|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee W.C.Y. Ч Mobile Communications Engineering |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
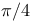 -DQPSK, constant envelope modulation scheme 298Ч299 -DQPSK, constant envelope modulation scheme 298Ч299
Adaptive antenna nulling 668Ч670
Adaptive delta modulation (ADM) 508
Adaptive equalizer 96
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN), channels 562Ч563
Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN), channels, Gaussian process 563Ч564
Adjacent-channel interference, problem of 431Ч432
Adjacent-channel interference, problem of, in Eayleigh-fading environment 434Ч435
Adjacent-channel interference, problem of, in nonfading environment 432Ч433
Adjacent-channel interference, problem of, out-of-band type 436
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) 2
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), FM frequency-reuse system used by 320Ч321
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), service features of, radio enhancement techniques 7Ч11
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), service features of, switch planning, and accommodation of expected growth 11Ч14
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS), trial of, by Bell Telephone System 5
Air jammer 651
Alien-interference, tolerance requirement of 550Ч556
ALOHA, comparison of thoughput vs.traffic load for 534
ALOHA, protocols of four versions of 533
Alternate-pilot-signal method, of feed-forward combining 384
AM-PM conversion, intermodulation interference problem of, feed-forward amplification 437Ч438
AM-PM conversion, intermodulation interference problem of, linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC) 438Ч440
Amplitude-modulated (AM) signaling, characteristics of, vs.frequency-modulated (FM) signaling 271
AMSC, GEO satellite system 541 544
Analog modulation, FM 257
Analog modulation, SSB 324Ч326
Angle arrival, wave, measured data 133Ч134
Angle arrival, wave, method of obtaining 135Ч139
Angle arrival, wave, model 134 135 138
Angle diversity, at base station, in-time angular diversity 336
Angle diversity, at base station, out-of-time angular diversity 336Ч337
Angle diversity, at mobile unit 337Ч339
Angle diversity, vectors 338
Angle spreading, with antenna height 566 597Ч601
Antenna design, effects of, on EF design and propagation 177Ч182
Antenna directivity, effects of, on EF design and propagation 182Ч185
Antenna downtilt 587
Antenna downtilt, electronic 587Ч589
Antenna downtilt, mechanical 589Ч590
Antenna downtilt, notch effect 590Ч591
Antenna downtilt, tilting antenna effect 590Ч592
Antenna height, angle spread with, and its application 597Ч601
Antenna height, effects of, on related mobile radio environment 565Ч566
Antenna height, gain 572Ч573
Antenna height, problem/solution examples of 333Ч334
Antenna height, spacing vs.correlation 331
Antenna pattern, ripple effects of 185Ч190
Approximation model, of time-delay distribution 341
Aries, big LEO satellite system 543 544
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) 3
AT&T, role of, in history of mobile-radio communications 4
Average in nonstationary environment 612Ч613
Average in stationary environment 615Ч616
Average real-time 610Ч611
B-ISDN (broadband ISDN) 3
Band A (or block A; 20-MHz band), allocated to nonwireline operators (RCC) 4
Band A (or block A; 20-MHz band), frequency management for 8 15
Band B (or block B; 20-MHz band), allocated to wireline operators (telephone companies) 4
Band B (or block B; 20-MHz band), frequency management for 8 16
Bandwidth-limited systems 581Ч582
BayesТ Theorem 68
BCH code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Bell Lab Research Division 13, role of, in history of mobile radio 564
Bell Telephone Laboratories, role of, in history of mobile-radio communications 3
Bell Telephone System, and trial of Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) 5
Biased time averages 62
Big LEO 543Ч544
Binary PCM waveforms, types of 401
Binomial distribution 75Ч76
Bit synchronization 409Ч411
Bit-error analysis, based on correlated signals, fast-fading condition 476Ч479
Bit-error analysis, based on correlated signals, slow-fading condition 479
Bit-error analysis, based on M-branch maximal-ratio combiner 469 470
Bit-error rate (BER) 586Ч587
Bit-stream waveform analysis, binary PCM waveforms, types of 401
Bit-stream waveform analysis, duobinary-waveform signaling 406Ч409
Bit-stream waveform analysis, power spectral density of random data sequence 400Ч402
Bit-stream waveform analysis, power spectral density of random data sequence, for Manchester-code-waveform signaling 403Ч404
Bit-stream waveform analysis, power spectral density of random data sequence, for NRZ baseband signaling 402 403
Bit-stream waveform analysis, time-delay-spread dependency factor 399Ч400
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, cosine-waveform 404 405
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, exponential-waveform 404 405
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, Gaussian-waveform 405 406
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, raised-cosine-waveform 404 405
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, squared-waveform 404 405
Bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping, pulse-shape types in, triangular-waveform 404 405
Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) 3
Broadband packet switching 3
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of 18
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, B-CDMA 17
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, CDMA-1900 17
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, DCS-1900 17
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, NA-TDMA-1900 17
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, Omnipoint 17
Broadband PCS (personal communication service), for cellular-like standard systems, types of, PACS-1900 17
Building-block approach, of microcell propagation prediction 585Ч586
Busy-tone multiple access (BTMA) 538
Capacity of cellular 2 541
Capacity of PCS 17Ч18
Capacity, radio 540 637Ч638
Capture division packet access (CDPA) 539
Carrier-sense multiple access (CSMA) 535Ч536
Carrier-sense multiple access (CSMA), Уlisten-before-talkingФ protocol 535
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) 538
Carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR), analysis method, for multibranched antenna arrays 389Ч390
Carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR), in selective diversity combining 351 352
CB radio, compared to mobile radiotele phone 6
Cells, basic features of 8 9
Cells, tailoring plan of, to severe density gradient 12
Cellular digital packet data (CDPD), packet radio system, introduced 2
Channel capacity 530 605
Channel capacity, in Gaussian environment 530 605Ч606
Channel capacity, in Rayleigh environment 606Ч610
Channels (two-way), distribution matrix arrangement of 8
Channels (two-way), switch planning 11Ч14
Circuit merit (CM), levels of, in voice quality analysis 505
Click-noise phenomenon 259Ч263 283
Cochannel cells, polar coordination of mobile unit related to 549
Cochannel interference 422Ч423
Cochannel interference, configuration of 517
Cochannel interference, in Eayleigh-fading environment 428Ч430
Cochannel interference, in nonfading environment 423Ч428
Cochannel interference, in SDMA system 548Ч549 550
Cochannel interference, overcoming problems of 10
Code division multiple access (CDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA TDMA, and CDMA, in C/I < 1 systems (CDMA) 521
Code division multiple access (CDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA TDMA, and CDMA, in C/I < 1 systems (FDMA and TDMA) 520Ч521
Code division multiple access (CDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA TDMA, and CDMA, where CDMA is greater 521Ч523
Code division multiple access (CDMA), digital cellular standard 17
Code division multiple access (CDMA), interference in system of 519
Code division multiple access (CDMA), multiple-access scheme on physical channel 511
Code division multiple access (CDMA), system coverage and capacity, equations for determination of 525Ч527
Coherence bandwidth 52Ч53
Coherent binary AM (PSK), nonfading digital modulation system 287Ч288
Coherent FSK, nonfading digital modulation system 289
Combined signal diversity 569Ч572
Combining technology, equal-gain 369Ч380
Combining technology, equal-gain, calculation of probability density function 369Ч370
Combining technology, equal-gain, cumulative probability distribution 370 371 372
Combining technology, equal-gain, finding level-crossing rate (LCE) 373Ч380
Combining technology, feed-combining 380Ч381
Combining technology, feed-forward 381Ч384
Combining technology, feedback (Granlund combiner) 384Ч386
Combining technology, for multibranched antenna arrays 386Ч389
Combining technology, for multibranched antenna arrays, CNE analysis method of 389Ч390
Combining technology, for multibranched antenna arrays, cumulative-distribution method of 390
Combining technology, macroscopic diversity techniques, techniques for combining long-term-fading signals 348
Combining technology, macroscopic diversity techniques, techniques for improving average SNE by selective combining 348Ч349
Combining technology, macroscopic diversity techniques, techniques for selective diversity combining 347Ч348 349
Combining technology, maximal-ratio 360Ч369
Combining technology, microscopic diversity, techniques for 349Ч350
| Combining technology, predetection and postdetection 350Ч351
Combining technology, reduction of time delay spread through 391Ч392
Combining technology, selective diversity 351Ч353 357 358
Combining technology, selective diversity, four special cases for 353Ч357
Combining technology, switched 350 357Ч359
Commercial mobile-radiotelephone communications, design considerations of, vs.military 17Ч18 19
confidence intervals 89Ч90
Constant envelope modulation schemes 294Ч295
Constant envelope modulation schemes, GMSK (Gaussian filtered minimum shift keying) 300Ч303
Constant envelope modulation schemes, OQPSK (offset quadrature phase-shift keying) 296Ч297
Constant envelope modulation schemes, OQPSK (offset quadrature phase-shift keying), 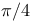 -DQPSK (differential quadrature phase-shift keying) 298Ч299 -DQPSK (differential quadrature phase-shift keying) 298Ч299
Constant envelope modulation schemes, QPSK (quadrature phase-shift keying) 295Ч296
Constant envelope modulation schemes, QPSK (quadrature phase-shift keying), subcarrier QPSK 299
Continuous spectral density 84Ч85
Continuous-wave (CW) radio signal 41
Convolutional code, convolutional encoder 458 459
Convolutional code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Convolutional code, tree diagram 460 461
Convolutional code, trellis diagram 460 462
Convolutional code, Viterbi convolutional decoding algorithm 462
Correlation bandwidth see УCoherence bandwidthФ
Correlation functions, autocorrelation 82
Correlation functions, cross-correlation 83Ч84
Correlation functions, random process 81Ч82
Correlation functions, random variable 81
Correlator receivers in spread spectrum modulation 323
Correlator receivers, despreading process 321Ч323
Cosine-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 404 405
Covariance of random variables 242Ч243
Covariance, matrix 248Ч249
Coverage, area of coverage 8Ч10
Coverage, cell boundary 9 553Ч554
Cpd curves, of lognormal fading 451
Cumulative probability distribution (CPD) 63
Cumulative probability distribution (CPD), in equal-gain combining 370 371 372
Cumulative probability distribution (CPD), method, for multibranched antenna arrays 390
Cyclic redundancy check (CEC) 457Ч458
Data transmission, via cellular systems 623
Data transmission, via cellular systems, analysis/summary of 629Ч632
Data transmission, via cellular systems, theoretical derivations of 623Ч629
Data-sense multiple access (DSMA) 538
Deinterleaving, illustrated 587
Delay spread 47Ч51
Delay spread, delay envelopes 48 49
Delay spread, distribution of 50 51
Delay spread, illustrated 47
Delay spread, in VHF 51Ч52
Delay spread, method of measurement 49Ч51
Delay-signal combining, as feed-forward combining technology 382Ч383
Delta modulation (DM) 508
Despreading process 321Ч323
Detroit Police Department, role of, in history of mobile-radio communications 3
Differential phase-shift keying ( DPSK), nonfading digital modulation system 290Ч292
Differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) 508
Diffraction loss, double knife-edge diffraction 143 144 145 146Ч147
Diffraction loss, over rounded hills 147Ч149
Diffuse reflection 29Ч31
Digital cellular 2
Digital cellular, standards of, CDMA 17
Digital cellular, standards of, North American TDMA 17
Digital European Cordless Telephone (DECT) 2
Digital FM (FSK) system 480Ч481
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, 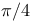 -QPSK 298 -QPSK 298
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, coherent binary AM (PSK), fading case, average error rate in 293
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, coherent binary AM (PSK), nonfading case 287Ч288
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, coherent FSK, fading case, average error rate in 293
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, coherent FSK, nonfading case 289
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, constant envelope modulation 294Ч303
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, differential PSK (DPSK), fading case, average error rate in 293
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, differential PSK (DPSK), nonfading case 290
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, FM with discrimination, fading case, average error rate in 293
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, FM with discrimination, nonfading case 288Ч289
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, GMSK 300Ч303
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, linear modulation 438Ч440
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, MSK 300
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, noncoherent FSK, fading case, average error rate in 293
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, noncoherent FSK, nonfading case 289Ч290
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, nonconstant envelope modulation 303Ч304
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, OQPSK 296
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, QAM 304
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, systems compared 294
Digital modulation, detection process systems of, TCM 463
Direct sequence (DS) signals 321Ч323
Direct-sequence-modulated system 309
Dispatching systems 1
Distance-dependency factors, in mobile radio-system functional design 397Ч398
Diversity gain 573
Diversity receivers, types of postdetection 351
Diversity receivers, types of predetection 350
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, angle, at base station 336Ч337
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, angle, at mobile unit 337Ч339
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, field-component 334Ч335
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, frequency 339Ч343
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, frequency, models of time-delay distribution 340Ч341
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, macroscopic 327Ч329
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, microscopic 329
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, polarization 335
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, polarization, at base station 336
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, receiving diversity 571Ч572
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, reducing delay spread 391Ч392
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, reducing signal margin 561
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, space, at base station 330Ч334
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, space, at mobile unit 329Ч330
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, time 343Ч344
Diversity schemes, and functional design of mobile-radio systems, transmission diversity 327
Doppler shift frequency 37 244 259
DPSK system 479Ч480
Dropped call rate 619Ч622
Duobinary-waveform signaling 406Ч409
Electronic counter-countermeasure (ECCM) technology 652Ч653
Ellipso, big LEO satellite system 543 544
Encoder trellis diagram 462
Energy-density antenna 193 335
Ensemble averages see УCorrelation functionsФ УStatistical
Environmental Sciences Services Administration (ESSA) 161
Equal-gain combining 350 369
Equal-gain combining, calculation of probability density function 369Ч370
Equal-gain combining, cumulative probability distribution 370 371 372
Equal-gain combining, finding level-crossing rate (LCE), at base station 373Ч377
Equal-gain combining, finding level-crossing rate (LCE), at mobile site 377Ч380
equalizers 93Ч97
Equalizers, adaptive 96
Equalizers, mean-square error (MSE) algorithm 95Ч96
Equivalent performance criteria 450
Ergodic processes 62Ч63
Error correction 455Ч456
Error detection 456Ч457
Error detection, cyclic redundancy check (CEC) 457Ч458
Error probability 90Ч92
Exponential-distribution model, of time-delay distribution 341
Exponential-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 404 405
Fading signals, fast-fading condition 468 471
Fading signals, long-term, determinants of 328
Fading signals, short-term fading 203Ч208
Fading signals, uncorrelated 328
Federal Communications Commission (FCC), allocation of frequencies by, for broadband PCS 17 18
Federal Communications Commission (FCC), allocation of frequencies by, for domestic public mobile-radio land use 4 (table)
Federal Communications Commission (FCC), allocation of frequencies by, for mobile telephone use 5 (tabled 7)
Federal Communications Commission (FCC), allocation of frequencies by, for narrowband PCS 17 18
Federal Communications Commission (FCC), role of, in history of mobile-radio communications 3Ч5
Feed-combining techniques 380Ч381
Feed-forward combining, alternate-pilot-signal method 384
Feed-forward combining, delayed-signal 382Ч383
Feed-forward combining, use of nonpilot signal in 381Ч382
Feed-forward combining, use of pilot signal with communication signal in 383Ч384
Feedback combining 384Ч386
Field strength, effects on prediction of 159Ч160
Field strength, effects on prediction of, attenuation within tunnels 162
Field strength, effects on prediction of, buildings and structures 163
Field strength, effects on prediction of, foliage 160Ч162
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



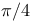 -DQPSK, constant envelope modulation scheme
-DQPSK, constant envelope modulation scheme