|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Matt Young — Optics and Lasers: Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Intensity, defined 5.1.1 see
Interdigitating transducer 12.1.6
Interference 1 5 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5.2 6.2 7.1.1 7.2.1 see "Diffraction" "Interferometer"
Interference by division of amplitude 5.4 5.6
Interference by division of wavefront 5.3
Interference by finite slits 5.5.2
Interference filter 1 6.4.3
Interference microscope 6.2.2 11.5.2
Interference, constructive 5.2 5.3.1 5.4.1 8.1 8.3.1 10.2
Interference, destructive 5.2 5.3.1 5.4.1
Interference, double-slit 5.3.1 5.6.2
Interference, multiple-reflection 5.4.2 8.1
Interference, multiple-slit 5.3.2 5.5.2
Interference, two-beam 5.4.1 7.1.1
Interferometer 1
Interferometer, confocal 6.3.3
Interferometer, Fabry — Perot 6.3 8.3.1
Interferometer, Fiber 6.2.2
Interferometer, Mach — Zehnder 6.2.2
Interferometer, Michelson 6.2
Interferometer, Twyman — Green 6.2.1
Interferometry 6.2 6.3
Interlace 7.4.1
Intermodal distortion 10.2.6
Internal reflection 2.1.4 9.1.5
Internal reflection, frustrated total 9.1.5 9.2.3
internal refraction 2.1.4
Inverse transform 7.2.3 see
Inverse-square law 4.1.3
Ion 4.2.3
Ion laser see "Laser"
Ion milling 12.2.4
Iris 3.1
Iris diaphragm 3.1 3.2.2 3.8.4
Irradiance 3.2.2 4.1.1 5.1.1 8.5 see
Johnson noise 4.3.3
Junction 4.2.4 4.3.1
Junction, cold 4.3.2
Junction, hot 4.3.2
Junction, pn 4.2.4
Junction, reference 4.3.2
KDP 9.3.2 9.4.2
Kernel (convolution) 7.4.3
Kerr cell 8.4.1 9.4.1 9.4.2
Kerr constant 9.4.1
Kerr effect 9.4.1
Koehler illumination 3.8.4
Krypton-ion laser see "Laser"
Lagrange invariant 2.2.11 4.1.8 7.2
Lambert's law 8.1.1
Lambertian reflector 4.1.5
Lambertian source 4.1.4 4.2.1
Lamp, arc 4.2.1
Lamp, gas-discharge 4.2.3
Lamp, tungsten 4.2.1
Lase 8
Laser 1 4.2.3 8
Laser mode 8.2.4
Laser safety 8.5
Laser wavelengths (table) 8.4.7
Laser, argon-ion 8.2.4 8.4.5
Laser, carbon-dioxide 8.4.6
Laser, classes I-IV 8.5
Laser, coherence of 5.6 5.6.3 8.3.5
Laser, diode 8.4.2
Laser, distributed feedback 12.1.4
Laser, dye 8.4.3
Laser, excimer 8.4.7
Laser, four-level 8.4.2
Laser, gallium arsenide 12.1.4
Laser, gas 8.4.7 see
Laser, glass 8.4.2
Laser, HCN 8.4.7
Laser, helium-cadmium 8.4.7
Laser, helium-neon 8.3.5 8.4.2 8.4.4 8.4.7 9.1.2
Laser, hydrogen- and deuterium-fluoride 8.4.7
Laser, injection 8.4.8
Laser, ion 8.4.5
Laser, junction 8.4.8
Laser, krypton-ion 8.4.5
Laser, laser-pumped 8.4.3
Laser, mode-locked 8.2.4 8.4.2 8.4.3 8.4.5 9.4.3
Laser, multimode 8.3.2
Laser, neodymium 8.2.4 8.4.2
Laser, nitrogen 8.4.7
Laser, optically pumped 8.2 8.2.3 8.2.4 8.4.3
Laser, organic-dye 8.4.3
Laser, output power of 8.2.2
Laser, Q-switched 8.2.3 8.4.1 8.4.2 8.4.6 9.4.2
Laser, quasicontinuous 8.4.2
Laser, ruby 8.2.2 8.2.3 8.4.1
Laser, semiconductor 8.4.2 8.4.8 10.1 12.1 12.1.4 see
Laser, single-mode 5.6.3 8.3.2 8.4.4
Laser, surface-emitting 12.2.5
Laser, TEA 8.4.6
Laser, three-level 8.2
Laser, titanium:sapphire 8.4.3
Laser, transversely excited 8.4.6 8.4.7
Laser, tunable 8.4.3
Laser, vertical cavity 12.2.5
Laser, water-vapor 8.4.7
Laser, YAG 8.4.2
Lasers, classification of 8.5
latent image 3.2.1
Launching conditions 1 11.1 11.3.4
Launching conditions, beam-optics 11.1.1
Law of reflection 2.1.2 see
Law of refraction 2.1.1 see
Lead glass 9.4.5
Lead sulfide 4.3.1 4.3.3
Lead telluride 4.3.1
Leakage current 4.3.3
Leaky mode 10.2.4
Leaky ray 1 10.2.4 10.3.4
Leaky ray in near-field scanning 11.5.3
Lens 2.2.4 2.2.5 2.2.7
Lens aberrations 2.2.12
Lens equation 1 2.2.4 5.5.3
Lens equation and thick lenses 2.2.7
Lens equation, Newton's form of 2.2.10
Lens of eye 3.1 8.5
Lens, aberration-limited 3.8.1
Lens, Barlow Problem 2.5
Lens, camera 2.2.11 2.2.12
Lens, close-up 2.2.12
Lens, collimating 2.2.12
Lens, concave 2.2.5
Lens, convex 2.2.5
Lens, copying 2.2.12
Lens, diffraction 12.2.4
Lens, enlarging 2.2.12
Lens, erecting 3.7.3
Lens, Fraunhofer diffraction in focal plane of 5.5
Lens, geodesic 12.2.3
Lens, graded-index 12.2.2
Lens, hand 3.4
Lens, high-aperture 2.2.12
Lens, Luneburg 12.2.2
Lens, macro 2.2.12
Lens, meniscus 2.2.5
Lens, mode-index 12.2.1 12.2.2
Lens, negative 2.2.5 3.1
Lens, photographic 2.2.12
Lens, planar 12.2
Lens, plano-convex 2.2.12
Lens, positive 2.2.5 3.1
Lens, specialized 2.2.12
Lens, telephoto Problem 2.5
Lens, thick 2.2.7
Lens, thin 2.2.4
| Lens, two thin, in contact 2.2.4
Lens, waveguide 12.2
Lens-maker's formula 2.2.4
Lifetime 8.2.1
Lifetime, cavity 8.2.3
Light source see "Source"
Light-Emitting Diode 4.2.4 8.4.8 10.1
Limit of resolution see "Resolution limit"
Limited phase space see "70-70 excitation"
Limiting aperture see "Aperture stop"
Line radiation see "Line source"
Line source 4.2 4.2.3
Linewidth standard 7.4.5
Linewidth, instrumental 6.1.2 6.3.1 6.3.2
Liquid crystal 9.2.6
Liquid crystal television 9.2.6
Liquid crystal, ferroelectric 9.2.6
Liquid crystal, nematic 9.2.6
Liquid crystal, smectic 9.2.6
Lithium niobate 9.4.2
Lloyd's mirror Problem 5.3
Local Area Network 11.3.1 12.2.5
Local numerical aperture 10.3.2 11.5.5
Longitudinal magnification 2.2.9
Lorentzian function 12.2.4
Lumen 4.1.2
Luminance 1 4.1.2 4.1.8
Luminance of aerial image 4.1.8
Luminous efficacy 4.1.2
Luminous efficiency of eye 4.1.2
Luminous energy 4.1.2
Luminous flux 4.1.2
Luminous intensity 4.1.2
Luminous power 1 4.1.2 see
Luneburg lens 12.2.2
Lux 4.1.2
Mach — Zehnder interferometer 6.2.2 12.1.6
Macula lutea 3.1
Macular degeneration 8.5.1
Magnesium fluoride (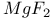 ) 6.4.1 ) 6.4.1
Magnetic-field vector 9
Magneto-optics 9.4.5
Magnification 2.2.9 3.5
Magnification, empty 3.8.3 3.8.4
Magnification, longitudinal 2.2.9
Magnification, useful 3.5 3.8.3 3.8.4
Magnifier, simple see "Magnifying glass"
Magnifying glass 3.4
Magnifying power 3.4 3.5 3.7 3.7.1 3.8.2—4
Magnifying power, empty 3.8.2
Magnifying power, useful 3.5 3.7.1 3.8.2—4
Malus's Law 9.2.2
Mandrel wrap 11.1.1 11.4
Matched filter 7.2.6 7.4.1 7.4.3
Mechanical tube length 3.5
Mercury cadmium telluride 4.3.1
Meridional ray 10.2.4
MgO (diffuser) 4.1.5
MICA 9.2.1
Michelson interferometer 6.2 see
Michelson stellar interferometer Problem 5.14
Microbend 10.3.5
Microscope 1 3.5 7.3.3
Microscope condenser 3.8.4
Microscope objective 3.5 3.8.3 7.2.1 7.4.4
Microscope, Abbe theory of 7.2.1
Microscope, coherence of 5.6.4
Microscope, impulse response of 7.3.3
Microscope, interference 6.2.2
Microscope, magnifying power of 3.5
Microscope, resolving power of 3.8.3 3.8.4
Microscope, scanning confocal 3.6 7.3.3
Microscope, simple see "Magnifying glass"
Microscope, video 3.5 7.4.4
Microscopy 3.5 7.2.1 7.4.4
Microscopy, Abbe theory of 7.2.1
Microscopy, phase 7.2.1
Microscopy, phase-contrast 7.2.5
Microscopy, video 3.5
Mirror 2.1.3 2.2.6
Mirror, concave 2.2.6
Mirror, convex 2.2.6
Mirror, focal length of 2.2.6
Mirror, multilayer 1 6.4.2
Mirror, radius of curvature of 2.2.6
Mirror, spherical 2.2.6
Mirror, thick Problem 2—4
Misalignment (of fibers) see "Connector"
Missing order 5.5.2 6.1.1
MODE 1 8.3.1 8.3.5
Mode coupling 10.3.5
Mode field diameter 11.7
Mode filter 11.1.2 11.4
Mode in circular waveguide 10.2.4
Mode in optical waveguide 10.2 10.4.2
Mode matching 8.3.3
Mode stripper 11.1.3
Mode unbound 10.2
Mode, 00 8.3.2 8.3.3 8.4.4
Mode, air 12.2.4
Mode, axial 8.3.1
Mode, bound 10.2
Mode, number of, in waveguide 10.2.5
Mode, single 8.3.2
Mode, single axial and transverse 8.3.2
Mode, spectral 8.2.4 8.3.1
Mode, substrate 12.2.4
Mode, transverse 8.3.2
Mode-index lens 12.2.1
Mode-locked laser see "Laser"
Modulation of film 7.3.8
Modulation transfer function 7.3.5
Modulator 8.4.5 9.4.4 12.1.6
Modulator, acousto-optic 9.4.4 12.1.6
Modulator, electro-optic 9.4.3 12.1.6
Modulator, loss 8.4.5
Modulator, traveling-wave 12.1.6
Monochromatic radiation 4.2.3
Monochromator 6.1
Monolithic devices 12.1
Monomode waveguide 10.2.6 see
Motion-picture projector 3.3
MTF 7.3.5 see
MTF of film 7.3.8
Multilayer mirrors 1 6.3
multimode fiber see "Optical fiber" "Optical "Optical
Myopia 3.1
Nd:glass laser see "Laser"
Nd:YAG laser see "Laser"
Near point 3.1 3.4
Near-field diffraction 1 5.5.4 see
Near-field scanning 1 3.9 11.5.3
Near-field scanning in core-diameter measurements 1 11.5.5
Near-field scanning of single-mode fiber 11.5.3
Near-field scanning, leaky rays in 11.5.3
Near-field scanning, refracted see "Refracted-ray method"
Near-sightedness 3.1
Negative 3.2.1
Neodymium laser see "Laser"
NEP 4.3.3
Neural inhibition 3.1
Newton's form of the lens equation 2.2.10
Nicol prism 9.2.3
Night glasses 3.7.1
Nipkow disk 3.6.1
Nitrobenzene 9.4.1
Nodal point 2.2.8
Nodal slide 2.2.8
Noise 7.4.1
Noise equivalent power (NEP) 4.3.3
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 )
)