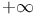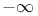|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gut A. Ч Stopped Random Walks: Limit Theorems and Applications |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 148 157 171Ч176 177 148 157 171Ч176 177
 149 154Ч157 164 172Ч176 178 149 154Ч157 164 172Ч176 178
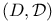 , , 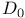 148 155 164 176 148 155 164 176
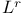 -convergence theorem 166 -convergence theorem 166
Ahlberg 6 119
Aleskeviciene 87
Anderson 61
Anscombe 3 8 15 42
Anscombe Ч Donsker invariance principle 147Ч149
Anscombe, condition 15 44
AnscombeТs theorem 3 4 15Ч16 36 44 56 85 137 147 151
AnscombeТs theorem, 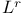 -analogue of 33 -analogue of 33
AnscombeТs theorem, multidimensional 150
Arjas 53
Asmussen 4 48 62 109 125
Athreya 53 61
Barlow 122Ч124
Basu 152
Baum 42 43
Belyayev 122
Berbee 107
Berry 61
Bickel 62
Billingsley 7 18 149 150 152 153 160 166 169 171 174 176
Bingham 103 156 178
Binomial process 1
Blackwell 8 23 26 27 44 52 61 76 87 88 90
Breiman 7
Brown 7
Brownian motion see УWiener processФ
Burkholder 20 29 167 169 170
Carlsson 62 89 100
Central limit theorem 1 7 8 15 17 18 29 36 38 55 61 72 85 92Ч96 102 108 111Ч114 130 137 147 168Ч169
Central limit theorem, moment convergence in 18 168Ч169
Central limit theorem, multidimensional 117
Chang 33 163
Choquet 53
Chow 7 17 23 24 33 34 67 92Ч95 103 106 107 132 137 142Ч144 146
Chromatography 6 118Ч121
Chung 4 15 62 65 73 90 100 165 166 168 170
Cinlar 4 48 62
Cluster set see УLimit points set
Combinatorial methods 4 46
composition 149 151 176
Continuity of function(al)s 164 174Ч175
Continuity of function(al)s, composition 149 151
Continuity of function(al)s, first passage time 156
Continuity of function(al)s, inversion 155
Continuity of function(al)s, largest jump 154
Continuity of function(al)s, projections 150 156 178
Continuity of function(al)s, supremum 155
Continuous mapping theorem 149 150 154 163 174Ч175
Convergence, almost sure (a.s.) 4 9 10Ч14 17 41 44 54 67 70 83Ч85 97 130 135 145 166 175
Convergence, complete 9 42Ч43 103
Convergence, in 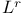 4 9 17 37 39 41 44 166 4 9 17 37 39 41 44 166
Convergence, in distribution 4 9 10 15Ч17 36 55 58 72 85Ч87 98 102 111Ч112 115Ч117 130Ч131 137Ч138 166 179
Convergence, in probability 4 9 10Ч13 39 166 176
Convergence, in r-mean 4 (see also УConvergence in
Convergence, moment 4 9 17Ч20 36Ч39 54 56 57 59 87 89 92Ч97 98Ч102 106 108 109Ч114 130Ч132 143Ч145 165Ч167
Convergence, of finite-dimensional distributions 150 156 171Ч172
Convergence, of probability measures 171Ч176 (see also УWeak convergenceФ)
Convergence, rate 42Ч44 103Ч104 131
Convergence, weak see УWeak convergenceФ
Counters 1 2 124Ч125
Coupling 53
Cox 106 109 122
Cramer 125
Daley 89
Davis 20 169
De Acosta 177 178
de Groot 23
de Haan 134 180
DENY 53
Doeblin 53
Domain of attraction see УStable lawФ
Doney 62 67
Donsker 7 147
DonskerТs theorem 147 149 158 164 172 177
DonskerТs theorem, Anscombe version of 147 162
Doob 21 48 53 54 87 167 168 170
Dynkin 61
Englund 61
Erdos 6 7 42 52 73 85
Erickson 53 61
Esseen 61
Essen 89
Farrell 62
Feller 4 6 24 36 48 52 54 60 61 65 90 134 180
First passage time(s) 2 5Ч9 22 24 39 50 74Ч107 108 109Ч118 132 133 147 151Ч159 163
First passage time(s), auxiliary 138 139 144
First passage time(s), central limit theorem 56 85 93
First passage time(s), complete convergence 103
First passage time(s), convergence rate 103Ч104
First passage time(s), excess over the boundary 76 97 overshootФ)
First passage time(s), for the ladder height process 77 81
First passage time(s), law of large numbers 55 83Ч84 93 105
First passage time(s), law of the iterated logarithm 102Ч103 163
First passage time(s), momentgenerating function 81
First passage time(s), moments, convergence 55 92Ч97 106
First passage time(s), moments, finiteness 50 78Ч81
First passage time(s), overshoot 76 97Ч102 106
First passage time(s), process 3 5 6 50 55 57 75Ч107 119
First passage time(s), subadditivity 55 83
First passage time(s), uniform integrability 55 57 90Ч92 94Ч95
First passage time(s), weak convergence 151Ч157
First passage times across general boundaries 7 75 109 133Ч146 159Ч161 163
First passage times across general boundaries, central limit theorem 137 144
First passage times across general boundaries, law of large numbers 135Ч137 143
First passage times across general boundaries, law of the iterated logarithm 145Ч146 163
First passage times across general boundaries, momentgenerating function 134
First passage times across general boundaries, moments, convergence 143Ч145
First passage times across general boundaries, moments, finiteness 133Ч134
First passage times across general boundaries, overshoot 145
First passage times across general boundaries, weak convergence 159Ч161
Fluctuation theory 4 46
Fuchs 4 65
Functional central limit theorem 147 172 weakФ)
Functional limit theorem 7 132 147Ч164
Gafurov 62
Garsia 61 167
Generalized arc sine distribution 61
Gikhman 151 173
Gnedenko 122
Goldie 103
Grubel 90
Gundy 7
Gut 6 7 22 26 28 34 35 40 43 44 75 76 78 84Ч86 93Ч98 100 102 103 107 109 111 113 115 117 119 122 126 127 133 134 136Ч140 144Ч146 150 152 153 156 158 161 182
Hall 163
Hartman 41 177Ч178
Hatori 54
Heath 128
Heyde 73 78 80 81 83 85 86 89 95 132 163
Hogfeldt 158
Hoist 126 127
Horvath 163
Hsiung 17 33 34 92 94 103 132 137 142Ч144 146 163
Hsu 42 43
Huggins 163
Hunter 62
Iglehart 156 164
Insurance risk theory 1 2 125Ч126
Invariance principle 147Ч164 (see also УFunctional limit
Invariance principle, almost sure see УInvariance principle strongФ
Invariance principle, Anscombe Ч Donsker 147Ч149
Invariance principle, strong 7 42 147 161Ч164 177Ч178
Invariance principle, weak 7 147Ч161 175
Inverse relationship 138 146 155
Inverse relationship between partial maxima and first passage times 75 80 85 103 132
Inverse relationship between renewal and counting processes 49 56 75
Jagers 4 48 53
| Janson 6 11 12 28 34 35 69 73 78 82 97 101 107 109 111 113 115 118 122 132 139 140 158
Kac 6 7 73
Kaijser 121
Karamata 180
Katz 42 43
Kemperman 62
Kesten 62
Kiefer 132
Kingman 83
Kolmogorov 14 27 52 84
Ladder, epoch 5 65Ч66 77Ч78 98 104Ч106 129
Ladder, epoch, ascending 8 65
Ladder, epoch, ascending, strong 5 65 68Ч70 77
Ladder, epoch, ascending, weak 67 70
Ladder, epoch, descending, strong 67
Ladder, epoch, descending, weak 66
Ladder, height 66Ч67 98 101 129
Ladder, height, first passage times for see УFirst passage timesФ
Ladder, height, strong ascending 66 68Ч69 77
Ladder, method 76 77Ч78 81 83 87Ч89 91 93 94Ч96 97 101 152
Ladder, variable 2 4 26 46 65Ч67 77
Lai 7 17 28 33 34 59 67 85 91 92 94 100 133 142Ч144
Lalley 62 87 102
Lamperti 61
Law of Large Numbers 1 8 13Ч14 17 29 33 37 44 54 70 83Ч84 92Ч94 108 109Ч111 130 135Ч137
Law of large numbers, convergence rate 42Ч43
Law of large numbers, converse 27
Law of large numbers, Erdos Ч Renyi 85
Law of large numbers, martingale proof of 44
Law of large numbers, moment convergence 17Ч18 44
Law of the iterated logarithm 1 8 9 41Ч42 43 102Ч103 108 117 131 147 161Ч164 177Ч178
Law of the iterated logarithm, Anscombe version of 42 162
Law of the iterated logarithm, converse 41
Limit points 41 177
Limit points, set of 41Ч42 162Ч164 177Ч178
Lindberger 161 164
Lindvall 53 175
Local limit theorem 87 106
Loeve 11 14 166
Lorden 100 101
Maejima 106 107
Marcinkiewicz 14 19 20 29 44 61 84 110 136 167 169
Martingale 44 53 167Ч171 178
Martingale, convergence 168
Martingale, moment inequalities see УMomentsФ
Martingale, optional sampling theorem 21Ч25 167 170Ч171
Martingale, reversed 44 168 178
McDonald 53
Meyer 53
Miller 122
Mohan 53 57 61
Moments, boundedness 39 40
Moments, convergence see УConvergenceФ
Moments, finiteness 24 25Ч28 49 51 78 79 97 132 133Ч134 145
Moments, inequalities for martingales 167 169
Moments, inequalities for stopped random walks 20Ч28
Moments, inequalities for sums of independent random variables 167 168Ч169
Moments, Marcinkiewicz Ч Zygmund 19 20 167 169
Mori 107
Nagaev 62
Negative binomial process 47 49 57 59 106
Nerman 100
Neveu 24 168
Ney 53 107
Niculescu 53
Number of renewals 48Ч49
Number of visits 6 64Ч65
Number of visits, expected 64Ч65 90
Nummelin 53
Optional sampling theorem see УMartingaleФ
Orey 90
Ornstein 4 6 65
Partial maxima 5 7 46 67Ч73 75 108 128Ч132 155 159 164
Partial minima 5 67Ч70 128 132
Plucihska 122
Point, persistent 4 65
Point, possible 4
Point, transient 65
Poisson process 47 48 53 57 59 125 126
Pollard 52 90
Port 6
Prabhu 4 48 65 68 69 73 75 90 109 125 126
Projections 150 171
Projections, continuity of see УContinuity of function(al)sФ
Proschan 122Ч124
Pyke 20 124
Queueing theory 1 2 126
Random change of time 148 151 160 176
Random index 1Ч9 17 46 68
Random walk 1Ч7 8 46 62Ч73 99Ч100
Random walk, arithmetic 47 65 97 105 107
Random walk, arithmetic with span d 47 63
Random walk, arithmetic, d-arithmetic 47 88 90 95Ч99
Random walk, Bernoulli 1 47
Random walk, Bernoulli, symmetric 1
Random walk, classification 63Ч68
Random walk, coin-tossing 1
Random walk, drifting 4 6
Random walk, drifting to 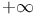 5 7 64Ч67 70 104 with 5 7 64Ч67 70 104 with
Random walk, drifting to 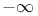 64Ч67 69 70 64Ч67 69 70
Random walk, maximum of see УPartial maximaФ
Random walk, minimum of see УPartial minimaФ
Random walk, nonarithmetic 47 63 65 88 90 95Ч100 102
Random walk, oscillating 4 6 64 66Ч68
Random walk, persistent 4 64Ч65
Random walk, randomly indexed 1Ч9 (see also УStopped random walkФ)
Random walk, simple 1 63Ч65 104Ч106 107
Random walk, simple, symmetric 1 24 35 66
Random walk, stopped see УStopped random walkФ
Random walk, transient 4 6 64Ч65
Random walk, two-dimensional 3 6 108 109 stoppedФ)
Random walk, with multidimensional indices 107
Random walk, with positive drift 3 5 73 74Ч107 108 128Ч132 133Ч146 151Ч157 159Ч161 163 164
Recurrent even 4
Regularly varying function 53 57 61 87 116 134 155 180Ч182
Relative compactness 162 Ч164 178
Reliability theory 1 2 8 123Ч124
Renewal counting process 2Ч6 8 9 48Ч57 68 82 118
Renewal counting process, Berry Ч Esseen theorem 61
Renewal counting process, central limit theorem 55
Renewal counting process, for random walks with positive drift 82
Renewal counting process, large deviation 62
Renewal counting process, law of large numbers 54
Renewal counting process, law of the iterated logarithm 61
Renewal counting process, momentgenerating function 49
Renewal counting process, moments, convergence 54Ч57
Renewal counting process, moments, finiteness 49
Renewal counting process, uniform integrability 54Ч57
Renewal function 5 6 49Ч53 61 90
Renewal function, extended 89
Renewal measure 63 90
Renewal measure, harmonic 90
Renewal process 1Ч6 46Ч62 74 76 82 105 108 113 118 125 152 164
Renewal process, age 60 61
Renewal process, alternating 6 122
Renewal process, arithmetic 47 48 54 66
Renewal process, arithmetic with span d 47
Renewal process, arithmetic, d-arithmetic 47 50 52 53 56Ч58
Renewal process, coupling proofs 53
Renewal process, delayed 62
Renewal process, integral equation 50 52
Renewal process, lifetime 58 60
Renewal process, lifetime, residual 58Ч60 61 97
Renewal process, nonarithmetic 47 48 52Ч54 56Ч60
Renewal process, pure 62
Renewal process, terminating 62 66
Renewal Theorem 6 8 51Ч53 61 87Ч90
Renewal Theorem, BlackwellТs 52 61 90
Renewal theorem, BlackwellТs, random walk analogue 88
Renewal theorem, elementary 5 51 61 89 90
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



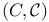
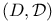
 -convergence theorem
-convergence theorem