|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee W.C.Y. Ч Mobile Communications Engineering |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Field strength, effects on prediction of, relationship between path loss and local mean 163
Field strength, effects on prediction of, street orientation 160
Field strength, effects on prediction of, tunnel, loss due to 162
Field-component diversity 334Ч335
Fire code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
FM frequency-reuse system 319
Fourier transform 67
Frame (word) error rate (FEE) 586Ч587
Frame synchronization 412Ч414
Free-space path loss 162
Frequency diversity, coherence bandwidth 342
Frequency diversity, correlation vs.frequency 341Ч342
Frequency diversity, statistical dependence on frequency 339Ч340
Frequency diversity, statistical dependence on frequency, approximation model of time-delay distribution 341
Frequency diversity, statistical dependence on frequency, exponential-distribution model of time-delay distribution 341
Frequency diversity, statistical dependence on frequency, Maxwell-distribution model of time-delay distribution 340
Frequency diversity, two frequencies with coherent bandwidth 343
Frequency diversity, two frequencies with noncoherent bandwidth 342Ч343
Frequency division duplexing (FDD) 571 582
Frequency division multiple access (FDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, in C/I < 1 systems (CDMA) 521
Frequency division multiple access (FDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, in C/I < 1 systems (FDMA and TDMA) 520Ч521
Frequency division multiple access (FDMA), where CDMA is greater 521Ч523
Frequency hopping (FH) system 310 653Ч656
Frequency hopping (FH) system, fast hopping 656
Frequency hopping (FH) system, slow hopping 654
Frequency modulation (FM) with discrimination, nonfading digital modulation system 288Ч289
Frequency modulation (FM), advantages of, for mobile radio 271Ч272
Frequency modulation (FM), advantages of, for mobile radio, nonfading case 273Ч279
Frequency modulation (FM), advantages of, for mobile radio, Rayleigh-fading case 279Ч286
Frequency reuse factor 319Ч320
Frequency reuse factor, K factor 319
Frequency-correlation function 482
Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems 310Ч312
Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, error rate and system efficiency of, with respect to, multipath-fading environments 318Ч319
Frequency-hopped Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, error rate and system efficiency of, differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, error rate and system efficiency of, with respect to, multiple-base-station intercell interference 317Ч318
Frequency-hopped Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, signal and noise representation in 312Ч313
Frequency-hopped Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, spectrum efficiency/number of channels per cell 319Ч321
Frequency-hopped Frequency-hopped differential phase-shift keying (FH-DPSK) systems, with respect to, single-active-base-station intracell interference 314Ч317
Frequency-selective fading 481Ч482
Fresnel integrals 141
Fresnel zone, first, reflections/scattering within 115 116
Fresnel zone, first, reflections/scattering within, microcell prediction formula 154Ч155
Future public land mobile telecommunication system (FPLMTS) 3
Gain, coding 454
Gain, diversity 569Ч570 572Ч575
Gain, nonreal 524
Gain, processing 504 523Ч524 654
Gain, real 524
Gaussian distribution 71
Gaussian filtered minimum shift keying (GMSK), constant envelope modulated scheme 300Ч303
Gaussian process 563Ч564
Gaussian-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 405 406
Geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) satellites 541 542
Geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) satellites, AMSC 541 543 544
Geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) satellites, Omni TRACS 541
Geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) satellites, Spaceway 543 544
Gilbert, E.N., statistical radio model of 564Ч565
Global positioning satellites (GPS) 24
Global positioning satellites (GPS), satellite MEO system 541Ч542
Global System Mobile (GSM), Digital Cellular in Europe 2
Global System Mobile (GSM), Digital Cellular in Europe, handoff 619Ч622
Globalstar, big LEO satellite system 543 544 545Ч546 547
Golay code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Granlund combiner, feedback-combining technique 384Ч386
Ground jammer 651
Hamming code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Handoff 10 13 619Ч622
Handoff, break before make 622
Handoff, intercell 11
Handoff, intracell 11
Handoff, make before break 621 622
Handoff, mobile-assisted 620
Handoff, soft handoff 619
High-gain antennas, effects of 190 191
Horizontal antenna separation, vs.vertical antenna separation 574 575 576
Human-made effect, and interpretation of path loss 151Ч152
Human-made noise, at different frequencies 44Ч46
Human-made noise, categories of 43 44
Human-made noise, characteristics of 43Ч46
HuygenТs principle, and properties of diffuse reflection 29Ч30
Idle signal multiple access (ISMA) 538
Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS) 2
Impulse response measurements 92Ч93
Inbuilding prediction model 157Ч158
Incoherent matched-filter receiver, error probability for 482 483Ч486
Inmarsat P, MEO global mobile satellite system 541Ч543 544
Instantaneous amplitude probability, component of mobile-telephone voice characteristics 495Ч496
Interference, adjacent-channel 431Ч432
Interference, adjacent-channel, in nonfading environment 432Ч433
Interference, adjacent-channel, in Rayleigh-fading environment 434Ч435
Interference, adjacent-channel, out-of-bound type of 436
Interference, cochannel 422Ч423
Interference, cochannel, in nonfading environment 423Ч428
Interference, cochannel, in Rayleigh-fading environment 434Ч435
Interference, effects of 421
Interference, intermodulation (IM), problem sources of, AM-PM conversion 437Ч441
Interference, intermodulation (IM), problem sources of, antenna terminal mismatch 441
Interference, intermodulation (IM), problem sources of, colocated transmitting antennas 441Ч442
Interference, intersymbol, and degradation effects of time-delay spread in signal timing 444Ч445
Interference, near-end to far-end ratio 436Ч437
Interference-limited onvironment, and evaluation of spectrum efficiency, in C/I < 1 systems 518Ч520
Interference-limited onvironment, and evaluation of spectrum efficiency, in C/I > 1 systems 516Ч518
Interleaving, illustrated 587
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of 421 592Ч593
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, AM-PM conversion, feed-forward amplification 437Ч438
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, AM-PM conversion, linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC) 438Ч440
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, antenna terminal mismatch 441
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, caused by front-end overload 592 593
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, colocated transmitting antennas 441Ч442
Intermodulation (IM) interference, problem sources of, means of reducing IM 592Ч593
Intersymbol interference (ISI), problem of 442Ч444 575
Intersymbol interference (ISI), problem of, and degradation effects of time-delay spread on signal timing 444Ч445
Iridium, big LEO satellite system 543 544
Irreducible error rate, due to frequency-selective fading 481Ч482
Irreducible error rate, due to random FM, digital FM (FSK) system 480Ч481
Irreducible error rate, due to random FM, DPSK system 479Ч480
IS-136 (TDMA), digital cellular standard 2
IS-95 (CDMA), digital cellular standard 2
KirchhoffТs theory, on diffraction 140Ч141
Lee models 147Ч159
Lee models, inbuilding 157Ч159
Lee models, macrocell 149Ч153
Lee models, microcell 153Ч155
LeeТs device (real-time averages in non-stationary environment) 614Ч615 616
LeeТs device (real-time averages in non-stationary environment), in calculations of radio communication environment 616Ч619
Level-crossing rate (LCE) 77Ч80 373Ч374
Level-crossing rate (LCE), at base station 373Ч377
Level-crossing rate (LCE), at mobile site 377Ч380
Linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC) 438Ч440
Linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC), feed-forward 437Ч438
Linear amplification with nonlinear components (LINC), inverse-sine modulation 439Ч440
Linear block code, components of coding gain 454
Linear block code, components of coding strength 455
Linear block code, components of cyclic redundancy check (CRC) 457Ч458
Linear block code, components of erasure correction 456Ч457
Linear block code, components of error detection/error correction 455Ч456
Linear block code, components of parity-check matrix 453Ч454
Linear block code, components of single-parity check code 452Ч453
Linear predictive coding (LPC) 508
Linear pulse-code modulation (PCM) 508
Local mean prediction, Lee macrocell model 149Ч153
Local mean prediction, vs.path loss prediction 566Ч567
Lognormal distribution 74Ч75
Long-term fading 561
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites 541 542
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, big LEO systems, Aries 543 544
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, big LEO systems, Ellipso 543 544
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, big LEO systems, Globalstar 543 544
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, big LEO systems, Iridium 543 544
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, big LEO systems, Teledesic 543 544
| Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, little LEO system, OrbComm 543 544
Low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites, operation, description/concept of 543 545Ч547
M-branch maximal-ratio combiner, in bit-error analysis 469 470
Macrocell model (Lee) 149Ч151 153
Macroscopic diversity 10
Macroscopic diversity, combining techniques for 349Ч350
Macroscopic diversity, scheme, applied on different-sited antennas 327Ч329
Majority-voting processes, in reduction of word-error rate 473
Majority-voting processes, in reduction of word-error rate, fast-fading condition 473Ч475
Majority-voting processes, in reduction of word-error rate, slow-fading condition 475Ч476
Manchester-code-waveform signaling 403Ч404
Marconi, Marchese Guglielmo 3
Mathematical Theory of Communication, The (Shannon and Weaver) 605
Maximal-ratio combining 350 360Ч369
Maximal-ratio combining, performance curves for 367 368
Maxwell-distribution model, of time-delay distribution 340
Mean opinion score (MOS), evaluation criterion for speech coders/system quality 506
Mean square modulation index 425
Mean-square error (MSE) algorithm 95Ч96
Metroliner telephone 2
Microcell model (Lee) 153Ч156
Microscopic diversity 10Ч11
Microscopic diversity, combining techniques for 347Ч349
Microscopic diversity, schemes, applied on cosited antennas 329
Midearth orbit (MEO) satellites 541 542
Midearth orbit (MEO) satellites, Inmarsat P 541Ч543 544
Midearth orbit (MEO) satellites, Odyssey 541Ч543 544
Military mobile communications, adaptive antenna nulling 668Ч670
Military mobile communications, coding schemes used in 656Ч659
Military mobile communications, combining technologies (in jammingv environment) used in 659Ч670
Military mobile communications, in jamming environment, electronic counter-countermeasure (ECCM) technology 652Ч653
Military mobile communications, in jamming environment, jammer strategy 651Ч652
Military mobile communications, use of frequency hopping (FH) spread-spectrum scheme in 653Ч656
Minimum tone separation 301Ч302
Mobile Broadband Systems, as FPLMTS (future public land mobile telecommunication system) 3
Mobile coverage 582Ч583
Mobile location 594
Mobile location, mobile-unit-based finding of, dead-reckoning system 596
Mobile location, mobile-unit-based finding of, GPS (Global Positioning Satellite) 595
Mobile location, mobile-unit-based finding of, Loren C 535
Mobile location, mobile-unit-based finding of, sign posts 596
Mobile location, station (cell-site based) finding 594Ч595
Mobile location, station (cell-site based) finding, angle arrival 594
Mobile location, station (cell-site based) finding, time arrival 594
Mobile location, station (cell-site based) finding, triangulation 594
Mobile radio environment, causes for 560
Mobile radio environment, causes of signal reception 562
Mobile radio environment, conditions for forming 560
Mobile radio environment, independence of electric and magnetic fields in 191Ч195
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, antenna height 561
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, area-dependent path loss 561
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, dispersive medium 561Ч562
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, excessive path loss 561
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, long-term fading 561
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, rough-terrain criterion 562
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, signal fading 561
Mobile radio environment, signal impacted by.factors/phenomena related to, signal strength 561
Mobile radiotelephone, advantages of, over CB radio 6
Mobile Satellite Service (MSS), satellite technologies of, compared 542 543 544
Mobile Satellite Service (MSS), satellite technologies of, GEO (geosynchronous earth orbit) satellites 541Ч544
Mobile Satellite Service (MSS), satellite technologies of, LEO (low-earth orbit) satellites 541Ч547
Mobile Satellite Service (MSS), satellite technologies of, MEO (midearth orbit) satellites 541Ч544
Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) 2
Mobile-assisted handoff (MAHO) 620
Mobile-radio communications, cellular network planning, AMPS service features 7Ч14
Mobile-radio communications, cellular network planning, digital cellular 17
Mobile-radio communications, cellular network planning, extended spectrum 14Ч16
Mobile-radio communications, cellular network planning, PCS (Personal Communication Service) 17
Mobile-radio communications, commercial vs.military 17Ч19
Mobile-radio communications, first 100 years of, historical survey of 1Ч6
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, coherence bandwidth 52Ч53
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, communication medium 21Ч26
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, delay spread 47Ч51
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, human-made noise 43Ч46
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, multipath fading 31Ч40
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, propagation-path loss 26Ч31
Mobile-radio communications, signal environment, factors in, thermal noise 40Ч43
Mobile-radio systems, Digital Cellular 2 17
Mobile-radio systems, dispatching systems 1
Mobile-radio systems, fading model of 564Ч565
Mobile-radio systems, FDD system 571 582
Mobile-radio systems, Mobile Broadband Systems 3
Mobile-radio systems, packet radios 2
Mobile-radio systems, PSC (personal communication service) 2 17 541
Mobile-radio systems, radio paging systems 1
Mobile-radio systems, radiophones (walkie-talkies) 1
Mobile-radio systems, radiotelephones (mobile phones) 2
Mobile-radio systems, TDD (Time Division Duplexing) systems 2Ч3
Mobile-telephone switching office (MTSO) 10 11Ч14
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain 133Ч135
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, diffraction loss 140Ч142 146Ч147
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, double knife-edge diffraction 143 144 145
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, first-reflected-wave conditions, absent 138Ч140
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, LeeТs models 147Ч159
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, second-reflected-wave conditions, absent 137Ч138
Model analysis, and prediction of path loss over hilly terrain, second-reflected-wave conditions, present 135Ч137
Modified single-sideband (SSB) system 323Ч325
Multicell system, capacity limit in 532
Multipath dispersive fading phenomenon 559
Multipath fading phenomenon, in 800- to 900-MHz region 54
Multiple access interference (MAI) 633 636
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA in 520Ч523
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, impact of ambient noise in cellular and PCS bands, on CDMA system capacity/coverage 524Ч530
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, in interference-limited environment 515Ч520
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, in noise-limited environment 512Ч515
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, limits of interference cancellation for CDMA system 530Ч533
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, mobile satellite systems in 540Ч547
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, mobile satellite systems in, comparison of GEO, LEO, and MEO systems 542 543 544
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, mobile satellite systems in, GEO (geosynchronous earth orbit) satellites 541Ч544
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, mobile satellite systems in, LEO (low-earth orbit) satellites 541Ч547
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, mobile satellite systems in, MEO (midearth orbit; satellites 541Ч544
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, nature of cochannel interference in SDMA system in 548Ч549 550
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on physical channels 511Ч512
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on physical channels, frequency (F)-time (T)-code (C)-space (S) dimensions of 512
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, 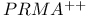 538 538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, ALOHA 533Ч534
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, BTMA 538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, CDPA 539
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, CSMA 535Ч536
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, CSMA/CD 538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, DSMA 538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, ISMA 538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, PRMA 537Ч538
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, RAMA 539
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, Reservation ALOHA 536Ч537
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, on virtual channels, protocols of, Slotted ALOHA 535
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, processing gain (P.G.) 523Ч524
Multiple-access (MA) schemes, requirement of alien-interference tolerance in 550Ч556
Multiple-base-station diversity see УMacroscopic diversityФ
Multiple-base-station intercell interference, in FH-DPSK systems 317Ч318
Multiuser detection, for CDMA 633Ч636
Narrowband PCS (personal communication service), for two-way paging systems 17 18
Near-end to far-end ratio interference, problem of 436Ч437
New York Police Department, role of, in history of mobile-radio communications 3
New York Telephone Company (NYTC) 5
Noise figure (NF) issues, ambient noise 578
Noise figure (NF) issues, antenna-temperature noise 580Ч581
Noise figure (NF) issues, receiver noise 578Ч580
Noise representation 312Ч313
Noise-limited environment, and evaluation of spectrum efficiency, in C/I< 1 systems 514Ч515
Noise-limited environment, and evaluation of spectrum efficiency, in C/I> 1 systems 512Ч514
Noncoherent FSK, nonfading digital modulation system 289Ч290
Nonconstant envelope modulation schemes 303Ч304
Nonconstant envelope modulation schemes, QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) 304Ч306
Nonpilot signal, use of, in feed-forward combining 381Ч382
Nonwireline operators (ECC) 4
NRZ baseband signaling, in bit-stream waveform analysis 402 403
Nyquist principle, illustrated 407
Offset quadrature phase-shift keying (OQPSK), constant envelope modulation scheme 296Ч297
Omni TRACS, GEO satellite system 541
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте