Duality, role of, in formulation of Maxwell's equations 280—282
Dubman, M.R. 300
Duerr, H.P. 80 n
Duff, G.F. 283 n 288
Dust-filled universe 60—62
Dust-filled universe, Friemann's model of 116 118
Dyson, F. 69 n 70 87
Earnshaw's theorem for charged particles 66
Earth, perihelion procession of 46
Eclipses and gravitational deflection of light 46
Eddington, A.S. xiv
Ehrenfest, P. 199 n 211 212
Eigenvalue characteristics of radial equation for simple spherical geon 159
Eikonal 222
Eilenberg, S. 268 n
Einstein curvature tensor 15 17 18
Einstein curvature tensor, standard 1916 general relativity xi
Einstein curvature tensor, views on cosmology 59
Einstein — Bose and Fermi — Dirac statistics, Klauder's formulation of , the distinction between 99—102
Einstein — Maxwell equations, as demand for Rainich — Riemann geometry 253
Einstein — Maxwell theory, variational principle for 215
Einstein — Rosen bridge, contrasted with wormhole 47 48
Einstein's equations 15
Einstein's equations, as bringing about a non-linearity in electrodynamics 254
Einstein's equations, derived from one initial value condition plus covariance 41 see field
Einstein's equivalence principle see "Equivalence principle"
Einstein's field equations 227 234
Einstein's field equations, as leading to consideration of multiply connected topology 47—49
Einstein's field equations, as starting point for deducing Schwarzschild line element 45
Einstein's field equations, as starting point for deriving geodesic equation of motion 133—134
Einstein's field equations, briefly summarized 131—133
Einstein's field equations, effect pi one mass on inertia of another as seen in 58
Einstein's field equations, geometric simplicity of 51
Einstein's field equations, non linearity of 51
Einstein's field equations, quantization of 66—68 71 75—83
Einstein's field equations, question of algorithm to construct all solutions of 51
Einstein's field equations, question of existence of singularity free solutions of, in a properly close space 53—66
Einstein's field equations, singular and non-singular solutions of 63—66
Einstein's general relativity, implications of, for density of mass-energy in universe 116
Einstein, A. xiv 8 12 24 32 47 48 49 58 64 82 129 130 131 133 199 226 230 231 232 236 237 297 302
Eisenhart, L.P. xiv
Elasticity, example of phenomenological theory 78
Electric charge associated with a given homology class 274—280
Electric field, as momentum in field theory 42
Electric field, as projection or trace 285
Electricity as an aspect of topology 232
Electrodynamics, non-linear, effect of on geon structure 140 174—178
Electrodynamics, non-linear, responsible for photon-photon collisions and escape of energy from geon 167—168
Electrodynamics, quantization of, by method of sum over histories 86 87
Electrodynamics, validity of, over unexpected number of powers of ten 66
Electromagnetic energy, density of, expression for 15 16
Electromagnetic energy, Poynting flux of, expression for 15 16
Electromagnetic field, coordinates 32
Electromagnetic field, deduced from geometry 20
Electromagnetic field, duality rotation of 91
Electromagnetic field, fluctuations in 71 73—75
Electromagnetic field, geometrized 227
Electromagnetic field, imprint of, on metric 230
Electromagnetic field, momenta 32
Electromagnetic field, number of parameters associated with 243
Electromagnetic field, occupation number description of 7
Electromagnetic field, space like description of 7
Electromagnetic field, varied types of states for 74
Electromagnetic forces and the structure of the electron 70 71 76—83
Electromagnetic potentials, geometrized 228
Electromagnetic radiation, contribution of, to density of mass-energy in universe 116—117
Electromagnetic wave, standing, trapped in geon 26
Electromagnetic waves, as aspect of Rainich — Riemann geometry 253
Electromagnetic waves, polarization 32 33
Electromagnetism, as an aspect of non-Riemannian geometry xi
Electromagnetism, as foreign field in arena of space-time 95
Electromagnetism, footprints of, on the metric xii
Electromagnetism, geometrical description of 8
Electron field 68—70
Electron, contrasted 129
Electron, dressed vs. undressed 70 71 76—83
Electronic calculator, analysis of geon 161
Electrons, pairs of, produced by gravitons 109—110
Elementary particle physics, concept of charge in, contrasted with classical or wormhole model of charge 50
Elementary particle problem, phenomenological approach to 78
Elementary particles xiii
Elementary particles, as affected by curvature tensor 120
Elementary particles, as small perturbations on vacuum physics 129
Elementary particles, charge of, distinguished from classical picture of charge 232
Elementary particles, nature of 68—71 77—83
Elementary particles, unrelated to classical charges and masses 234
Emptiness of space, in terms of number of geons 136
Empty curved space, as contrasted to space containing matter 47
Energy criterion relating mass and charge of a classical object 82
Energy density, as affecting expansion and recontraction of universe 60 61
Energy density, associated with field fluctuations 77
Energy density, associated with zero point energy of electromagnetic field 221
Energy density, in spherical geon 150—153
Energy density, of electromagnetic field, positive definite character of 18 243
Energy density, of vacuum xiii
Energy, localized concentration of, associated with time-symmetric gravitational wave 57
Energy, not defined for a closed universe 64 66
Energy, of electromagnetic field, inappropriateness of concept in closed space 294
Energy, of one mode of vibration of electromagnetic field, problem of defining 208
Engel, F. 306 n
Epistemology, standpoint for supposing space to be closed 58
Equation of motion, as derived from field equations 49
Equation of motion, of masses derived from field equations xii
Equation of motion, of test particle, derived from field equations 24
Equation of motion, of vortex ring 188
Equation of state, as affecting expansion and recontraction of universe 59—61
Equation of state, for fluid of which a mass is built 25
Equation of state, in analysis of big A problem 120—127
Equilibrium, conditions for, in terms of temperature and Fermi energy 4—6
Equivalence principle, and local linearity of gravitational field equations 80
Equivalence, Einstein's principle of xii
Ernst, F.J., Jr. 142 n 192 216
Euclidean geometry, ruler and compass in 10
Euclidean n-space 256
Euclidean, locally, character of a manifold 256
Euclidean, quasi-Euclidean, character of space at great distances see "Asymptotic flatness"
Euler characteristic 270—271
Euler, H. 140 n 176 219
Euwema, R.N. 4 n 104 109 128
Everett, H. 75 n 111 228 307
Exact form, distinguished from closed form 278—279
Exchange forces, due to neutrinos 89—90
excitons 79
Excitons, as guide to consideration of collective phenomena in vacuum 129
Expansion, and recontraction of universe 58—64
Expansion, of universe 46 59—61
Expansions of fields about a point, either arbitrary or of special symmetry 187
Explosion, of star 125—126
Explosion, production of undersea bubble by 62
Explosion, re-explosion, of gravitational wave 56 57
Exterior derivative 31 32
Exterior differential calculus xv
Exterior differential forms see "Forms"
Extremal field, defined 241 245
Extrinsic curvature invariant, used to formulate content of Einstein's field equations relative to a 3-surface 51
Extrinsic curvature, and initial value condition 41—43
Extrinsic curvature, vanishing of, for time-symmetric gravitational wave 54
Fabric of history, choice in how to unroll 84—87
Faraday, M. 232
Farley, A.E. xiv
Feinberg, G. 6
Fermi coupling 2—3
Fermi coupling, compared with gravitational coupling 110
Fermi coupling, in neutrino processes 103—110
Fermi coupling, universality of 7
Fermi energy, in cold dense star 122
Fermi energy, in neutrino equilibrium 4—6
Fermi field 1 2
Fermi interaction, as relevant to collisions in a neutrino geon 179—180 182
Fermi statistics 8
| Fermi — Dirac and Einstein — Bose statistics, Klauder's formulation of the distinction between 99—102
Fermi — Dirac degree of freedom 98—99
Fermi — Dirac statistics 2
Feynman's method of sum over histories, and quantum fluctuations in geometry 183—184
Feynman's method of sum over histories, extended to Fermi field 97—102
Feynman's method of sum over histories, topological aspect of 83—87
Feynman's quantum propagator and classical field action 283
Feynman, R.P. 70 n 87 103 122 131 183
Field equations of general relativity, as basis for deriving equation of motion of test particle see "Equation of motion"
Field equations of general relativity, as statements about 4-space in which 3-space is imbedded 34 35
Field factor, 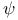 , in expression for metric at moment of time symmetry 55 57 , in expression for metric at moment of time symmetry 55 57
Field oscillators, in description of electromagnetism 7
Field, G.B. 117 n
Field, W. xiv
Fields vs. particle, distinction 2
Fields, electromagnetic, measured in purely geometric units 13 14
Fields, number of independent interacting 68 82
Fierz, M. xv 90 111 235 307
Fine structure constant ("137") 10
Fine structure phenomena, in spectral lines 9
Finkelstein, D. 94
Fission and fission bomb as source of gravitational radiation 114
Fission products, neutrino spectrum of 107
Flat space time, as trivial solution of Einstein's field equations 53
Flat spaces, classification of 244
Fletcher, C.H. 188 n
Fletcher, J.G. 96 n
Fluctuations in geometry 71 72 75—83 129
Fluctuations, meaning of 73
Fluctuations, quantum, in electromagnetic field 2
Fluctuations, quantum, in geometry xiii 2 183—184
Fluctuations, quantum, in vacuum 69—72 75—83
Fluegge, S. 78 n
Fluid, incompressible and gravitating, conditions within 121
Flux integral, as measure of electric charge 49 50
Foam from breakup of wave crest 67 68
Foam-like structure of space, virtual 76 79 81 82 94 129
Fock V. and D. Ivanenko, coefficients 95
Fock, V. xiv 96
Focussing properties of irregularly curved space 114—117
Focussing, of geodesies 65
Footprints, of electromagnetic field on metric 16 20
Form factor in neutrino interactions 104 106
Form, exterior differential, of p-th order 262
Forms, closed, compared with closed chains 279
Forms, differential, for electromagnetism 31
Forms, exterior differential xv
Forms, exterior differential, of 1st and 2nd order 261
Forms, integration of 264—266 272—279 281—282
Four dimensions, reason for xii
Foures-Bruhat, Y. 31 n 33 62 288 295 297
Fourier analysis of perturbations in metric, inappropriate in a space, which departs greatly from flatness 44
Fourier analysis, at moment of time symmetry 55
Fourier analysis, in curved space 289—294
Fourier analysis, of electromagnetic field 8
Friedmann dust-filled model for universe 60—62 116 118
Fronsdal, C. 47 n
Frontiers, unexplored, elementary particle physics 6
Frontiers, unexplored, gravitation physics 6
Fuller, R.W. 65
Fundamental length, as conceived by Ivanenko and Heisenberg 79—80
Fundamental spinor field, as conceived by Ivanenko and Heisenberg 79—80
Galactic separations, and wave length of gravitational radiation 115 130
Galaxies, density of mass-energy contributed by 116—117
Galaxies, difference between conditions in and between, as relevant to geon destruction 29
Galaxies, minimum angular diameter of, in Einstein's picture of universe 118—119 130
Galaxy, distant, and red shift 59
Gamow, G. 4 n 90 127 143
Gas currents, as smudging ideal gravitational red shift 46
Gast, P.F. v
Gatto, R. 105 n
Gauge invariance, in wave function of electromagnetic field 74
Gauge invariance, in wave function of geometrodynamics 75
Gauss, C.F., theorem of 268 273—275
Gauss, C.F., theorem of, as applied to charge 50
Gauss, C.F., theorem of, derived by metric-free arguments 280
Gauss, C.F., theorem of, escape from in a multiply connected space 182—184
Gauss, C.F., theorem of, unexpected character of in a multiply connected space 233
GEHENIAU, J. 187 n 307
Gell-Mann, M. 103 n
General relativity, as a "master theory" of physics xii 25
General relativity, changed status of cosmological term in 59
General relativity, equation for hydrostatic equilibrium in 123 124
General relativity, local character of field equations in 231
General relativity, observational tests of, question of position of Hubble expansion among 59
General relativity, problem of quantization of 184
General relativity, quantization of 66—68 71 75—83
General relativity, quantization of, by method of sum over histories 86
General relativity, relation to geometrodynamics 9
General relativity, scope and simplicity of 21
Generating formalism, in problem of minimal surface, and as sought in relativity 52
Geodesic clock 10—12
Geodesic equation of motion, as derived from Einstein's field equations 133—134
Geodesic, its inability to connect some pairs of points 64
Geodesically parallel space-like hypersurfaces, family of, which eventually becomes singular 53
Geodesies of photons 221—224
Geometrical optics, as related to superposition of waves 221—224
Geometrization of electromagnetic field 226
Geometrized charge 82
Geometrized charge, measure of 274
Geometrized components of electromagnetic field, defined 14
Geometrized electromagnetic field 237
Geometrized mass 82
Geometrodynamical zoo, list of objects presently contained in 50
Geometrodynamics xv
Geometrodynamics, as a "master theory" of physics 25
Geometrodynamics, as a subcase of Riemannian geometry 244
Geometrodynamics, briefly outlined 237
Geometrodynamics, defined xi 9 21
Geometrodynamics, equations of, number of solutions of 37—40
Geometrodynamics, examples of, time-symmetric gravitational wave 54
Geometrodynamics, inconsistent because of singularities 65
Geometrodynamics, of curved empty space, as illustrated by two body problem 49
Geometrodynamics, omits cosmological term 59
Geometrodynamics, on recontraction of universe 62
Geometrodynamics, quantum xiii
Geometrodynamics, quantum, as a "model theory" xiii
Geometrodynamics, status of 129
Geometrodynamics, topology of, and topology of sum over histories, question of relation between 87
Geometrodynamics, unexplored features of, related to hydrodynamics (table) 187—189
Geometry, fluctuations in 71 72 75—83
Geons 133—224
Geons, active region of 26
Geons, analogy to vortex ring 188
Geons, and wormhole mouths in combination 301
Geons, as members of geometrodynamical zoo 50
Geons, breakup by strong inhomogeneous fields 135
Geons, briefly described xii 226
Geons, built of neutrinos 111
Geons, collective disturbances within 170
Geons, composed of mixture of neutrinos and photons 181
Geons, defined 27
Geons, diagram for regions of strong field in 133
Geons, distinguished from matter 68 82
Geons, early overall assessment of 184—185
Geons, excitation and breakup of by inhomogeneous fields 30
Geons, excitation of internal degrees of freedom of 134—135
Geons, fission of 171
Geons, gravitational tensions in 71
Geons, interaction between 171—173
Geons, leakage of energy from 28 143—146 163—168
Geons, leakage of neutrinos from 178
Geons, loss of energy from by acceleration of swept up ions 29
Geons, metric in simple spherical (diagram) 26
Geons, model for, offered by glass sphere 144
Geons, neutrino 175
Geons, neutrino, fission of 178
Geons, neutrino, limit on density of, set by neutrino interactions 179—181
Geons, no reason to consider now present 29
Geons, order of magnitude analysis of toroidal 141—143
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



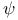 , in expression for metric at moment of time symmetry
, in expression for metric at moment of time symmetry