|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lambert J.B., Mazzola E.P. Ч Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Data points, for 1D spectral description (np/2) 49Ч52
Data points, for first (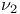 ) dimension spectral acquisition 241 247 251 ) dimension spectral acquisition 241 247 251
Data points, for second (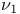 ) dimension spectral acquisition 247 251 ) dimension spectral acquisition 247 251
Data points, number (np) for 1D spectral acquisition 41 49Ч51
Data sets, imaginary 247
Data sets, real 247
Data-processing parameters 243Ч250
DAVINS 116 314
Decalins 124
Decane, carbon relaxation 135
Deceptive simplicity 116Ч117 315
Decoupler, calibration 60Ч61
Decoupler, field strength 47 60
Decoupler, modulation frequency 58 61
Decoupler, offset 47
Decoupler, sample heating effects 243 258 260
Decoupler, status 47
Decoupling 18 25 46Ч47 80 105 136 144Ч146 150 152 155 158Ч160 189 see "Heteronuclear "Double
Degassing 34
Delay time 132
Dephasing 203Ч204
DEPT 156Ч157 161Ч162 204 207 220 221Ч222 225Ч226 229Ч231 236Ч237 280Ч282
Depth gauge 34
Deuterated solvents for locking 33 35
Deuterated solvents, chemical shifts 55
Diamagnetic anisotropy 64Ч69 71Ч74 81 86
Diamagnetic anisotropy, shielding 62 68 80
Diamagnetic anisotropy, susceptibility 65Ч66
Diamagnetic anisotropy, susceptibility, bulk 77
Diastereotopic groups 103Ч104 138 140 146 179Ч180 182 189 193 261Ч262 279 334Ч335 339Ч341
Dichloroethene, HCC coupling 108
Dichlorophenols,  spectra 125Ч126 spectra 125Ч126
dielectric constant 77Ч78
Dienes, vicinal couplings 112
Diethyl ether,  spectrum 16 spectrum 16
Difference decoupling 145
Difference NOE 151
Difference spectra 237 see
Difluoromethane 99Ч100
Digital resolution, in 1D spectra 50Ч52 180
Digital resolution, in the first (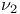 ) dimension in 2D spectra 246Ч247 ) dimension in 2D spectra 246Ч247
Digital resolution, in the second (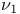 ) dimension in 2D spectra 246Ч247 ) dimension in 2D spectra 246Ч247
Digital resolution, optimizing 247
Digital signal filtration 46
Dihedral angle 283 285Ч286 291 293
Dimensionless spin 295 298
Dimethyl sulfoxide, nonexchanging solvent 75
Diphenylketimine, 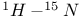 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Dipolar decoupling 25 27
Dipole-dipole coupling 25Ч26 267
Dipole-dipole coupling, relaxation 131Ч132 150 152 195Ч196 198 205 317Ч321 331Ч332
DIPSI-2 256 see
Dirac notation 303
Direct coupling (D) 105
Dispersion mode 53 183Ч184 247 300Ч301 330 see
Dispersive tails, in phase-sensitive COSY spectra 252
Dispersive tails, with absolute-value data 246 see phase-twisted"
Disulfides, hindered rotation 138
DNMR3 142
Double bond, shielding 67Ч68
Double irradiation 26 see
Double quantum coherence 162Ч163 165 183 189 199 204 326Ч332
Double quantum filtration 183Ч185
Double quantum transition 304
Double resonance 18 131 136 143Ч155 160
Doublet of doublets 20
DPFGSE 205
DPFGSE-NOE 240 268 see
DQF-COSY 183Ч184 207 214Ч216 221 246 253Ч257 332
Dreiding model 291
Dummy scans see "Steady-state scans"
Dwell time 40
Dynamic effects 23Ч25
Dynamic effects, NMR 136Ч143
EBURP 166
Echo experiment 331
Effective correlation time 132 135 198 317Ч319
Effective correlation time, nuclear charge 106
Effective correlation time, spin-lattice relaxation time 233
Effective correlation time, spin-spin relaxation time 241 248
Electric-field effect 77Ч79
Electric-field effect, shielding 69
Electromagnets 31 36Ч37
Electron density 80
Electron density, spin relaxation 321
Electron spin resonance 183
Electronegativity 6 62Ч63 81
Electronegativity and vicinal couplings 111 see
Empirical correlations, for  chemical shifts 82Ч88 92 chemical shifts 82Ч88 92
Empirical correlations, for  chemical shifts 71Ч76 91 chemical shifts 71Ч76 91
Enantiotopic groups 99Ч100 103 279 334Ч335 337Ч341
Energy-level diagram 304Ч310
Enol ethers,  chemical shifts 86 chemical shifts 86
Epoxides, vicinal coupling 111
Equatorial position 66Ч67 83Ч84 110 291Ч292
Equatorial position, protons, relaxation 134
Ernst angle 43
Esters,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Esters,  chemical shifts 70 chemical shifts 70
Ethane,  chemical shift 81Ч82 chemical shift 81Ч82
Ethane, 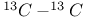 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Ethane,  chemical shift 63 66 69Ч70 chemical shift 63 66 69Ч70
Ethane, HCC coupling 108
Ethanol 68
Ethene,  chemical shift 81 chemical shift 81
Ethene, 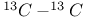 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Ethene,  chemical shift 63Ч64 66 71 chemical shift 63Ч64 66 71
Ethene, 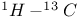 coupling constant 105 coupling constant 105
Ethene, HCC coupling 108
Ethene, HCH coupling 107
Ethers,  chemical shifts 84 chemical shifts 84
Ethers,  chemical shifts 70 chemical shifts 70
Ethyl trans-crotonate 144
Ethyl trans-crotonate,  chemical shift 63 chemical shift 63
Ethyl trans-crotonate,  spectrum 19Ч20 spectrum 19Ч20
Ethylbenzene 102Ч103
Ethyne,  chemical shift 81 chemical shift 81
Ethyne, 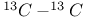 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Ethyne,  chemical shift 63 66 71 chemical shift 63 66 71
Ethyne, 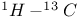 coupling constant 105 coupling constant 105
Ethyne, HCC coupling 108
Evolution period 173 192
EXAN II 318
Exchangeable protons 75
Excitation sculpting 205
Exponential weighting 48Ч49
EXSY 196 198Ч199 207 232 268Ч269 331Ч332
EXSY, phase-sensitive 199
Extreme narrowing condition 318Ч321
Extreme narrowing condition, limit 132 149Ч151 197
F,F-COSY 187
False peaks 180
Fast exchange 23Ч24 137 143 198
FDM see "Filter diagonalization method"
Fermi contact mechanism 104Ч105
FID see "Free induction decay"
Field sweep 7
Filter bandwidth 42 57
Filter diagonalization method 250
Filtering of sample solutions 33Ч34
Filters, analog 42 46
Filters, digital 46
First-order spectra 13 56 98Ч99 101Ч102 115 123 125 145 303Ч305
First-order spectra, pseudo 56
Flip angle, 1D 43Ч45
Flip angle, 2D 242 see
Flip-flop mechanism 134
Flock 192Ч193 264Ч266
FLOCK, BIRD pulse functions 265Ч266
Fluorine couplings 109 114Ч115 119
| Fluoromethane 5
Fluxional molecules 140Ч142
Folding 180 see
Forbidden transitions 304
Formaldehyde, HCH coupling 107
Four-dimensional NMR 203
Fourier analysis 12
Fourier transformation 13 49 172 174 183 201 330
Fourier transformation, number 50 56
Fourier transformation, spectrometer operation 31Ч32
Free-induction decay 11Ч13 36 172 174 187
Frequency domain 13
ft see "Fourier transformation"
Full width at half maximum 52 see
FWHM see "Full width at half maximum"
Gamma effect, on  chemical shifts 82Ч85 chemical shifts 82Ч85
GARP 258Ч259 see
Gated decoupling 48 151Ч152 158
Geminal coupling 17 105Ч109 120 123 176 182 189 207 315
Gentamycin, DEPT spectra 156Ч157
Glycine 177Ч178 180
Gradient coils 39
Gradient coils, echo 204Ч205
Gradient coils, pulse 203 see
Gyromagnetic ratio ( ) 2Ч4 22 106Ч107 132 146 149Ч150 153 159 193 295 319 321 ) 2Ч4 22 106Ч107 132 146 149Ч150 153 159 193 295 319 321
Half-chair conformation 291
Haloalkanes,  chemical shifts 80Ч81 84Ч85 chemical shifts 80Ч81 84Ч85
Haloalkanes,  chemical shifts 62Ч63 68 71 chemical shifts 62Ч63 68 71
Haloalkanes, hindered rotation 138
Halogenated alkanes 138
Hamiltonian matrix 304Ч305 307Ч309
Hamiltonian matrix, operator 302Ч304 322Ч324
Hard pulses 165
Hartmann Ч Hahn condition 27 185
Heavy atom effect 81
Heisenberg uncertainty principle 22
Heptamethylbenzenium ion 198
HETCOR 187Ч189 193Ч195 203 207 216Ч217 220 222Ч232 261Ч262
Heterocycles, ring reversal 139
Heteronuclear correlation 187Ч195
Heteronuclear correlation, decoupling 146Ч148 151 164Ч165
Heteronuclear correlation, multiple quantum coherence 161
Heterotopic groups 340
Hindered rotation 137Ч139
HMBC 193Ч194 207 262Ч264 284
HMBC, 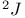 , , 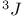 -HMBC modification 274Ч276 -HMBC modification 274Ч276
HMBC, gradient version 263Ч264
HMBC, nongradient version 263Ч264
HMQC 189Ч190 193 201Ч202 204 207 258Ч259
HMQC, gradient version 258
HOHAHA 185 198
Homoallylic coupling 113 282 287
Homogeneity see "Magnetic-field homogeneity"
Homomorphic groups 340
Homonuclear decoupling 146 151
Homotopic groups 99Ч100 335Ч337
HSQC 192Ч193 258Ч261 281Ч282
HSQC, gradient version 259Ч261
HSQC, multiplicity-edited 271Ч273
HSQC-TOCSY 266Ч267
hybridization 63 66Ч68
Hybridization and coupling 105Ч106
Hydride shifts 141
Hydrogen bonding 78
Hydrogen-bonding effects, on  chemical shift 68 75 chemical shift 68 75
Hydroxyl protons 75
Hydroxyl protons, resonance 23
Hypercomplex Fourier transform 241
Hyperconjugation 107 113
Imaginary part 49 183 299Ч300
Imaginary part, spectrum 50 see
Imines, HCN coupling 108
INADEQUATE 106 162Ч163 165 183 189 204
INADEQUATE, 2D 199Ч200 207 213 232 332Ч333
Increments see "Time increments"
Indene, allylic coupling 113
Inductive effect 63 68Ч70 72Ч74 80 84Ч85 112 182 193 see
INEPT 156Ч162 187 192 325
INEPT-INADEQUATE 200 207
Inhomogeneity effects 37Ч38
Integration 19 21 57Ч58
Interleaved acquisition 237 243 see
Inverse detection 189Ч190
Inverse-gated decoupling 48
Inversion recovery 133 135 163Ч165 168 234 327Ч328
Isobutane,  chemical shifts 83 chemical shifts 83
Isobutylene,  chemical shift 86 chemical shift 86
Isobutylene,  chemical shift 71 chemical shift 71
Isochronous 102 334Ч336 338
Isomontanolide 213
Isonitrile 167
Isopropyl group 17 103
Isotope effects, on chemical shifts 79 118
Isotropic groups 63Ч64
Isotropic mixing sequences, DIPSI-2 256
Isotropic mixing sequences, GARP 258Ч259
Isotropic mixing sequences, MLEV-17 256
Isotropic mixing sequences, WALTZ-16 256 258 262 266
Isotropic mixing sequences, WURST 258Ч259
J-filter, in HMBC experiment 262
J-resolved spectroscopy 186Ч187 207
Jeener experiment 172 176
Karplus equation 76 109Ч112 193 285 324
Ketones,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Laboratory time scale 136
Lactones,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Lanthanide shift reagents 116
LAOCN 3 116 314
Larmor frequency 3Ч4 8Ч10 12 131 143 148 162 187 190 203 296 317Ч318 321 323Ч324 328 333
Leucine 177Ч180
Line broadening 48 238 240
Line broadening, functions 48Ч49
Line broadening, parameter 58Ч61
Line shape 36
Line shape, absorption mode 52
Line shape, phase-twisted 246 252
line width 10 12 302
Line width at half-height see "Full width at half maximum"
Linear prediction 247Ч250
Linear prediction, backward 250
Linear prediction, extensions 248 251 258 260
Liquid crystal solvent 105
Local electron currents 62Ч63
Lock, external 35
Lock, internal 35
Lock, optimizing 36
Lock, phase 35Ч36
Lock, receiver 35
Lock, saturation 35 37 237Ч238
Lock, signal 33 35Ч36
Lock, transmitter 35
Locking, automatic 35
Locking, field/frequency 35Ч36
Lone pair, shielding 63Ч68
Long-range COSY 182Ч183 207 253
Long-range COSY, coupling 105 112Ч115 124 177 182Ч183 192Ч193 207
Longitudinal relaxation see "Spin-lattice relaxation"
Lowering operator 306
Lutidines,  spectra 124Ч125 spectra 124Ч125
Lysine 184Ч185
Magic angle 65
Magic-angle spinning 26 32
Magnetic equivalence 99Ч104 106 115 117 122 334 336Ч339
Magnetic equivalence, moment 1 3 5 14 131 144 295 298 302 321
Magnetic equivalence, resonance imaging 203
Magnetic-field homogeneity 36 52
Magnetic-field homogeneity, optimizing 37
magnetization 8Ч12 131 134 158Ч159 161 163 172Ч173 175 180 184Ч185 187 189Ч190 192 195Ч197 203Ч204 297Ч301 322Ч331
Magnetization, transfer 143 146 175Ч176 181Ч183 185 187 196Ч199 see
Magnetogyric ratio 2 see
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



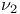 ) dimension spectral acquisition
) dimension spectral acquisition 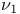 ) dimension spectral acquisition
) dimension spectral acquisition  spectra
spectra 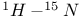 coupling constant
coupling constant  chemical shifts
chemical shifts 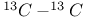 coupling constant
coupling constant 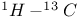 coupling constant
coupling constant  )
) 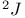 ,
, 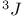 -HMBC modification
-HMBC modification