|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Winkler G. — Stochastic Integrals |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
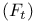 -Brownian motion 3.0.2 -Brownian motion 3.0.2
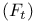 -Poisson process 3.0.2 -Poisson process 3.0.2
 -field of the past 2.1.2 -field of the past 2.1.2
 -field, strictly before T 6.4.8 -field, strictly before T 6.4.8
 -field, up to T 2.2.3 -field, up to T 2.2.3
A.s. regular process 4.4.6
Adapted process 2.1.2
Admissible measure 6.5.1
Almost sure equality 2.0
Backward equation 1.1
Band Pass Filter 1.2(C)
Blumenthal’s-0-l-law (2.1.4) 9.7.2
Bochner — Khintchine theorem 1.2.(B)
Borel- -field 1.1 -field 1.1
Brownian filtration 9.7.3
Brownian motion 1.1
Brownian motion, 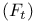 - 3.0.2 - 3.0.2
Brownian motion, complex 9.5.1
Brownian motion, d-dimensional 9.0
Brownian motion, planar 9.7.1
Brownian motion, standard 1.1
Brownian motion, starting at x 9.0
Brownian motion, stopped 9.1.6
Brownian transition function 1.1
Burkholder — Davies — Gundy, inequality 11.2.1
Cameron — Martin formula 10.2.8
Cauchy process 9.2.6
Change of drift (10.2.5) 10.2.6
Compensator 6.6.4
Complex, Brownian motion 9.5.1
Complex, Ito formula 8.6.5
Complex, mutual variation 8.6.4f
Complex, quadratic variation 8.6.4 f
Conformal martingale 9.5.3f
Convergence theorem for (sub-) martingales 3.2.4
Dambis — Dubins — Schwarz theorem 9.2.3
Desintegration predictable 6.5.5
Differential 7.3.3
Diffusion 12.0.1
Diffusion, matrix 12.0.1
Diffusion, operator 12.0 12.2
Diffusion, process 12.0.1
Dirichlet problem 9.3.3
Dominated convergence for stochastic integrals 8.3.1
Doob — Meyer decomposition 6.6.1
Doob’s 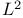 -inequality 3.1.4 3.2.10 -inequality 3.1.4 3.2.10
Doob’s for local martingales 5.6.5
Doob’s maximal inequalities 3.1.2
Doob’s upcrossing inequality 3.1.5
Drift vector 12.0.1
Dual predictable projection 6.5.5
Dubins — Schwarz see “Dambis — Dubins — Schwarz”
Dynkin’s formula 12.1.5 (12.5.2)
Elementary process 4.4.1
Elementary stochastic integra 5.2.1
Elliptic operator 12.2.1f
Entrance time 2.3.3
Equal a.s. (processes) 2.0
Event known up to T 2.2.3
Exponential 8.2.1f
Exponential martingale 8.2
Exponential of a process 8.2.1f
Exponential process 8.2
Extension Principle 5.1.3f
Feynman — Kac formula (12.3.5) (12.5.3)
Filter 1.2(C)
Filter, band pass 1.2(C)
Filter, differentiation 1.2(C)
Filter, integration 1.2(C)
Filter, low pass 1.2(C)
Filtration 2.1.1
Filtration, natural 2.1.2
Filtration, own 2.1.2
Filtration, right-continuous 2.1.3
Finite variation 5.1.2
Fokker — Planck equation 1.1
Follmer — Doleans measure 6.2.5
Forward equation 1.1
Function of finite variation 5.1.2
Function, regular 3.2.5
Functional differential equation 11.0
Generator of semigroup 12.5.3f
Girsanov — Maruyama theorem 10.2.1
Girsanov’s theorem 10.2.1
Gronwall’s lemma 11.2 f
Harmonic function 9.3.1
Hermite polynomial 9.6.2
Homogeneous transition function 9.4
Increasing process 5.6.1
Increasing process of Brownian motion 5.6.6
Increasing process of the Poissonmartingale 5.6.7
Increasing process, predictable 6.6.4
Indistinguishable 2.0
Infinitesimal mean 12.0
Infinitesimal parameter 12.0
Infinitesimal variance 12.0
Initial value problem (stochastic) 11.1.1
Integral, elementary 5.2.1
Integral, pathwise 5.3.3
Integral, Stieltjes 5.1.3
Integral, Stochastic 5.4.5 6.2.3 6.3.4
Integration by parts 7.3.1f
Interval partition 5.5.5
Interval, stochastic 4.1.1
Ito exponential 8.2
Ito formula 8.1.1
Ito formula with jumps 8.4.1
Ito formula, complex 8.6.5
Ito formula, matrix-valued 8.6.2
Ito formula, multidimensional 8.6.1
Ito process 10.2.6
Jump process 7.3.17f
Kelvin transformation 9.5.8f
Knight’s theorem 9.2.6
l.u.p. convergence 4.3.2
Langevin equation 1.2(B)
Left-continuous process 2.0
Levy’s theorem 9.1.1
Linear filter 1.2(C)
Lipschitz (stochastic) condition 11.1
Lipschitz (stochastic) constant 11.1
Local (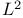 -)martingale 4.2.1 -)martingale 4.2.1
Local time 8.3.1f
Localizing sequence 4.1.2
Locally 4.1
Locally bounded 4.1.2
Locally finite variation 5.3.1
Locally integrable 6.2.7f
Locally uniformly in probability 4.3.2
Low pass filter 1.2(C)
M/G/1-queue 5.7
Markov property 9.1.11 11.3.2 12.5
Martingale 3.0.1
Martingale, characterization of 3.2.9
Martingale, closed 3.2.3
Martingale, conformal 9.5.2f
Martingale, convergence theorem 3.2.4
Martingale, criteria 4.2.3 5.6.3 9.2.4 10.2.3
Martingale, problem 12.6.1
| Maximal inequalities 3.1.2
Maximum principle 12.2.1f
Modification 2.0
Monotone class theorem 6.1.4
Mutual variation 7.3.1
Mutual variation, complex 8.6.4f
Natural filtration 2.1.2
Neighbourhood recurrent 9.3.5f
Nonanticipating 2.1.2f
Novikov’s criterion 10.2.2
Nullset, augmentation 2.1.5
Nullset, elimination 2.1.5 f
Optional  -field 6.1.6f -field 6.1.6f
Optional sampling 3.2.8
Ornstein — Uhlenbeck process 1.2.(B)
Orthogonal increments 1.1
Own filtration 2.1.2
Partial integration 7.3.1f
Partition 5.5.5 7.3.3f
Pasta 5.7
Path 2.0
Pathwise, integral 5.3.3
Pathwise, solution 12.4.1
Picard — Lindelof theorem (for SDEs) 11.1.1
Picard’s Theorem 9.5.6f
Planar Brownian motion 9.5.1
Poisson martingale 1.1
Poisson process 1.1
Poisson transition function 1.1
Polish space 1.1
Predictable 6.1.1
Predictable, desintegration 6.5.5
Predictable, increasing process 6.6.4
Predictable, measure 6.5.7f
Predictable, process 6.1.1
Predictable, projection 6.5.3
Predictable, rectangle 6.1.2
Predictable, set 6.1.1
Predictable, stopping theorem 6.4.10
Predictable, stopping time 2.3.5 6.4.1
Process with orthogonal increments 1.2.(B)
Process, elementary 4.4.1
Process, predictable 6.1.1
Process, progressively measurable 2.3.8
Process, separable 2.3.1
Process, stationary 1.2.(B)
Process, weakly-stationary 1.2.(B)
Product measurable 6.3.1
Progressively measurable 2.3.8
Projection, dual predictable 6.5.4
Projection, predictable 6.5.3
Quadratic variation 5.6.1 7.3.1
Quadratic variation, complex 8.6.4f
Recurrence of Brownian motion 9.3.5
Regular function 3.2.5
Riesz representation theorem 1.2
Right-continuous filtration 2.1.3
Schrbdinger equation 12.3
SDE 11.0
Second order process 1.2(C)
Semigroup 12.5.3
Semimartingale 7.1.1
Separability set 2.3.1
Separable process 2.3.1
Signed measure 1.2
Signum 8.3 12.4.3
Sojourn time 12.3.7F
Solution of SDE 11.1.0
Space-time-harmonic 12.1.2f
Special semimartingale 7.2.7
Spectral density 1.2(C)
Spectral measure 1.2.(C)
Spectral representation 1.2.(C)
Standard Brownian motion 1.1
Stationary (weakly) 1.2.8
Stationary increment 1.2.8
Step function 4.4.1
Step function, left-continuous 4.4.1
Stieltjes integral 5.1.3
Stochastic differential 7.3.3
Stochastic differential equation 11.0
Stochastic differential equation, solution of 11.1
Stochastic integral 5.2.1 5.3.6 5.4.5 6.1.5 6.2.3 6.3.4 7.1.5
Stochastic integral for semimartingales 7.1.5
Stochastic integral, elementary 5.2.1
Stochastic interval 4.1.1
Stochastic process 2.0
Stopped Brownian motion 9.1.6
Stopping theorem, continuous 3.2.7
Stopping theorem, discrete 3.1.2
Stopping time 2.2.1
Stopping time, predictable 2.3.5 6.4.1
Stopping time, strict 2.2.1
Stopping time, wide sense 2.2.1f
Stratonovich — Fisk, differential 8.5.1
Stratonovich — Fisk, integral 8.5.1
Strict stopping time 2.2.1
Strong Markov property 9.1.11 11.3.2 12.5
Submartingale 3.0.1
Submartingale, closed 3.2.3
Submartingale, convergence theorem 3.2.4
Supermartingale 3.0.1
Symmetric multiplication 8.5.3
System function 1.2(C)
T-past 2.2.3
Tanaka’s differential equation 12.4.3
Test-function 12.0.1
Time change 9.2
Total variation 5.1.2
Transience of Brownian motion 9.3.5
Uniformly elliptic 12.2.1f
Uniformly integrable 3.2.1f
Uniqueness in distribution 12.4.1
Uniqueness theorem for SDEs 11.1.1 12.1.8
Uniqueness, pathwise 12.4.1
Uniqueness, weak 12.4.1
Upcrossing 3.1.4f
Upcrossing inequality 3.1.5
Usual conditions 2.1.5 12.5
Variation 5.1.2
Variation, locally finite functions 5.1.2
Variation, locally finite processes 5.3.1
Variation, mutual 7.3.1
Variation, quadratic 7.6.2f
Variation, total (functions) 5.1.2
Version 2.0
Version of the pathwise integral 5.3.3 5.3.6
Walds identity 5.6.6
Weak maximum principle 12.2.1f
Weak solution 12.4.?
Weak uniqueness 12.4.?
Weight function 1.2(C)
White noise 1.2(C)
Wide sense stopping time 2.2.1f
Wiener, chaos 9.6.8 f
Wiener, integral 1.2(C)
Wiener, measure 1.1
Wiener, space 1.1
Yamada — Watanabe theorem 12.4.4
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



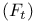 -Brownian motion
-Brownian motion  -field of the past
-field of the past 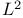 -inequality
-inequality