|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Matt Young — Optics and Lasers: Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Rayleigh scattering 11.2 11.2.1
Receiver 12.1
Reciprocity failure 3.2.2
Reciprocity law 3.2.2
Recombination radiation 4.2.3
Reconstruction 7.1 7.1.1
Reconstruction, conjugate 7.1 7.1.2
Reconstruction, minimum angle of 7.1.1
Reconstruction, primary 7.1 7.1.2
Reconstruction, virtual 7.1.1
Reference beam 7.1 7.1.1 7.2.6
Reflectance 5.4.2 9.1.3
Reflectance of silver and aluminum 9.1.7
Reflectance, amplitude 5.4.2 9.1.3
Reflectance, effective, of resonator mirror 8.3.1
Reflection 2.1.3 9.1.3
Reflection from metal 9.1.7
Reflection hologram see "Hologram"
Reflection, angle of 2.1.3
Reflection, frustrated total internal 9.1.5
Reflection, law of 2.1.3
Reflection, phase change on 5.4.1 7.4.5 9.1.3
Reflection, total internal 2.1.4 9.1.5
Refracted near-field scanning see "Refracted-ray method"
Refracted-ray method 1 11.5.4 11.5.5
Refraction 2.1.1
Refraction, angle of 2.1.1 2.2.1
Refraction, internal 2.1.4
Refraction, law of 2.1.1
Relative aperture 3.2.2 6.1 see
Relative intensity noise 4.3.3
Relaxation oscillations 4.3.3
Relay lens 3.7.3
Resolution 3.8
Resolution in coherent light 5.7.2
Resolution in diffused, coherent light 5.7.3
Resolution in incoherent light 5.7.1
Resolution limit 1 3.2.3 3.2.4 3.8 3.9 5.7 5.7.1 7.2.7 7.3.5 7.3.7 7.4.5 see
Resolution of camera 3.8.1
Resolution of eye 3.1
Resolution of microscope 3.8.3
Resolution of NSOM 3.9
Resolution of photographic film 3.2.3
Resolution of pinhole camera 5.5.4
Resolution of points 5.7.1 5.7.2
Resolution of refracted-ray method 11.5.4
Resolution of telescope 3.8.2
Resolution target 5.7.3 7.2.4
Resolution, Abbe theory of 7.2.1 Problem
Resolution, angular, of eye 3.8.2
Resolution, coherent 5.7.2
Resolution, of hologram 7.1.1 Problem
Resolution, spurious 7.3.5
Resolution, theoretical 3.8 5.7
Resolution, two-point 5.7.1
Resolving power 3.2.3 3.8 7.1.1 7.3.7 see "Resolution
Resolving power of camera 3.8.1
Resolving power of film 3.2.3
Resolving power of microscope 3.8.3—4
Resolving power of refracted ray method 11.5.4
Resolving power of telescope 3.8.2
Resonators see "Optical resonators"
Response time 4.3.3
Response time of bolometer 4.3.3
Response time of photoconductor 4.3.3
Response time of photodiode 4.3.3
Response time of thermocouple 4.3.3
Response time of thermopile 4.3.3
Responsivity 4.3.3
Responsivity, of photocathodes (graph) 4.3.3
Responsivity, spectral 4.3.3
Restricted launch 10.3.4
retina 3.1 8.5
Retroflector 2.1.5
Reverse bias 4.3.1
Reverse telephoto lens Problem 2.5
Ribbon-filament lamp 3.8.4 11.1.1
RIN 4.3.3
Rods 3.1
Rowland circle 6.1 Problem
Ruby laser see "Laser"
Ruling 6.1.1
Safe light 3.2.1
Safety, laser 8.5
Sag formula 5.5.3 7.2.7
Sampling 7.4.4
Sampling theorem 7.4.4
SAPpHiRe 8.4.1
Saturable dye 8.4.1 8.4.2
SAW wave 12.1.6
Scalar equation 5.2
Scanning confocal microscope 1 3.6 7.3.3
Scanning confocal microscope, impulse response of 7.3.3
Scanning confocal microscope, Nipkow disk in 3.6.1
Scattering 11.2
Scientist, near-sighted Problem 3.8
Scotopic 3.1
Second harmonic generation see "Harmonic generation"
Secondary electron 4.3.1
Secondary maximum 5.3.2 5.5.1 5.7.2
Secondary maximum, apodization of Problem 7.8
Seidel aberration 2.2.12
Selenium cell 4.3.1
Semiconductor 4.2.4 4.3.1
Semiconductor laser see "Laser" see
Semiconductor, doped 4.2.4 4.3.1
Semiconductor, energy-level structure of 4.3.1
Semiconductor, impurity 4.3.1
Semiconductor, intrinsic 4.3.1
Semiconductor, n type 4.3.1
Semiconductor, p type 4.3.1
Senile macular degeneration 8.5.1
Sensitivity see "Responsivity"
Sensitizing dye 3.2.1
Sensitometry 3.2.2
Serpentine-bend mode filter 11.1.2
Shape factor 5.7.5
Shortest distance of distinct vision see "Near point"
Shot noise 4.3.3
Shoulder (of D vs log 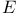 curve) 3.2.2 curve) 3.2.2
Shoulder (of D vs log 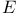 curve) of microscope objective 3.5 curve) of microscope objective 3.5
Shutter 3.2.2
shutter speed 3.2.2
Shutter, acousto-optic 8.4.1
Shutter, electro-optic 8.4.1
Shutter, passive 8.4.1
Sign convention 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3
Silicon cell 4.3.1
Silver 9.1.7
Silver halide 3.2.1
Silver image 3.2.1
Sine condition 2.2.11
Sine function 7.3.1
Single-mode waveguide 1 10.2.6 10.4.2
Single-pixel operation 7.4.2
Skew ray 10.2.4 10.3.5 see
Sky, emissivity of 4.2.1
Slab interference microscopy 11.5.2
Slab of glass Problem 2.2
Slide projector 3.3
Slit see "Diffraction" "Diffraction
Snell's law 2.1.1 9.1.2 9.2.1
Snell's law in layered media 10.3.1
Solar cell 4.3.1
Solid angle 4.1.1
Sombrero function 7.3.1 7.3.3
Source 4.2 see "Blackbody" "Laser"
Source of blackbody radiation 4.2.1
Source, coherence of 5.6
Source, emissivity of 4.2.1
| Source, quasi-thermal 5.7.4
Source, thermal 4.2
Spatial coherence see "Coherence"
Spatial filter 7.2.1 7.2.4
Spatial filtering 1 7.2.4
Spatial frequency 7.2.2 7.4.4
Spatial light modulator 7.2.4
Specific detectivity see "D*"
Speckle 5.7.3 5.7.4
Speckle noise Problem 5.16
Spectral lines, table 4.2.3
Spectral mode see "Mode"
Spectral radiance 4.1.1
Spectral range see "Free spectral range"
Spectral responsivity 4.3.3
Spectral sensitivity of eye 3.1
Spectral width 5.6.1 6.2
Spectrometer 6.1
Spectrometer, grating 6.1
Spectrum 2.1.2 3.1
Spectrum analyzer 1 12.2
Spectrum of blackbodies 4.2.1
Spectrum, angular 7.3.7
Spectrum, line 4.2.3
Spectrum, visible 3.1
Specular illumination 5.7.2 7.3.2
speed of light 5.1.1 see
Speed of response 4.3.3
Spherical aberration Problem 2.10 2.2.12 2.2.13 3.5
Spherical refracting surface 2.2.1 5.5.6 see
Spiking 4.4.3 8.4.1 8.4.4
Splice 1 10.4 see "Coupler"
Spontaneous emission 4.2.3 8.1 8.2.1
Spontaneous-emission lifetime 8.2.1
Spot size 8.3.3 see "Beam
Spurious resolution 7.3.5
Square-law detector 5.1.1
Square-law profile see "Parabolic profile"
Stability diagram 8.3.4
Stability parameters 8.3.3
Star coupler 10.4.3 12.1.3
State see "Energy level"
Stefan — Boltzmann constant 4.2.1
Stefan's law 4.2.1
Step-index fiber, defined 10.3 see
Stimulated emission 8 8.1.1 8.2.1
Stops, iris diaphragms calibrated in 3.2.2 see "Field "Pupil"
Straight edge, diffraction by 5.5.3
Strip waveguide see "Optical waveguide"
Substrate, various 12.1
Sugar solution 9.2.5
Sun 4.2.1 8.5
sunglasses 8.5.1
Superpolished substrate 6.3.3
Superposition of waves 5.2
Surface-acoustic wave (SAW) 12.1.6
Surface-emitting laser 1 12.2.5
Switch, integrated-optical 12.1.6
Synch (video) 7.4.1
Target (resolution) 5.7.3
TEA laser see "Laser"
Teflon (diffuser) 4.1.5
Telecommunications Industry Association 1
Telephoto lens Problem 2.5
Telephoto lens, reverse Problem 2.5
Telescope 1 3.7 3.8.2 4.1.7
Telescope objective 2.2.12 3.8.2
Telescope, erecting 3.7.3
Telescope, Galilean 3.7.3
Telescope, resolving power of 3.8.2
Telescope, terrestrial 3.7.3
Television see "Liquid crystal" "Video "Video
Temporal coherence see "Coherence"
Tensor 9.3.1
Theoretical resolution limit see "Resolution limit"
Thermal detector see "Detector"
Thermal noise 4.3.3
Thermal source see "Source"
Thermistor 4.3.2
Thick hologram see "Hologram"
Thick lens see "Lens"
Thin film see "Integrated optics" "Interference "Quarter-wave
Thin lens see "Lens"
Third-order aberration 5.7.5
Tilted object plane Problem 2.6
time constant see "Response time"
Time domain 11.3.4 see "Optical
Titanium dioxide 6.4.1
Toe (of D vs log 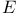 curve) 3.2.2 curve) 3.2.2
Total internal reflection 1 2.1.4 9.1.5 9.2.3
Tourmaline 9.2.4
Transducer 12.1.6
Transfer function 1 7.3.5—8
Transfer function, of film 7.3.8
Transfer, coherent 7.3.6 7.3.7
Transfer, diffraction-limited 7.3.5 7.3.6
Transfer, modulation 7.3.5
Transfer, optical 7.3.5
Transform plane 7.2.4 7.2.7 see
Transition 4.2.3
Transition, forbidden 4.2.3
Transmittance 3.2.2 5.4.2 9.1.3
Transmittance, amplitude 5.4.2 7.1 9.1.3
Transmittance, of hologram 7.1
Transmitter 12.1
Transverse backscattering 11.5.1
Transverse mode see "Mode"
Transverse scattering 11.5.1
Transverse wave 1 5.2
Trifocal 3.1
Trigger 7.4.1
Triplet level 8.4.3
Triplicity of light 1
Truncated-wave analysis 7.3.7
Tube length 3.5
Tumbling-E chart 5.7.3
Tungsten lamp 3.8.4 4.2.1 4.2.2 11.1.1
Tunneling ray 10.2.4 10.3.4 see
Turning point 10.3.1
Twisted nematic see "Liquid crystal"
Twyman — Green Interferometer 6.2.1 see
Ultramicroscope Problem 7.5
Ultrasonic light modulator see "Acousto-optic light modulator"
Ultrasonic wave 10.2.3 see
Unstable resonator 8.3.2
Useful magnification see "Magnifying power"
Useful magnifying power see "Magnifying power"
V number 10.2.5
VCSEL 12.2.5
Veiling glare 7.1.3
Velocity of light 2.1.1
Velocity of light, group 5.2.1
Velocity of light, phase 5.2 10.2.1
Verdet constant 9.4.5
Video camera 3.5 7.4.1 7.4.4
Video microscope 1 3.5 7.4.4
Vignetting 3.3 3.7.1—3
Virtual image see "Image"
Virtual object see "Object"
Visibility (of fringes) 6.2
Vision see "Eye"
Vitreous silica 11.5.4 Problem 12.1.6
Waist 8.3.3
Water, Kerr constant of 9.4.1
Wave ellipsoid 9.2.1
wave nature of light 5.1
Wave packet 4.2 5.6 8.1 8.1.1 8.2.4 see
Wave plate 7.2.2
Wave vector 10.2.1
Wave, electromagnetic 5.1.1
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



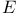 curve)
curve)