|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Patten T. — Systemic text generation as problem solving |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
! 37 see
# 35 36
$ 64 see
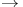 87 88 89 90 102 87 88 89 90 102
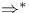 87 88 87 88
% 36
* 62 see
+ 38 see
-- 111 114
-<> 111 112 113
-[ 113
-{= 111 114—115
/ 34 37 93 see
: 37 see
< 38 79 93
= 34 36 93 see
=}- 111 112 113
Abstraction 33 43 98 102 132 139
Actor 27 28 29 30
Acyclic system networks 91 92
adjacency 35 66 87 93 94 123
Affected 30
Agent 27 30 34 40 48 58 59 107 108 109 126 153
Alternatives 9 52 53—54 55 75 76 119 132 138 141 147
Ambiguity 155
Anaphoric reference 48
Anatomy 23 51
And/or graphs 98—99 99—102 144 145
Anthropology 19 20 22 147
Appelt, D. 63 133 136—141 146 149
Architecture 55
Architecture of AI problem solving 6—8
Architecture of OPS5 106 107
Architecture of the implementation 104 105
Architecture of the linguistic component 137
Assert 107 129 130
Asterisk 61 152 see
ATNs 133
Attribute 29
Attribute-value pairs 115 120 121 124 157 158 159
Automatic compilation of knowledge 16 61
Backtracking 9 13 60 118 133
Backward-chaining 12—14 18 75 78 88 91 102 105 120 141 142 143 146 148 149 153 154
Backward-chaining in the implementation 106—107 110 115 117—118 120 127 130 131 132
Backward-chaining, through system networks 57 58—70 100
Barr, A. 9 16
Behaviour potential 53 63 75 142
Beneficiary 28 30
Berwick, R. 60
Beta 28
biology 23 27 40 51
Blind search 9 15 119 141
Bloomfieldian tradition 20
Boundaries 35—36
Brachman, R. 15 17 63 151
Bracketing 33 41
Brady, M. 60
Brownston, L. 8 12 14 16 106 115 157
Brute-force search 9 14
Buchanan, B. 16 152
Bundy, A. 10 16
CALL 159 160
capitalization 161
Carrier 29
Causer 30
Chandrasekaran, B. 203
Chemistry 57 72 147
Choice 9 10 21—22 24—27 47 49 54 118 119 133 134 135 136 137 141 144 145
Chomsky, N. 74
Choosers 136 137 141 143 144
class 6 9 131 24 34 42
Classification 5 6 27 72 149
Classification, linguistic 23 24 37 51
Clause 24 26 27 28 32 33 35 36 38 44 50 59 62 66 87 109 127 131 135 136 144 145 186—188
Clause-complex 26 33 149 152
Cohen, P. 155
Combinational view of language 21
Compilation 4 14—15 60 61
Compilation of knowledge see "Knowledge compilation"
Compiled knowledge 6 14—18 59—63 75 131 178 see
Compiled knowledge in the semantic stratum 143 145 148 151 153
Compiled knowledge, sources of 15—16
Completeness 5 89—93 148
Computational paradigm 73—74
Conflation 52—74 75 142 145
Conflation, linguistic 34 36 87 93 94 122 123 124 127
Conflicting feature set 85
Conjunction 98 111 116 118 120
Conjunction, linguistic 31 69 131 193
Consistency 85 90
Consistent feature set 85
Constituency 54 78
Constituent tree 33 37 38 80 127
Constraints 84 88 94 139 158
Context of situation 20 45 154
Context, linguistic 20 21 24 53 135
Context, social 19 46 47 53 155
Control strategy 110
correctness 77 89
CRLF 160
DATA 6 8 11
Daughter nodes 80 81 93 94 95 97
Davey, A. 42 77 134 136
de Joia, A. 23 26 33 52 72
Deadlock 127
defaults 135 152—153
Deictic 32 33 39 69
Delicacy 27 33—34 43 134 136
Depth-first search 9
Derivation of feature sets 94 96
Descendancy 79
Deterministic search 75 145
Dialect 73
Diamond notation 112
DICTIONARY 152 161 203 see
Direct descendants 79
Discourse 39 46 133 138 141 155
Disjunction 13 61 63 82 101 111 115 116 119 145 158
Disjunctive entry conditions 25 42 61 62 101 107 118 119 130 see
Disjuncts, dependent 62 145
Disjuncts, independent 62 63 118 119 145
domains 6
Edges 78 79
Efficiency 3 7 14 16 17 52 53 55 60 75 76 77 129 131 132 137 141 142 145 147 149 154
Ellipsis 134 155
Embedding 28 38 136
Encoding 8 14
Entry conditions 57 59 64 84 85 88 91 93 101 102 106 107 113 114 115 119 120
Entry conditions and system networks 24 25 26 42
Entry conditions to gates 25 26 50 59 111 116—118
Entry conditions to systems 24—25 54 55 118 130 152
Entry conditions, disjunctive 61—63 118 130
Ergativity 28 30 40
Establish and refine 203
Ethnography 19
Evolution of language 23 74
Exclusive-OR 100
Exophoric reference 48
expansion 34—36 87 93 109 123 125
Expert Systems 3 6 8 11 13 14 15 16 17 64 156 161
Expert systems as application for SLANG 105 130 150—151 152
ExPlan 166 178 179
Explanation 17 74 151 153 161—165 166—181
Expressive system network 91 92
Feature assignment 82 86 93 94 95
Feature heap 86—87
features 24 25 26 27 34 37 39 42 43 57 78
Field 46 47 48 50 154 155
finite 31 37 38 40 56
First-order logic 97
| Firth, J.R. 19 20—21 22 24 43 50 53 54 147
Fleck, M. 97
Forgey, C. 115
Formal model 1 4 5 77—103 148
Formalization 2 77 81 87 103 148
Forward-chaining 10—12 13 14 56 57 59 65—71 88 106 107 111 115 116 146 148
Function nodes 81 94 95
Functional analysis 27—33 34 40 41 79 80 94 152
Functional description 22—23 51 148
Functional description in unification grammar 140 141
Functional linguistics 3—4 203
Functional Unification Grammar 140 141
Functions of language 20 22 23 33 45 46 72 73 74
Functions, grammatical (syntactic) 27—32 34—40 42 68 79 93 94 178 181
Future research 1 5 130 146 151—156
G-features 88 89 90 92 93
Gates 25—26 49 56 57 59 62 88
Gates, implementation of 105 106 107 111 112 113 116 118 120 131 132
Genatom 108 121 160
Generation of a feature set 87—90 92
Generation of a string 86
Generation of text 2—3 60 64 66 72 75 77 78 86 87 89 95 97 98 100 102 110 121 126 127 132 133 135 139 140 143 153 173 203
Generation relationship 87 89 90
Generative grammar 4
GENSYM 108 120 126 160
Given 32 152
Goal 68 71 107 129 130
Goal-directed processing 12—13 53 118 137 139 140 142 146 148 149 156
Grammar and conflation with knowledge base 59
Grammar, Functional Unification 140 141 149
Grammar, generative 4
Grammatical (syntactic) functions 27—32 34—40 42 68 79 93 94 178 181
Grammatical function scheme 80 81 82 85
Grammatical stratum 44 46 47 48 51 57 60 61 63 66 131 143 148 150 152 153—154
Granularity 14—15 16 18
Greenbaum, S. 189 193
Grosz, B. 155
Group 32 33 36 37 38 44 80
Group, nominal 22 32 33 37 38 39 45 68 69 87 88 91 109 127 136 143
Group, tone 32
Group, verb 32
Halliday, M.A.K. 20 24 26 28 29 30 31 32 41 42 52 54 60 66 77 144 150 152 181 188 189 190 197
Halliday, MAK on Firth 20 43 53 54
Halliday, MAK on functional linguistics 23 39 40 72 73 203
Halliday, MAK on register 46 47 154 155
Halliday, MAK on the semantic stratum 43 44 45 48
Halliday, MAK, as developer of systemic grammar 19 21—22 50 147
Halliday, MAK, the Mann/Halliday grammar 34 36 37 38 56 57 59 62 186 193
Hasan, R. 31 193
Hashing 130
Hasling, D. 155 161
Hayes-Roth, F. 13 17 52 132
head 32 37 45 71 109
Heuristic search 9—10
Hindle, D. 97
history 4 19—22 24 73 74 75 77 147
Hjelmslev, L. 19 21 22 43 50 54
Hobbs, J. 14
Hopcroft, J. 79
hubs 108 109 110 121—129 179 181
Hudson, R. 41—42 61—62
Human experts 8 16
Hypercompilation 153
Hypotheses 15 154
Ideational metafunction 39 40 41 47 48 203
Identified 29
Identifier 29
implementation 22 77 90
Implementation of PROTEUS 135
Implementation of SLANG 1 5 97 104—132 148—149 152 157
Implementation of TELEGRAM 141
inclusion 38—39
Inconsistent feature set 85
Induction 92 93
Inference Engine 6—8 10—13 130
Inference engine of OPS5 105 130 132
Information analysis 32
Information theory 24
inheritance 131
inheritance hierarchies 131 132
Initial feature sets 86 87 88 89 90 94 101 145 203
insertion see "Inclusion"
Intentions 47 137 155
Interpersonal 31
Interpersonal metafunction 39 40 41 47 48 73 203
Intonation 32 152
Kamp 137—139 140 141 142 149
Knowledge acquisition 151
Knowledge base 6 7 8 13 16
Knowledge base, conflation with grammar 75 105 142 145
Knowledge compilation 6 14—17 60 61 148 153 see "Compiled
Knowledge compilation by hand 16
Knowledge compilation, automatic 16 61
Knowledge engineering 16 151
Kress, G. 19 21
Lamb, S. 21 43 54
Law 3 156
leaf nodes 79 80 81 139
Least commitment 119 130 131
Leech, J. 189
Lexicon see "Dictionary"
Lexification 36 42 45 69 70 87 203
Lexification, implementation of 123 125
Lexverb 31 68 71
lhs 106 107 121 131 157—159 160
Lisp 108 110 149 160
LISP, called from OPS5 107 123 125 160
LISP, representation of system networks 111 112 113 116 132 186
Logic 78 85 89 96—98
Logic circuits 59
logical expressions 82 83
Loops in system networks 41 42 43
Loops in trees 79
Macro-functions 40 203
MACROPs 16
make 107 121 129 159
Malinowski, B. 19—20 21 22 39 40 45 50 53 88 147
Mann, W. 26 34 35 36 37 38 56 57 59 62 77 108 136 137 143 144 149 150 186 193
Marcus, M. 97
Martin, J. 20 24 39 41 42
Mathematics 22 147 148
Matthiessen, C. 77 137
McCord, M. 42
McDonald, D. 2 60 137 139 149
McKeown, K. 133
Meaning potential 43 52 53 63 72
Medicine 3 156
Medium 30 109
Mentioned in 83 91 92 93
Metafunctions 39—41 46 50 73 152 203
Metafunctions and paradigmatic description 39—40
Metafunctions and register 47—48
Minimal bracketing 33 41
Mishler, E. 150
modal 66 67
Modality 203
MODE 46 47 48 50 154 155
Modify 159—160
Modulation 203
Monaghan, J. 20
Mood 28 30 31 34 35 36 48 109 127 128 136
Moodtag 30 31
Morphology 33 39 139 149 150 152
multiple inheritance 131
MUMBLE 137 139—140 149
MYCIN 155
Natural-language understanding 154—156
NEW 32 152
Nigel 135 136 137 141 142 143—145 149 186 203
Nilsson, N. 12 98 99 144
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте