|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Campbell S.A. Ч The Science and Engineering of Microelectronic Fabrication |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
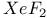 vapor etching 527 vapor etching 527
2-D growth 363
Accelerometer, MEMS 544
Acoustic waves 136
Actinic absorbance 195
Actuators, MEMS 546Ч551
Adatoms 387
Adiabatic heating 127Ч128
Advanced silicon vapor phase, epitaxial growth techniques 378Ч381
Aerogel 430
Agglomeration 18
Air bridges 479
Aligners, optical 153Ч154 165Ч172
Alloyed contacts 421Ч423
Alloys 304Ч305 317
Aluminum 317Ч318 419Ч421
Ambient, particle detection and 496
Analog bipolar technologies 507Ч508
Analysis of variance (Anova) 569Ч571
Anisotropic etching 269Ч272
Anisotropy 258Ч259
Annealing processes 138Ч140
Anode dark space 250
Anodic bonding 537
Antipov emitter 501
Antireflective coatings 177Ч178
Antisite defect 413
APCVD 337Ч339
Aqua regia 417
Arc lamps 131 159Ч160
Area defect 19
Areal image 153
Aromatic ring 184
Arrenhius function 16
Aspect ratio 301
Atomic flux divergence 426Ч427
Autodoping 365Ч366
Avalanche 490
Backstreaming 244
Bamboo effect 426
Bandgap narrowing 494
Barrier height 415Ч416
Barrier metals 318 349 421
BCF theory 387Ч389
Bias sputtering 315Ч316
BiCMOS 504Ч507
Bipolar junction transistors (BJT) 488Ч489
Bleaching 195
Blowers 242Ч244
Boats 90
Boron penetration 455
Borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) 343
Boule 21 23 24 31
Boundary layers 333Ч336
Breakdown histogram 79
Bridging oxygen 76
Bridgman growth 27
Bridgman growth, horizontal 29
Bridgman growth, vertical 29Ч30
Buffered FET logic 474
Buoyancy driven recirculation cells 27
Buried channels 454
Buried collector 494Ч495
Buried dielectrics 118Ч120
C-V profiling 55
CAIBE 276Ч277
Cantilever beam deflection 524
Cantilever beam processing 539 544Ч545
Capacitive pressure sensor 519
Capping layer 139
Carboxylic acid 186
Chain scission 185
Channel implants 445
channeling 110Ч112
Charge to breakdown test 79Ч80
Charge transfer compounds 199
Charged vacancy 43
Chemical beam epitaxy 391Ч392
Chemical equilibrium 328Ч330
Chemical mechanical polishing 264Ч266
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, borophosphosilicate glass 343
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, copper 349Ч350
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, metals 347Ч350
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, phosphosilicate glass 327
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, polysilicon 341Ч342
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) materials, tungsten 347Ч349
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, atmospheric 337Ч339
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, cold wall 341Ч342
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, high-density plasma 345
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, hot wall 336 339Ч341
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, low-pressure CVD 339Ч343
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, plasma enhanced 343Ч347
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems, vertical chamber 340Ч341
Chemically amplified resists (CARs) 197
Chlorine plasmas 277Ч281
Chlorosilanes 341Ч343
Chromium doping 412
cleaning 356Ч359
Climb 18
Clustering factor 563
Collimated sputtering 314Ч315
Comer compensation 529
Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS), design 442
Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS), technologies 442Ч447
Compton effect 206Ч207
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) 575Ч577
Concentration dependence diffusivities 42
Condensation nuclear counters (CNCs) 567
Conductance 239
Confounded variables 572
Contact aligners 165Ч166
Contacts, ohmic, alloyed 421Ч423 455
Contacts, ohmic, implanted 418Ч421
Contacts, resistance (FET) 450
Contacts, Schottky 414Ч418
Contrast enhancement layers (CELs) 198
Contrast, optical 187Ч189
control charts see "Statistical process control"
Convection 127
Convection, natural 26 334Ч335
Coplanar waveguides 424Ч425 479Ч480
copper 432
Core doping 31
Coulomb scattering 104Ч105
Critical angle 110
Critical layers 564
Critical modulation transfer function (CMTF) 190Ч191
Crooke's dark space 250
Cross linking 185 227
Crucible-heating techniques 302Ч304
Cryopump 246
Crystal rate monitor 300
Crystals, defects in 15Ч21
Crystals, lattices in 13Ч15
Czochralski growth 21Ч28
Damage, radiation 228Ч231
Damage, reactive ion etching 281
Damascene process 265 431Ч432
Dark spaces 250Ч251
Deal triangle 81
Deal Ч Grove model 68Ч71 73
Deep trench 408Ч410
Defect selective etching 263Ч264
Defects, crystal 15Ч21
Defects, epitaxial growth 366Ч368
Defects, killing 561
Defects, oval 385
Degree of saturation 361
Dehydration bake 191
Delta doping 418
| Denuded zone 21
Depth of focus 168
Design of Experiments (DOE) 572
Design rules 4 151
Developers 192
Diamond structure 16
Diamond-like carbon 429Ч430
Diazoquinones (DQ) 186
Diborane 366
Dichlorosilane 362
Dielectric isolation (DI) 411
Dielectrics, high permittivity 88Ч89
Dielectrics, rapid thermal processing 140Ч141
Diffraction 155Ч157
Diffusion 8
Diffusion in  59Ч60 59Ч60
Diffusion, atomistic models of 41Ч45
Diffusion, furnaces 60Ч61 90Ч92
Diffusion, heavy doping effects 47Ч52
Diffusion, oxidation enhanced 44
Diffusion, predeposition 45
Diffusion, profiles 48Ч52
Diffusion, pump 245
Diffusion, transient enhanced 138Ч139
Dimethylzinc (DMZ) 375
Direct-coupled FET logic 474
Discharges DC glow 249Ч251
Discharges DC glow, RF 251Ч252
Dislocations 18 367
Dislocations, loops 25
Doping in epitaxial growth 365Ч366
Double diffused drain 457
DQN positive photoresist 186Ч187
Drain engineering 457Ч458
Drain-induced barrier lowering 461Ч462
Drive in diffusion 45Ч46
Dry developable resists 199Ч200
dry etching see "Etching"
Dry oxidation 68 71
Dry pumps 245
Dry pumps, Fraunhofer 157
Dry pumps, Fresnel 156 166
Dry pumps, grating 158
E-beam evaporation 303Ч304
E-beam exposure see "Photoresist"
Early effect 489Ч490
ECR plasma 253Ч254
EL2 sites 413
Electromigration 426
Electron beam lithography (EBL) 208Ч215
Electron beam lithography (EBL), resists 227Ч228
Electron beam MBE systems 390Ч391
Electron diffraction (RHEED) 384Ч385
Electronic stopping 106
Electrostatic scanning 103
Ellipsometry 78Ч79
Emissivity 134Ч135
End point detection 272Ч274
Enhancement/depletion technology 441Ч442
Epitaxial growth BCE theory 387Ч389
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, chemical beam 391Ч392
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, Deal model 360
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, defects 366Ч368
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, dopants 365Ч366
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, extended lateral overgrowth 369
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, halide transport GaAs vapor phase 369Ч370
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, heteroepitaxial 370Ч373
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, kink sites 388
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, metallorganic 373Ч378
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, molecular beam 381Ч386
Epitaxial growth BCE theory, selective 368Ч369
Equilibrium, chemical 328Ч330
Etching, anisotropic 269Ч270
Etching, damage 281
Etching, doping selective 263
Etching, HDP systems 282Ч283
Etching, plasma 266Ч274
Etching, reactive ion 277Ч281
Etching, wet 259Ч264
evaporation 295Ч301
Evaporation, deposition rates 297Ч299
Evaporation, electron beam 303Ч304
Evaporation, heating techniques 302Ч304
Evaporation, radiation damage 303Ч304
Evaporation, reactive 300
Evaporation, step coverage 301Ч302
Evaporation, sublimation and 296Ч297
Excimer laser sources 162Ч164
Exciplex lasers 162
Exposure 163 164 165
Extended lateral overgrowth (ELO) 369
Extrinsic breakdown 79
Extrinsic gettering 19
Factors 571Ч575
Fair's vacancy model 42
Faraday cup 103
Faraday dark space 250
Fast ramp furnace 92
Fault kernel 563
Faults, stacking 366Ч367
Feed gas ratio 362
Fick's laws 39Ч41
Field implant 444Ч445
Film stress, extrinsic 518
Film stress, intrinsic 518
Fixed charge 81
FLATS 32
Flexural rigidity 524
Float zone refining 30Ч31
Flow plug 332
Flow process 399
Fluorinated oxide 429
Fluorine to carbon ratio 271
Flux 40
Four point probe 52
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy 368
Frank Ч Turnbull method 45 51
Fraunhofer diffraction 157
Freeman ion source 100
Frenkel defect 16
Fresnel diffraction 156Ч157
Full factorial experiments 570Ч571
Fused silica 76
GaAs on silicon 372
GaAs, anisotropic etching 280Ч281
GaAs, device isolation 412Ч414
GaAs, FET technologies 471Ч481
GaAs, implant activation in 139Ч140
GaAs, liftoff 283Ч285
GaAs, MESFET 471Ч473
GaAs, MOCVD 373Ч378
GaAs, Schottky diodes 417
GaAs, vapor phase epitaxy 369Ч370
Gas ballast 242
Gas immersion laser doping 462
Gas source MBE 391
Gas throughput 239
Gas-flow dynamics 331Ч336
Gate materials for MESFETs 475Ч476
Gate materials for MOSFETS 454Ч455
Gate oxidation 88Ч92
Gettering 19
Glide 18
Glow discharge 249Ч251
Gold air bridges 479
Grain boundary 19
Grain boundary, stuffing 142
Gross fail area 562
Hall effect 54 520
Halo implants 464
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



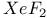 vapor etching
vapor etching 