Constant difference of integral, at opposite edges of cross-cut 375
Constant difference of integral, how related for cross-cuts that meet 376
Constant difference of integral, how related for cross-cuts that meet, for canonical cross-cuts 377 see
Constant modulus for cross-cut 377
Constant, uniform function is, everywhere if constant along a line or over an area 59
Contiguous regions 591
Continuation 55
Continuation, of function by successive domains 54
Continuation, of function with essential singularities 99
Continuation, of multiform function to obtain branches 151
Continuation, Schwarz's symmetric 57
Continuity of a function, region of see "Region of continuity"
Continuity, region of 55
Continuous group 584
Continuous substitution 584
Contraction of areas in conformal representation 537
Convergence, uniform unconditional 127
Convex curve, area of, represented on half-plane, deduced as the limit of the representation of a rectilinear polygon 548
Convex normal polygon for division of plane, angles at corners of second category and of third category 597
Convex normal polygon for division of plane, changed into a closed surface 608
Convex normal polygon for division of plane, in connection with an infinite group 595
Convex normal polygon for division of plane, sum of angles at the corners in a cycle of the first category is a submultiple of four right angles 598
Convex normal polygon for division of plane, when given leads to group 600
Convexity of normal polygon 594
Corner of region 591
Corners, cycles of homologous 593
Corners, cycles of homologous, categories of cycles 596
Corners, cycles of homologous, closed, and open 596
Corners, cycles of homologous, how obtained 596
Corners, of first category are fixed points of elliptic substitutions 600
Corners, of regions 591
Corners, of second and third categories are fixed points of parabolic substitutions 600
Corners, open cycles of, do not occur with Kleinian groups 613
Corners, sub-categories of cycles of 607
Corners, three categories of, for Fuchsian group 592
Coupure 140 186
Crescent changed into another of the same angle by a linear substitution 514
Crescent changed into another of the same angle by a linear substitution, represented on a half-plane 554
Criterion of character of singularity 66
Criterion of character of singularity, class of transcendental integral function 91
Critical integer, for expansion of a function in an infinite series of functions 124
Critical point 15
Cross-cut 314
Cross-cuts, and irreducible circuits 330
Cross-cuts, chosen for resolution of Riemann's surface 352
Cross-cuts, defined 314
Cross-cuts, difference of values of integral at opposite edges of, is constant 375
Cross-cuts, effect of, on any surface 316
Cross-cuts, effect of, on connectivity of surface 319
Cross-cuts, effect of, on number of boundaries 323
Cross-cuts, effect of, on simply connected surface 316
Cross-cuts, in canonical resolution of Riemann's surface 354
Cross-cuts, in resolution of Riemann's surface in its canonical form 366
Cross-cuts, moduli of periodicity for 377
Cross-cuts, moduli of periodicity for, introduced in proof of existence-theorem 430
Cross-cuts, moduli of periodicity for, number of independent moduli 379
Cross-cuts, on Riemann's surface 351
Cross-line 339
Curvilinear polygon, bounded by circular arcs, represented on the half-plane 549
Curvilinear polygon, bounded by three arcs 555 see
Curvilinear polygon, bounded by two arcs 554
Curvilinear polygon, equation which secures the representation of 553
Curvilinear polygon, equation which secures the representation of, connected with linear differential equations 553
Curvilinear polygon, function for representation of 550
Curvilinear triangles, connected with solution of differential equation for the hypergeometric series 555
Curvilinear triangles, equation for representation of, on half-plane 555
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary 561
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary, cases when the relation is algebraical in both variables and uniform in one 564
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary, cases when the relation is algebraical in both variables and uniform in one, equations which establish the representation in these cases 567
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary, cases when the relation is algebraical in both variables but uniform in neither 574
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary, connected with division of spherical surface by planes of symmetry of inscribed regular solids 564
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is imaginary, stereographic projection on sphere so as to give spherical triangle bounded by great circles 562
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is real 557
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is real, any number of, obtained by inversions, lie within the orthogonal circle 558
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is real, discrimination of cases 559 560
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is real, equation is transcendental 559
Curvilinear triangles, when the orthogonal circle is real, particular case when the three arcs touch 561
Cycles of corners 593 see
Cyclical interchange of branches of a function which are affected by a branch-point 156
Cyclical interchange of branches of a function which are affected by a branch-point, when the function is algebraic 171
Darboux 20 46 57 69 538 549
De Sparre 92
Dedekind 633 637
Deficiency 356
Deficiency of a curve 356
Deficiency of a curve, is an invariant for rational transformations 367
Deformation of loop 357
Deformation of surface 333
Deformation, connected surfaces, can be effected from one to another if they be bifacial, be of the same connectivity, and have the same number of boundaries 334
Deformation, connected surfaces, geometrical and physical 333
Deformation, of a circuit on a Riemann's surface over branch-point impossible 350
Deformation, of loops 358
Deformation, of path of integration, how far it can take place without affecting the final branch 152 153—155
Deformation, of path of integration, of holomorphic function does not affect value of the integral 26
Deformation, of path of integration, of multiform function see "Integral of multiform function"
Deformation, of path of integration, of multiform function, effect of, when there are more than two periods 208
Deformation, of path of integration, of multiform function, form of, adopted 190
Deformation, of path of integration, of path of variable for multiform functions 152
Deformation, of path of integration, on Riemann's surface see "Path of integration"
Deformation, of path of integration, over pole of meromorphic function affects value of the integral 34
Deformation, to its canonical form of Riemann's surface with simple winding-points 365
Degree of pseudo-automorphic function 651
Derivative, Schwarzian 529
Derivatives, a holomorphic function possesses any number of, at points within its region 32
Derivatives, do not necessarily exist along the boundary of the region of continuity 32 133
Derivatives, of elliptic functions with regard to the invariants 265
Derivatives, superior limit for modulus of 33
Description of closed curve, positive and negative directions of 3
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable 470
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, application of general results to binomial 482
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, application of general results to binomial, discrimination of solutions into the three classes 484
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, conditions that integral of, is a uniform function 471
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, conditions that integral of, when the integral is uniform, it is either a rational, a simply-periodic, or a doubly-periodic, function 476
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, example of integral that is two-valued 490
Differential equation of first order, not containing the independent variable, reference to functions which possess addition-theorem 490
Differential equation of first order, satisfied by function which possesses an algebraic addition-theorem 309
Differential equation of first order, satisfied by uniform doubly-periodic functions 237
Differential equation of first order, satisfied by uniform doubly-periodic functions, in particular, by elliptic functions 238
Dihedral function, automorphic for dihedral group 632 see
Dihedral group 623
Dihedral group, function automorphic for 632
Dihedral group, of homogeneous substitutions 624
Dihedral group, of linear substitutions 625
Dihedral group, of rotations 623
Dingeldey 335
Dini vi
Diramazione, punto di 15
Directions of description of closed curve 3
Dirichlet's principle 408
Discontinuity, polar 16
Discontinuous groups 584
Discontinuous substitution 584
Discontinuous, all finite groups are 586
Discontinuous, division of plane associated with 591 see
Discontinuous, groups 584
Discontinuous, properly and improperly 585
Discrete group 584
Discrete substitution 584
Discriminating circle 111
Discriminating circle for uniform function 111
Discrimination between accidental and essential singularities 53 66
Discrimination of branches of a function obtained by various paths of the variable 152—155
Division of surface into polygons, Lhuilier's theorem on 325
Domain 52
Domain of ordinary point 52
Double (or fixed) circle of elliptic substitution 613
Double points of linear substitution 514
Double-pyramid, division of surface of circumscribed sphere by planes of symmetry 564
Double-pyramid, equation giving the conformal representation on a half-plane of each triangle in the stereographic projection of the divided spherical surface 567
Doubly-infinite system of zeros, transcendental function having 84
| Doubly-periodic function of first, second, third, kind 273 274
Doubly-periodic functions 198
Doubly-periodic functions, are connected by an algebraical equation if they have the same periods 236
Doubly-periodic functions, can be expressed rationally in terms of a homoperiodic function of the second order and its first derivative 239
Doubly-periodic functions, differential equation of first order satisfied by 237
Doubly-periodic functions, differential equation of first order satisfied by, in particular, by elliptic functions 238
Doubly-periodic functions, equivalent 220
Doubly-periodic functions, expressed in terms of the 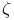 -function 256 -function 256
Doubly-periodic functions, expressed in terms of the 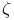 -function, and of the -function, and of the  -function 260 -function 260
Doubly-periodic functions, fundamental properties of uniform 219
Doubly-periodic functions, graphical representation 199
Doubly-periodic functions, integral of, round parallelogram of periods, is zero 221
Doubly-periodic functions, number of zeros equal to number of infinities and of level points 226
Doubly-periodic functions, of any order with simple infinities can be expressed in terms of homoperiodic functions of the second order 234
Doubly-periodic functions, of first order do not exist 223
Doubly-periodic functions, of second order consist of two classes 223
Doubly-periodic functions, of second order, can be expressed in terms of any assigned homoperiodic function of the second order with an appropriate argument 223
Doubly-periodic functions, of second order, characteristic equation of 231
Doubly-periodic functions, of second order, properties of see "Second order"
Doubly-periodic functions, of second order, zeros and infinities of derivative of 232
Doubly-periodic functions, order of 220
Doubly-periodic functions, possesses algebraical addition-theorem 299
Doubly-periodic functions, sum of residues of, for parallelogram, is zero 222
Doubly-periodic functions, sum of zeros congruent with the sum of the infinities and with the sum of the level points 228
Doubly-periodic functions, those considered have only one essential singularity which is at infinity 218 227
du Bois-Reymond 133
Durege 54 316 335
Dyck 335 583 585
Edge of region 591
Edges of cross-cut, positive and negative 374 375 438
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group 591
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group, congruent, are of the same kind 592
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group, conjugate 592
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group, each pair of conjugate, implies a fundamental substitution 593
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group, of first kind are even in number and can be arranged in conjugate pairs 593
Edges of regions in division of plane by an infinite group, two kinds of, for real groups 592
Einaendrig 15
Eindeutig 15
Einfach zusammenhaengend 313
Eisenstein 85 87
Element 56
Element of doubly-periodic function of third kind 291 293
Elementary function of second kind 448 see
Elementary functions of third kind 449 see
Elementary integral of the second kind, third kind 396 402
Elementary integrals of third kind 402
Elementary integrals of third kind, connected with integrals of second kind 403
Elementary integrals of third kind, number of independent, with same logarithmic infinities 403
Elementary integrals, connected with those of third kind 403
Elementary integrals, determined by an infinity, except as to additive integral of first kind 398
Elementary integrals, number of independent 399
Elementary integrals, of second kind 396
Elements of analytic function 56
Elements of analytic function, any single one of the, is sufficient for the construction of the function 57
Elements of analytic function, can be derived from any one when the function is uniform 56
Ellipse, area within, represented on a rectangle 504
Ellipse, area within, represented on a rectangle, and on a circle 505
Ellipse, area without, represented on a circle 501
Ellipsoid conformally represented on plane 500
Elliptic functions, obtained by integrating multiform functions, in Jacobian form 193
Elliptic functions, obtained by integrating multiform functions, in Weierstrassian form 196 249
Elliptic functions, on a Riemann's surface 383
Elliptic substitution 517
Elliptic substitutions 517 519
Elliptic substitutions are either periodic or infinitesimal 521
Elliptic substitutions, occur in connection with cycles of corners 607 613
Enneper 637
Equivalent homoperiodic functions 220
Equivalent homoperiodic functions, conditions of equivalence 225
Essential singularities 17 53
Essential singularities of groups 522 606
Essential singularities of groups are essential singularities of functions automorphic for the group 606
Essential singularities of groups, lie on the fundamental circle 606
Essential singularities of groups, may be the whole of the fundamental circle 607
Essential singularities, classification of, into classes 146
Essential singularities, classification of, into species 148
Essential singularities, classification of, into wider groups 148
Essential singularities, continuation of function possessing 99
Essential singularities, form of function having finite number of, as a sum 100
Essential singularities, form of function in vicinity of 96
Essential singularities, functions having unlimited number of vii
Essential singularities, lacunary space of 141
Essential singularities, line of 140
Essential singularities, of automorphic functions 651
Essential singularities, of pseudo-automorphic functions 642
Essential singularities, of transcendental integral function at infinity 74
Essential singularities, uniform function must assume any value at 54 94
Essential singularity 17 53
Existence-theorem 369 405
Existence-theorem for functions on a given Riemann's surface xvii
Existence-theorem for functions on a given Riemann's surface, abstract of Schwarz's proof of 409
Existence-theorem for functions on a given Riemann's surface, methods of proof of 408
Existence-theorem for functions on a given Riemann's surface, results of, relating to classes of functions proved to exist under conditions 436
Expansion of a function in the vicinity of an ordinary point, by Cauchy's theorem 43
Expansion of a function in the vicinity of an ordinary point, within a ring, by Laurent's theorem 47
Expression of multiform function in the vicinity of branch-point 158
Expression of uniform function, having an assigned infinite number of singularities over the plane 115
Expression of uniform function, having an assigned infinite number of singularities over the plane, generalised 116
Expression of uniform function, having finite number of essential singularities, as a product when without accidental singularities and zeros 104
Expression of uniform function, having finite number of essential singularities, as a product, with any number of zeros and no accidental singularities 108
Expression of uniform function, having finite number of essential singularities, as a product, with any number of zeros and of accidental singularities 110
Expression of uniform function, having finite number of essential singularities, as a sum 100
Expression of uniform function, having infinity as its single essential singularity 117
Expression of uniform function, having unlimited singularities distributed over a finite circle 117
Expression of uniform function, in the vicinity of any one of an infinite number of essential singularities 113
Expression of uniform function, in vicinity of a zero 61
Expression of uniform function, in vicinity of accidental singularity 64
Expression of uniform function, in vicinity of essential singularity 96
Expression of uniform function, in vicinity of ordinary point 43
Factor, fractional, for potential-function 422
Factor, generalising, of transcendental integral function 81
Factor, primary 82
Factorial functions 464
Factorial functions, constant factors (or multipliers) for crosscuts of 465
Factorial functions, constant factors (or multipliers) for crosscuts of, forms of, when cross-cuts are canonical 466
Factorial functions, cross-cut multipliers and an assigned number of infinities determine a limited number of independent 470
Factorial functions, expression of, in terms of normal elementary functions of the third kind 466
Factorial functions, general form of 466
Factorial functions, pseudo-periodic on a Riemann's surface 464
Factorial functions, their argument 464
Factorial functions, zeros and infinities of 468
Factorial periodicity 586
Factors (or multipliers) of factorial functions at cross-cuts 465
Factors (or multipliers) of factorial functions at cross-cuts, forms of, when cross-cuts are canonical 466
Falk 201
Families of groups 606
Families of groups, for one set, the whole line conserved by the group is a line of essential singularity for the other set, only parts of the conserved line are lines of essential singularity 607
Families of groups, seven 606
Finite groups 586
Finite groups of linear substitutions 586 620
Finite groups of linear substitutions, anharmonic, containing two elliptic fundamental substitutions 587
Finite groups of linear substitutions, containing a single fundamental substitution 586
Finite number of essential singularities, function having, expressed as a sum 100
First kind of Abelian integrals 394
First kind of integrals on Riemann's surface 394
First kind of integrals on Riemann's surface, are not uniform functions 395
First kind of integrals on Riemann's surface, general value of 396 see
First kind of integrals on Riemann's surface, number of, linearly independent in particular case 395
First kind of pseudo-periodic function 273
First kind, derivatives of, as algebraical functions 461
First kind, derivatives of, infinities and zeros of 461
First kind, doubly-periodic function of the 273
First kind, inversion of, leading to multiply periodic functions 453
First kind, moduli of periodicity of functions of 439
First kind, moduli of periodicity of functions of, relation between, and those of a function of second kind 442
First kind, moduli of periodicity of functions of, when the functions are normal 447
First kind, normal functions of 446
First kind, number of linearly independent functions of 443
First kind, of functions on a Riemann's surface 436
Fixed (or double) points of substitution 514
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



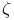 -function
-function  -function
-function