|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Lambert J.B., Mazzola E.P. Ч Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
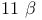 -Hydroxyprogesterone, NOE 205Ч206 -Hydroxyprogesterone, NOE 205Ч206
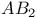 spectrum 115 312Ч313 spectrum 115 312Ч313
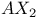 spectrum 15 17 100 115 312Ч313 spectrum 15 17 100 115 312Ч313
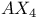 spectrum 17 spectrum 17
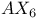 spectrum 17 spectrum 17
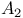 spectrum 306Ч308 310 spectrum 306Ч308 310
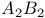 spectrum 339 spectrum 339
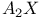 spectrum see " spectrum see "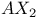 spectrum" spectrum"
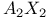 spectrum 100 116Ч117 118 339 spectrum 100 116Ч117 118 339
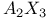 spectrum 16 17 103 spectrum 16 17 103
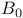 (static magnetic field) 31 36 295 (static magnetic field) 31 36 295
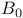 (static magnetic field), effects of inhomogeneity on spectra 37Ч38 (static magnetic field), effects of inhomogeneity on spectra 37Ч38
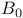 (static magnetic field), homogeneity see "Magnetic-field homogeneity" (static magnetic field), homogeneity see "Magnetic-field homogeneity"
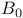 (static magnetic field), optimizing homogeneity 37 (static magnetic field), optimizing homogeneity 37
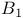 (radiofrequency magnetic field), calibration 58Ч60 (radiofrequency magnetic field), calibration 58Ч60
 (radiofrequency magnetic field), transmitter 31Ч32 (radiofrequency magnetic field), transmitter 31Ч32
 (double resonance magnetic field), calibration 60Ч61 (double resonance magnetic field), calibration 60Ч61
 (double resonance magnetic field), decoupler 32 (double resonance magnetic field), decoupler 32
 see "Spin-lattice relaxation time" see "Spin-lattice relaxation time"
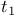 noise 180 250 254 259Ч260 263Ч264 noise 180 250 254 259Ч260 263Ч264
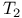 see "Spin-spin relaxation time" see "Spin-spin relaxation time"
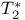 see "Effective spin-spin relaxation time" see "Effective spin-spin relaxation time"
 , ,  -Unsaturated ketones, -Unsaturated ketones,  chemical shifts 86 chemical shifts 86
 -Thujene 103 -Thujene 103
 -Chloroacrylic acid 175Ч176 -Chloroacrylic acid 175Ч176
 -Chloroacrylic acid, COSY spectrum 175 -Chloroacrylic acid, COSY spectrum 175
 -Methylglutaric acid 117 -Methylglutaric acid 117
 -Quinolmethanol clathrate 26 -Quinolmethanol clathrate 26
 -Anti effect 83Ч84 -Anti effect 83Ч84
 -Gauche effect 83 -Gauche effect 83
1,1,2-Trichloroethane,  spectrum 15 spectrum 15
1,1-Difluoroethene 99Ч101 109
1,1-Dimethylallene, long-range coupling 113
1,2-Dichlorobenzene,  spectrum 101Ч102 123 spectrum 101Ч102 123
1,3-Butadiene, long-range coupling 113Ч114
1,3-Cyclohexadicne,  chemical shifts 72 chemical shifts 72
1,3-Cyclohexadicne, HCCH coupling 112
1,3-Cyclopentadiene,  chemical shifts 72 chemical shifts 72
1,3-Cyclopentadiene, HCCH coupling 112
1,3-Dioxane 123
1,4-Cyclohexadiene, homoallylic coupling 113
1,4-Dioxane, isotope effects 79
1-Butene,  chemical shift 86 chemical shift 86
1-Chloro-2-fluorobenzene 69
1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene,  spectrum 13Ч14 spectrum 13Ч14
1-Decanol 168
1-Dehydrotestosterone,  spectrum 145 spectrum 145
2,3-Dibromopropionic acid, COSY spectra 181
2-Butyne, long-range coupling 113
2-Chloroethanol,  spectrum 102 316 spectrum 102 316
2-Methylacryloin, allylic coupling 113
3,4-Homotropilidine 140
3-Fluorocamphor 211Ч212
3-Hydroxybutyric acid 12Ч13
3-Hydroxybutyric acid,  spectrum 18 146 spectrum 18 146
3-Methylcyclopropene 100
4-Chlorobenzaldenyde 74
AA'BB' spectrum 101Ч102 116Ч117 136Ч137 315Ч316 339
AA'XX' spectrum 100Ч102 106 115Ч117 315Ч316 339
AB spectrum 98Ч99 115 144 302Ч303 308Ч314
ABC spectrum 111 116 314
Absolute-intensity representation 59 234
Absolute-value representation 183 244 246 250 252
Absorption mode 52Ч53 183Ч185 247 300Ч301 330 see
ABX spectrum 103 105Ч106 111 116Ч117 182 313Ч314
Accordion excitation 275 see modification"
Acetaldehyde,  chemical shift 84 88 chemical shift 84 88
Acetaldehyde,  chemical shift 71 73 chemical shift 71 73
Acetaldehyde, diethyl acetal 103
Acetaldehyde, HCC coupling 108
Acetamide, 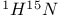 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Acetic acid,  chemical shift 88 chemical shift 88
Acetic acid,  chemical shift 71 75 chemical shift 71 75
Acetone 12Ч13 17 26
Acetone,  chemical shift 84 88 chemical shift 84 88
Acetone,  chemical shift 71 chemical shift 71
Acetone, HCC coupling 108
Acetone, HCH coupling 107
Acetonitrile,  chemical shift 86 chemical shift 86
Acetonitrile,  chemical shift 71 chemical shift 71
Acetonitrile, 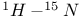 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Acetonitrile, HCH coupling 107
Acetonitrile, NH coupling 167
Acetonitrile, solvent effect 77Ч78
Acetonitrile, vicinal coupling 111
Acetyl chloride  chemical shift 71 chemical shift 71
acetylene see "Ethyne"
Acid chlorides,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Acquisition parameters, 1D 39Ч48
Acquisition parameters, 2D 241Ч243
Acquisition time, 1D 42
Acquisition time, 2D 242
Acrolein, dimethyl acetal 194Ч195
Acrylonitrile,  spectrum 111 spectrum 111
Active coupling 182 246 254
Adiabatic relaxation 320
Alcohols,  chemical shifts 84 chemical shifts 84
Alcohols,  chemical shifts 70 75 chemical shifts 70 75
Aldehydes,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Aldehydes,  chemical shifts 73 chemical shifts 73
Aldehydes, shielding 68
Aliasing 40Ч41 see
Aliasing, folded signals 41
Aliasing, noise 46
Alkanes,  chemical shifts 82 85Ч86 89 90 chemical shifts 82 85Ч86 89 90
Alkanes,  chemical shifts 69Ч73 chemical shifts 69Ч73
Alkanes, vicinal coupling 111Ч112
Alkynes,  chemical shifts 86 chemical shifts 86
Alkynes,  chemical shift 71 chemical shift 71
Alkynic coupling 113
Allene, long-range coupling 113
Allenes,  chemical shifts 81 88 chemical shifts 81 88
Allowed transitions 304Ч307
Allylic coupling 112Ч114 282 287Ч288
Alpha effect, on  chemical shifts 82Ч85 chemical shifts 82Ч85
Amide bond rotation 137
Amides,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Amides,  chemical shifts 70 76 chemical shifts 70 76
Amine inversion 139Ч140
Amines,  chemical shifts 84 chemical shifts 84
Amines,  chemical shifts 70 76 chemical shifts 70 76
Amines, HCN coupling 108
Ammonium ion, 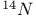 splitting 136 splitting 136
Ammonium ion, 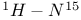 coupling constant 106 coupling constant 106
Ammonium salts,  chemical shifts 70 76 chemical shifts 70 76
AMX spectrum 103 106 111 115 182 185Ч186
Angular frequency 3
Angular frequency, methyl group 124
Angular frequency, momentum 1Ч2 80Ч81 296
Anhydrides,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Aniline, 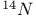 line width 167 line width 167
Anilines,  chemical shifts 76 chemical shifts 76
Anisochronous 334 339Ч341
Anisole 63 74
Anisotropic rotation 134Ч135
Antiecho experiment 331
Antiphase 156 158 160 163 184 187 189
Antiphase, component 325Ч331
Antisymmetric wave function 310Ч312
Apodization 50Ч51 166 244 246 248
apt see "Attached proton test"
Aromatic solvent-induced shifts 77Ч79
Aromatics,  chemical shifts 87 90 chemical shifts 87 90
Aromatics,  chemical shifts 73Ч75 chemical shifts 73Ч75
Aromatics, ortho coupling 111
Artifacts, 2D 196Ч197 248 250Ч252 254 259 262 268 269
ASIS see "Aromatic solvent-induced shifts"
Atomic inversion 139Ч140
Atomic inversion, mass 1Ч2
Attached proton test 155 161 235Ч236
| Attached proton test, optimizing sensitivity 235
Autogain feature 45
Average energy of excitation 80
AX spectrum 13Ч14 17 98Ч99 115 148Ч149 162 174Ч175 187 303Ч304 308 310 312
Axial peaks 180 see
Axial peaks, position 66Ч67 83Ч84 110 291Ч292
Axial peaks, protons, relaxation 134
Axial-equatorial interchange 137
Aziridines, nitrogen inversion 139
Barbaralone 141
Baseline correction 54 58
Baseline correction, noise 250
Baseline correction, roll 250
Benzaldehyde,  chemical shift 88 chemical shift 88
Benzene,  chemical shift 81 86 chemical shift 81 86
Benzene,  chemical shift 64 73 chemical shift 64 73
Benzene,  spectrum 4 17 spectrum 4 17
Benzene, 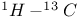 coupling constant 105 coupling constant 105
Benzene, long-range coupling 113Ч114
Benzene, shielding of 64Ч65 72
Benzene, solvent effect 77Ч78
Benzoquinones 117
Benzylic coupling 113Ч114
Beta effect on  chemical shifts 82Ч85 chemical shifts 82Ч85
Biphenyl rotation 138
Bird 189Ч192 258Ч261 265
Bismethylene 315Ч316
Biuret 136
Bloch equations 297Ч301 322
Bloch size 45 243 see
Bloch Ч Siegert shift 146
Boltzmann population 148 151 158
Boltzmann's law 3
Bond anisotropy 67 71
Bond anisotropy, order 81 112
Bond anisotropy, shifts 141Ч142
Boron-11 couplings 106
Branching effect 83Ч84
Broadband decoupling 35 47 146 164 204 242
Bromine relaxation 320Ч321
Bromochloromethane 99Ч100
Bromoethane 99
Brucine,  spectrum 204 spectrum 204
Buildup rate see "NOE"
Bullvalene 141
BURP 166
Butyroacetone 101Ч102
calibrations 58Ч61 237
Calibrations, decoupler pulses 60Ч61
Calibrations, pulse widths 58Ч60
Calicene 138
CAMELSPIN 198
Camphor, HMQC spectrum 189Ч190
Carbocations, shielding 80
Carbon disulfide, solvent effect 77Ч78
Carbon tetrachloride 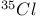 line width 136 line width 136
Carbon-13 couplings 105Ч106 108 119 121 123 162Ч163 192Ч194 199Ч200
Carbonyl group, shielding 67 72 80
Carbonyl groups,  chemical shifts 88 91 chemical shifts 88 91
Carboxylic acid, derivatives,  chemical shifts 88 chemical shifts 88
Carboxylic acids,  chemical shifts 68 75 chemical shifts 68 75
Chair conformation 110 291
Chemical equivalence 99Ч103 106 117Ч118 334Ч335 337
Chemical exchange 136Ч143
Chemical exchange in 2D 195Ч196 198Ч199
Chemical shielding anisotropy 25
Chemical shielding anisotropy, relaxation 132 320
Chemical shift 5Ч8 56 62Ч88 302Ч303
Chemical-shift criterion 102
Chemical-shift difference, AB spectrum 309
Chlorobenzene, relaxation time measurement 133
Chloroform 14
Chloroform,  spectrum 159Ч160 spectrum 159Ч160
Chloroform,  chemical shift 63 chemical shift 63
Chloroform, INEPT spectrum 159Ч160
Chloroform, isotope effects 79
Cholestane 215
Cholesteryl acetate,  spectrum 155 spectrum 155
Cholesteryl acetate, APT spectrum 155
cis-1,2-Dichlorocyclopropane 104
Cleaning of NMR tubes 33
Closely coupled nuclei 185Ч186 see
Coalescence temperature 142Ч143
Coherence 9 326
Coherence, order 204 326Ч333
Coherence, selection 165 204
Coherence-level diagram 327Ч333
COLOC 192Ч193 264Ч266
Combination line 115 312
Complete line shape analysis 142Ч143
Composite pulses 148Ч165
Conformation 335Ч340
Conformation, anti 335 337Ч339
Conformation, gauche 335 337Ч339
Conformation, population effects 335Ч336 338Ч339
Conjugated coupling 113
Conjugation see "Resonance effects"
Connectivity 199 203
Contact shifts 321
Continuous-wave operation 7 31 35
Contour Plot 176 250Ч251
Cope rearrangement 140Ч141
COSY 172Ч186 196Ч198 207 208Ч212 217 219 222Ч232 252Ч253 281Ч285 328Ч332
COSY, gradient version 252 see "Phase-sensitive
COSY45 181Ч182 207 211Ч212 252Ч253
Coupling constant 13Ч19 56 98Ч130 302Ч303 305
Coupling constant, mechanism 104Ч105
Coupling constant, relative signs 105
Coupling constant, residual 60Ч61
Coupling constant, sign 104Ч105
Coupling, between equivalent nuclei 98 101 107 118Ч119
Coupling-constant criterion 102 122
Cross peaks 176 330Ч333
Cross polarization 27 185
Cross sections, in spectral analysis 250 see "Contour
Crotonaldehyde,  chemical shift 72 chemical shift 72
Cubane, 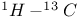 coupling constant 105 coupling constant 105
CW see "Continuous wave"
Cyclobutane,  chemical shift 83 chemical shift 83
Cyclobutane,  chemical shift 63 69 chemical shift 63 69
Cycloheptatriene 124
Cycloheptatrienyltin 142Ч143
Cyclohexane 104
Cyclohexane ring, shielding 66
Cyclohexane,  chemical shift 83 chemical shift 83
Cyclohexane, dynamic  spectrum 24Ч25 spectrum 24Ч25
Cyclohexane, HCH coupling 107
Cyclohexane, isotope effects 79
Cyclohexane, ring reversal 137
Cyclohexanes,  chemical shifts 83Ч84 89 chemical shifts 83Ч84 89
Cyclohexanes, long-range coupling 114
Cyclohexanes, vicinal couplings 110
Cyclohexanone  chemical shift 88 chemical shift 88
Cyclohexene,  chemical shift 86 chemical shift 86
Cyclohexene, HCCH coupling 112
Cyclooctane, conformation 139
Cyclooctatetraene, bond shifts 141Ч142
Cyclooctatetraene, ring reversal 139
Cyclooctatetreneiron tricarbonyl 142
Cyclopentanol,  chemical shift 85Ч86 chemical shift 85Ч86
Cyclopropane,  chemical shift 83 chemical shift 83
Cyclopropane,  chemical shift 69 chemical shift 69
Cyclopropane, 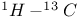 coupling constant 105 coupling constant 105
Cyclopropane, HCH coupling 107
Cyclopropane, shielding 67
Cyclopropanes, vicinal couplings 110Ч111
Cyclopropene 100 118Ч119
Cyclopropene, HCCH coupling 112
Cyclops 45 165 180
Dante 166
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



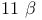 -Hydroxyprogesterone, NOE
-Hydroxyprogesterone, NOE 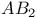 spectrum
spectrum 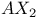 spectrum
spectrum 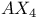 spectrum
spectrum 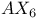 spectrum
spectrum 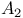 spectrum
spectrum 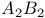 spectrum
spectrum 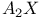 spectrum
spectrum 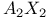 spectrum
spectrum 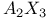 spectrum
spectrum 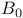 (static magnetic field)
(static magnetic field) 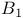 (radiofrequency magnetic field), calibration
(radiofrequency magnetic field), calibration 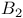 (double resonance magnetic field), calibration
(double resonance magnetic field), calibration 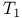
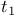 noise
noise 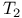
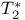
 ,
,  -Unsaturated ketones,
-Unsaturated ketones,  chemical shifts
chemical shifts  -Anti effect
-Anti effect  spectrum
spectrum 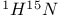 coupling constant
coupling constant 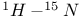 coupling constant
coupling constant 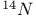 splitting
splitting 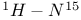 coupling constant
coupling constant 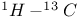 coupling constant
coupling constant 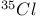 line width
line width