|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lee W.C.Y. Ч Mobile Communications Engineering |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
OrbComm, little LEO satellite system 543 544
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modem 306Ч309
Out-of-band adjacent-channel interference, problem of 436
Packet data transmission for data, long-length transmission 540
Packet data transmission for data, short-length transmission 540
Packet data transmission for voice 540
packet radio 2
Packet reservation multiple 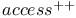 ( (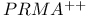 ) 538 ) 538
Packet reservation multiple access (PRMA) 537Ч538
Parity-check matrix 453Ч454
Path loss prediction, effect of human-made structures 567Ч568
Path loss prediction, generation of path loss curve 566
Path loss prediction, intercept, 1-mile 568Ч569
Path loss prediction, pathloss slope 158 568Ч569
Path loss prediction, relates to human-made effect 567Ч569
Path loss prediction, standard deviation of path loss 566
Path loss prediction, vs.local mean prediction 566Ч567
Path-clearance criteria 149
Personal access communication system (PACS) 3
Personal Communication Network (PCN) 541
Personal communication service (PCS) 2 541
Personal communication service (PCS), broadband, standards of 17
Personal communication service (PCS), capacity of 17Ч18
Personal communication service (PCS), narrowband, standards of 17
Personal digital phone (PDC), digital cellular in Japan 2
Personal handy-phone system (PHS) 2
Phase-shift keying (PSK) detection see УCoherent binary AM (PSK)Ф
Pilot signal, use of, in feed-forward combining technology 383Ч384
Ping-pong handoff, dropped call rate for 619Ч621 622
Poisson distribution 76
Polarization diversity 335
Polarization diversity, at base station 336
Polarization diversity, horizontal and vertical signals 335
Polarization division multiple access (PDMA) 511
Polarization waves 195Ч199
Polarization waves, 45-degree tilting 336
Polarization waves, vertical and horizontal 105Ч106 148 196Ч197 335Ч336
Portable coverage 583
Postdetection combining 351
Power spectral density 84Ч85
Power spectrum, of speech 496Ч497
Power-limited systems 581
Predetection combining 350
Prediction methods/models, inbuilding model 157Ч159
Prediction methods/models, LeeТs macrocell model 149Ч153
Prediction methods/models, LeeТs microcell model 153Ч155
Prediction methods/models, local mean prediction 153 163 566Ч567
Prediction methods/models, simplified method 156Ч157
Pretraining equalizer 96
Probability density function (PDF), calculation of, in equal-gain combining 369Ч370
Probability density function (pdf), conditional 68Ч70
Probability density function (PDF), joint characteristic functions 67Ч68
Probability density function (PDF), joint, of two variables 65Ч66
Probability density function (pdf), marginal 67
Probability density function (PDF), of single variable 64Ч65
Processing gain (PC) 523Ч524
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of 123Ч124
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, for UHF 124Ч126
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, general formula (accounting for different environments) 128Ч130
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, method of Okumura et al. 127Ч128
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over rough terrain 108Ч111
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over rough terrain, analysis of active scattering region 115Ч116
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over rough terrain, normally distributed surface characteristics 111Ч113
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over rough terrain, resolution interval 114
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over rough terrain, surface roughness as function of distance 113Ч114
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, over smooth terrain, reflection coefficient factor in 105Ч108
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, effect of surface waves 104
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, mobile-unit antenna height 104
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, radio horizon 102Ч103
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, signal averaging 103
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, sky reflections 103
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, prediction of, factors to be considered in, terminal in motion 103
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, primary causes of 26Ч31
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, rules for calculating average signal strength (local mean), mean approach 121
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, rules for calculating average signal strength (local mean), median approach 121
Propagation-path loss, models for prediction of, two-wave model, calculations for 116Ч120 (see also УField strengthФ)
Pulse-FM (or УchirpФ) modulation system 310
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), nonconstant envelope modulation scheme 304Ч306
Quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), constant envelope modulation scheme 295Ч296
Radio capacity 540 637Ч638
Radio Common Carrier (RCC) 4
Radio enhancement, techniques of, channel distribution/assignments 7Ч10
Radio enhancement, techniques of, macroscopic and microscopic diversity 10Ч11
Radio horizon 102Ч103
Radio paging systems 1
Radio-wave polarization, effects of 195Ч199
Radiophones (walkie-talkies) 1
Radiotelephones (mobile phones), types of 2
Raised-cosine-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 404 405
Rake receivers, in spread spectrum modulation 323
Ray tracing, technique for finding signal strength through wave propagation 584Ч585
Rayleigh distribution 72Ч74
Rayleigh fading 410
Rayleigh fading, adjacent-channel interference 434Ч435
Rayleigh fading, cochannel interference 428Ч430
Rayleigh signals 327
Real-time running average 610 611
Real-time running average, off-line average, in nonstationary environment 612Ч613
Real-time running average, off-line average, in stationary environment 612
Real-time running average, real-time averages, in nonstationary environments 614 615 616
Real-time running average, real-time averages, in stationary environment 613Ч614 615 616
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of average duration of fades, calculation of 224Ч226
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of coherent bandwidth 231Ч234 253
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of cumulative probability distribution (CPD) 208Ч215
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of envelope correlation of base-station received signal, based on space separation 234Ч237
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of envelope correlation of mobile received signal, based on, frequency and time separation 231Ч234
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of envelope correlation of mobile received signal, based on, time and space separation 230Ч231
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of envelope correlation of mobile received signal, based on, time separation 226Ч229
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of level-crossing rate (LCR) 215Ч224
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of model analysis of short-term fading 205Ч208
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of power-spectrum analysis 237
Received-signal envelope, characteristics of short-term vs.long-term fading 203Ч205
Received-signal phase, characteristics of click-noise phenomenon 259Ч263
Received-signal phase, characteristics of coherent bandwidth 231Ч234 253
Received-signal phase, characteristics of phase correlations 249Ч253
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random FM, level-crossing rate (LCR) of 257Ч258
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random FM, power spectrum distribution of 254Ч257
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random FM, probability distribution of 254
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random variable related to mobile-radio signals 241Ч242
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random variable related to mobile-radio signals, covariance matrix 248Ч249
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random variable related to mobile-radio signals, covariance of random variables 242Ч243
Received-signal phase, characteristics of random variable related to mobile-radio signals, power spectra 243Ч248
Received-signal phase, characteristics of simulation models, multipath- and selective-fading simulator 268Ч269
Received-signal phase, characteristics of simulation models, Rayleigh multipath fading simulator 263Ч268
Reed Ч Muller code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Reed Ч Solomon (R Ч S) code 659Ч660
Reed Ч Solomon (R Ч S) code, binary, fast-fading case 664
Reed Ч Solomon (R Ч S) code, binary, slow-fading case 660Ч663
Reed Ч Solomon (R Ч S) code, error-correcting block coding scheme 457 (table)
Reed Ч Solomon (R Ч S) code, nonbinary 665Ч667
Reference Data for Radio Engineers (ITT) 43
Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs) 4
Reservation ALOHA, as combination of Slotted-ALOHA and TDM protocols 536Ч537
Resolution interval, of terrain data 114
Resource auction multiple access (RAMA) 539
Rician cumulative probability distribution (CPD) 545
Rician Fading 543 545 546
Rough-terrain criterion 562
Rough-terrain criterion, antenna height effect 565Ч566
Sample averages 61
Scaling function 648
Scaling method, for determination of reflection point on sloping plane 28
Scaling vector 648
Schwarz inequality, application of, in maximal-ratio combining 361
Selective diversity combining 351Ч353 358
Selective diversity combining, four special cases for 353Ч357
Self-interference 524
Serving cell, in CDMA cellular system 525Ч527
Shannon Ч Hartley theorem 606
Shannon, C.E. 605
| ShannonТs channel capacity 530
Signal processes, bit and frame synchronization 409Ч414
Signal processes, bit-stream waveform analysis, binary PCM waveforms, types of 401
Signal processes, bit-stream waveform analysis, duobinary-waveform signaling 406Ч409
Signal processes, bit-stream waveform analysis, power spectral density of random data sequence 400Ч404
Signal processes, bit-stream waveform analysis, time-delay-spread dependency factor 399Ч400
Signal processes, bit-stream waveform analysis, waveform shaping 404Ч406
Signal processes, mobile-radio-system functional design, distance-dependency factors 397Ч398
Signal processes, mobile-radio-system functional design, velocity-dependency factors 399
Signal processes, syllabic companding 414Ч417
Signal-coverage area, prediction of 164Ч169
Signal-threshold, prediction of 163Ч164
Single-active-base-station intracell interference, in FH-DPSK system 314Ч317
Single-cell system, capacity limit in 532
Single-parity check code 452Ч453
Single-sideband-frequency/amplitude (SSB-F/A) system 324Ч325
Slotted ALOHA 535
Slow-fading condition 470Ч472
SnellТs law, application of 27 29 104Ч105
Space diversity at base station 330Ч334
Space diversity at mobile unit 329Ч330
Space division multiple access (SDMA) 511Ч512
Spaceway, GEO satellite system 543 544
Spectrum allocation, by FCC 4 5
Spectrum allocation, new channel-numbering scheme 14
Specular reflection 27 28
Speech power, average, distribution of 493Ч495
Speech power, spectrum of 496Ч497
Spread spectrum systems, direct-sequence-modulated 309
Spread spectrum systems, for military security applications 19
Spread spectrum systems, frequency-hopping 310
Spread spectrum systems, time-hopping 310
Spread spectrum systems, time/frequency-hopping 310
Spread spectrum systems, УchirpФ or pulse-FM modulation 310
Spread-spectrum (SS) modulation 523
Spread-spectrum (SS) modulation, correlators and rake receivers 323
Spread-spectrum (SS) modulation, direct sequence (DS) signals in 321Ч323
Spread-spectrum (SS) modulation, reduction of interference by 323
Spreading process 321Ч322
Squared-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 404 405
Stationary average device 612
Statistical averages 61Ч62
Statistical communications, theory of, and advantages of statistical approach 59Ч60
Statistical communications, theory of, averages, biased time 62
Statistical communications, theory of, averages, ensemble 62
Statistical communications, theory of, averages, sample 61
Statistical communications, theory of, averages, statistical 61Ч62
Statistical communications, theory of, averages, unbiased 62
Statistical communications, theory of, binomial distribution 75Ч76
Statistical communications, theory of, confidence intervals 89Ч90
Statistical communications, theory of, continuous spectral density 84Ч85
Statistical communications, theory of, correlation functions 81Ч82
Statistical communications, theory of, correlation functions, autocorrelation 82
Statistical communications, theory of, correlation functions, cross-correlation 83Ч84
Statistical communications, theory of, cumulative probability distribution (CPD) 63
Statistical communications, theory of, duration of fades 80Ч81
Statistical communications, theory of, equalizers 93Ч97
Statistical communications, theory of, ergodic processes 62Ч63
Statistical communications, theory of, error probability 90Ч92
Statistical communications, theory of, Gaussian distribution 71
Statistical communications, theory of, impulse response measurements 92Ч93
Statistical communications, theory of, level-crossing rate (LCE) 77Ч80
Statistical communications, theory of, lognormal distribution 74Ч75
Statistical communications, theory of, Poisson distribution 76
Statistical communications, theory of, power spectral density 84Ч85
Statistical communications, theory of, probability density functions (PDFs), conditional 68Ч70
Statistical communications, theory of, probability density functions (PDFs), joint characteristic functions 67Ч68
Statistical communications, theory of, probability density functions (PDFs), joint, of two variables 65Ч66
Statistical communications, theory of, probability density functions (PDFs), marginal 67
Statistical communications, theory of, probability density functions (PDFs), of single variable 64Ч65
Statistical communications, theory of, Rayleigh distribution 72Ч74
Statistical communications, theory of, sampling distributions 85Ч89
Statistical communications, theory of, uniform distribution 70Ч71
Subcarrier QPSK, constant envelope modulation scheme 299
Switched combining 350 357Ч359
Syllabic companding 414Ч417
System block diagram 13
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, bit-error analysis, based on correlated signals 476Ч479
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, bit-error analysis, based on M-branch maximal-ratio combiner 469 470
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, convolutional code, convolutional encoder 458 459 460
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, convolutional code, tree diagram 460 461
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, convolutional code, trellis diagram 460 462
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, convolutional code, Viterbi convolutional decoding algorithm 462
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, effects of fading on word-error rate 470 472
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, effects of fading on word-error rate, fast-fading condition 471
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, effects of fading on word-error rate, slow-fading condition 471Ч473
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, error probability, for differentially coherent receivers 486Ч490
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, error probability, for incoherent matched-filter receivers 483Ч486
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, error reduction, based on majority-voting processes 473
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, error reduction, based on majority-voting processes, fast-fading condition 473Ч475
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, error reduction, based on majority-voting processes, slow-fading condition 475Ч476
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, irreducible error rate, due to frequency-selective fading 481Ч482
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, irreducible error rate, due to random FM 479Ч481
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, coding gain 454
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, coding strength 455
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, cyclic redundancy check (CRC) 457Ч458
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, erasure correction 456Ч457
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, error detection/error correction 455Ч456
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, parity-check matrix 453Ч454
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, linear block code, single-parity check code 452Ч453
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, system and signaling criteria, equivalent performance 452
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, system and signaling criteria, performance 449Ч450
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, system and signaling criteria, testing 450Ч452
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, trellis coded modulation (TCM) 463Ч464
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, trellis coded modulation (TCM), coding gain for 464 465 466
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, types of signaling errors 467Ч468
System error analysis, vs.system performance, components of, word (frame) error rate 470 586Ч587
Telecommunication Reform Act Bill (1996) 4
Teledesic, big LEO satellite system 543 544
Terrain-contour effect 152Ч153
Thermal noise, characteristics of 40Ч43
Time diversity 343Ч344
Time Division Duplexing (TDD) systems, DECT (digital European cordless telephone) 2
Time Division Duplexing (TDD) systems, PACS (personal access communication system) 3
Time Division Duplexing (TDD) systems, PHS (personal handy-phone system) 2
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) 2
Time division multiple access (TDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA and CDMA in C/I < 1 systems (CDMA) 521
Time division multiple access (TDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA and CDMA in C/I < 1 systems (FDMA and TDMA) 520Ч521
Time division multiple access (TDMA), comparison of radio capacity between FDMA, TDMA and CDMA where CDMA is greater 521Ч523
Time-delay distributions 340
Time-delay distributions, models of, approximation 341
Time-delay distributions, models of, exponential-distribution 341
Time-delay distributions, models of, Maxwell-distribution 340
Time-delay spread 562
Time-delay spread  575Ч578 575Ч578
Time-delay-spread dependency factor, in bit-stream waveform analysis 399Ч400
Time-delay-spread dependency factor, in bit-stream waveform analysis, reduction by diversity 391Ч392 569 577Ч578
Time-hopping system 310
Time/frequency-hopping system 310
Total access communication system (TACS) 2
Transmission diversity see УDiversity schemesФ
Tree diagram 460Ч461
Trellis coded modulation (TCM) 463Ч464
Trellis coded modulation (TCM), coding gain for 464 465 466
Trellis diagram 460 462
Triangular-waveform pulse, in waveform shaping 404 405
UHF mobile-radiotelephone systems 6
Unbiased time averages 62
Uniform distribution 70Ч71
Universal mobile telecommunication systems (UMTS) 4
Van Allen belts 542
Velocity-dependency factors, in mobile radio-system functional design 399
Vertical antenna separation, vs.horizontal antenna separation 574 575 576
VHF mobile-radiotelephone systems 6
VincentТs device (real-time averages in stationary environment) 613Ч615 616
VincentТs device (real-time averages in stationary environment), in calculations of radio communication environment 619
Viterbi convolutional decoding algorithm 462
Voice processing, in FM system, compandor, compressor and expandor 502Ч503
Voice processing, in FM system, preemphasis and deemphasis 500Ч501
Voice quality analysis, vs.system performance, components of digital processing of voice signals 508
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 (
( )
) 