum use of previous programming experience, including a "universal" program that takes up less than a page.* The number of exercises included has more than tripled.* Automata theory, computational logic, and complexity theory are presented in a flexible manner, and can be covered in a variety of different arrangements.
Язык: Рубрика: Computer science /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 2-nd editionГод издания: 1994Количество страниц: 628Добавлена в каталог: 30.03.2014Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Semantics, of W-terms 511—520 Semantics, operational 468 499 557—592 Semi-decision procedures 80 392 Semi-Thue Processes 169—180 182 186 334 see Semi-Thue processes, derivations in 170 Semi-Thue productions 169 Semi-Thue productions, inverses of 175—176 177 335 Sentences 377 Sentences, models of 380 Sentences, prenex 384 Sentences, rooted 412 413 414 Sentences, satisfiable see "Satisfiability in Sentences, semantically equivalent 380 Sentences, Skolemized 384—387 393 405 Sentences, undecidable 409 Sentences, universal 385 388 Sentences, valid 380 383 391 Sentential logic see "Propositional calculus" Sequence number theorem 62 Sets 1 78 Sets, characteristic functions of 6 78 79 Sets, complement of 2 Sets, computable 78 Sets, difference of 2 Sets, empty 1 Sets, equality of 1 Sets, finite 2 Sets, G-recursive 211—214 Sets, infinite 2 Sets, intersection of 2 Sets, recursive 78 80 88 91 210 Sets, recursively isomorphic 231 Sets, union of 2 Shoenfield, Joseph R. 594 Sieber, Kurt 594 Simulation 70—75 127 135—144 163—167 171—176 333—336 Skolem — Loewenheim Theorem 406 Skolemization 384—387 Skolemization, generalized 386—387 405 Snapshots of a program 27—28 70 74—76 197 420 Snapshots of a program, initial 29 Snapshots of a program, successor of 27 Snapshots of a program, terminal 27 75 76 197 Soare, Robert I. 594 Socrates 393 Solutions to W-programs 520—530 534 536 Spanning sets 263 Speedup theorem 428—438 Splitting rule 361 363 364 stacks 310—311 Start symbols 269 state transition diagrams 147 240 statements 25 see States 26 145 197 238 States, accepting 238 310 States, dead 248 States, final 238 310 330 331 States, INITIAL 29 238 310 331 Step-counter predicates 74—75 78 81 82 83 224 225 Step-counter predicates, relativized 201—205 211 212 Step-counter theorem 74 Step-counter theorem, relativized 202—204 Stoy, Joseph E. 594 strings 4 12 113—144 Strings, computable functions on 116 121 Strings, computations on 113 121 Strings, concatenation of 117—118 strings, length of 4 118 Strings, numerical representation of 113—117 Strings, partially computable functions on 116 121 Strings, primitive recursive functions on 117 Strings, programming languages for 121—126 subsets 1 Subsets, proper 2 Substitution lemma 558 570 Substitutions on alphabets 252 296 344 Substitutions to individual variables 395 397—398 399—404 see Substitutions, answer 404 Subsumption 366 symbols 4 see "Function "Relation Syntax of 25—26 Syntax of 121 Syntax of propositional calculus 347—348 Syntax of quantification theory 375—377 Syntax of W-programs 505—511 Tautological consequence 352 373 Tautological inference 352—353 Tautologies 348 352 355—356 Terminals 186 269 Terms 376 see Theorems 8 Theoretical computer science 189 359 see "Complexity" "Computability "Languages" "Semantics of Thue Processes 177—181 411 Thue, Axel 169 TOT 90 224—229 Tractability 444 Transition functions 238 Truth values 5 Turing Machines 145—168 176 191 197 415 444 445 447 see of "Linear Turing machines, deterministic 146 159 174 176 177 178 189 415 Turing machines, functions computed by 146—152 Turing machines, languages accepted by 153—157 186—187 189 Turing machines, multiple tape 167 168 Turing machines, multiple track 163—168 337—343 Turing machines, nondeterministic 146 159—162 171—176 186 189 330 446—456 Turing machines, one-way infinite 162—167 Turing machines, quintuple 149 150 Turing machines, Universal 152—153 Turing reducibility 207—211 Turing, Alan 129 153 411 Turing, Alan, analysis of computation process 129 145 Types 505—506 Types, domain 506 Types, function 506 Types, individual 506 Types, product 506 Types, range 506 unconditional branch 19—20 Undecidable sentences 409 Unification 399—404 560 Unification, algorithm 399 Unifiers 403 Unit clauses 361 362 363 Unit rule 362 Universal Computers 153 Universal programs 70 Universal sentences 385 Universality Theorem 70 209 Universality theorem, relativized 201—202 Unsolvability of halting problem 68 82 99 157—158 197 420 Unsolvability of Post's correspondence problem 181—186 Unsolvability of problems involving grammars 191—192 297—301 339 Unsolvability of problems involving programs see "Rice's theorem" Unsolvability of satisfiability problem in predicate logic 392 410—415 Unsolvability of word problems 176—180 195 411 Validity see "Sentences valid" Variables 17 25 65 Variables, auxilliary function 508 Variables, bound 376—377 Variables, free 376—377 Variables, function 506 Variables, in grammars 186 269 Variables, in predicate logic 375—376 Variables, individual 506 Variables, initialization of 18 121 Variables, input 17 25 variables, local 17 25 Variables, occurrences of 376—377 Variables, of 17 25 Variables, output 17 25 Variables, principal function 508 Variables, propositional 347 Variables, type 505 vocabularies 375 506 Vocabularies, interpretations of 377 Vocabularies, standard 509 511 543 550 Vocabularies, standard constructor 509 511 Vocabularies, typed 506 W-formulas 376 see W-programs 508 580 W-programs, denotational semantics for 530—538 W-programs, operational semantics for 557—592 W-programs, partially correct 536 W-programs, solutions to 520—530 534 536 W-programs, totally correct 536 W-recursion equations 507—508 W-sentences 377 see W-structures 513 W-structures, complete 513 539 W-structures, computable elements of 587 W-structures, continuous 513 539 W-structures, data structure systems based on 531 W-structures, Herbrand ideal 546 W-structures, infinitary 544—545 548 587 W-structures, representable elements of 530—531 534 539 551 554 587 W-structures, simple 539 W-structures, simple Herbrand 542 W-substitutions 558 580 W-term rewriting systems 559 W-term rewriting systems for infinitary data structure systems 584—585 W-term rewriting systems for simple data structure systems 561—562 W-term rewriting systems, strategies for 559 560 564—565 W-terms 376 507 580 W-terms, ground 507 W-terms, normal 559 565 W-terms, semantics of 511—520 Word problems 176—180 411 Word problems, of normal processes 193—195 Words 4 see Words, length of 4 Young, Paul 427 594
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



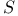 programs
programs 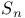 programs
programs