|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hopcroft J.E., Motwani R., Ullman J.D. — Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
 see “Transition function” see “Transition function”
 see “Empty string” see “Empty string”
 -closure 75 -closure 75
 -NFA 72—80 96 101—105 151 -NFA 72—80 96 101—105 151
 -production 255 259—262 -production 255 259—262
 -transition 72 77—78 219 -transition 72 77—78 219
 see “Extended transition function” see “Extended transition function”
 473 477—478 473 477—478
 419 423 426 470 479 497—498 505—508 419 423 426 470 479 497—498 505—508
 469 473 477—479 469 473 477—479
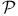 414 423 425—426 479 497 414 423 425—426 479 497
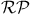 469—470 488 492—498 504 469—470 488 492—498 504
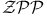 469—470 488 495—497 469—470 488 495—497
 see “Input symbol” see “Input symbol”
2SAT 437 446
3SAT 435—436 445—446 462
Acceptance by empty stack 230—235 249—250
Acceptance by final state 229—235 249—250
Accepting state 46 57 222 319
Accessible state 45
Ackermann's function 381
Address, of memory 357—358
Adelman, L. 499 511
Aho, A.V. 35 123 217
Algebra 85—86 114—120
Algorithm see “Recursive language”
Alphabet 28—29 132
Alphabetic character 109
Alphanumeric character 109
Alt, of languages 147 292
Ambiguous grammar 205—212 249—251 302 404—406
Ancestor 182
Annihilator 95 115
Arithmetic expression 23—26 208—210
Associative law 114—115
Automaton 26—28 (see also “Counter machine” “Deterministic “Finite “Nondeterministic “Pushdown “Stack “Turing
Backus, J.W. 217
Balanced parentheses 192—193
Bar-Hillel, Y. 166 304 411
Basis 19 22—23
BLANK 318—319 346
Block, of a partition 161
body 171
Boolean expression 426—428 436
Borosh, I.I. 468
Bottom-of-tack marker 351
Cantor, D.C. 217 411
CFG see “Context-free grammar”
CFL see “Context-free language”
Character class 108
Child 182
Chomsky normal form 266—269 295—296
Chomsky, N. 1 191 217 266 411
Church — Turing thesis 318
Church, A. 318 366
Clause 436
Clique problem 462 465
Closure 85 87 104 109 117 199 284 382 425—426
Closure property 131 (see also “Alt of “Closure” “Complementation” “Concatenation” “Cycle of “Derivative” “Difference of “Homomorphism” “Init of “Intersection” “Inverse “Max of “Min of “Partial-removal “Permutation of “Quotient” “Reversal” “Shuffle of “Substitution” “Union”)
CNF see “Conjunctive normal form”
Co-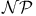 469—472 508 469—472 508
Co-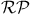 496 496
Cobham, A. 468
Cocke, J. 298 304
Code, for Turing machine 369—370
Coloring problem 462—463
Commutative law 114—115
Complementation 132—133 289 375—377 388 426
Composite number 499
Computer 315 355—363
Concatenation 30 84 86—87 95 104 115—116 199 284 382 425—426
Conclusion 6
Conjunctive normal form 436 (see also “CSAT”)
Containment, of languages 408
Context-free grammar 4 169—181 237—245 294—296
Context-free language 177 249
Contradiction, proof by 16—17
Contrapositive 14—16
CONVERSE 16
Cook's theorem 428—434
Cook, S.C. 1 424 468
Countable set 310
Counter machine 351—354
Counterexample 17—19
Cryptography 470 499—500
CSAT 436—445 462
Cummutative law 14
Cycle, of a language 148 292
CYK algorithm 298—301
dead state 67
Decidability 5 (see also “Undecidable problem”)
Decision property see “Emptiness test” “Equivalence of “Membership
Deductive proof 6—17
Derivation 174—175 184 190—191 “Rightmost
Derivative 146
Descendant 182
Deterministic finite automaton 45—55 60—64 67 70—72 79 91—101 150—151
Deterministic pushdown automaton 246—251
DFA see “Deterministic finite automaton”
DHC see “Directed Hamilton-circuit problem”
Diagonalization 368 370—372
Difference, of languages 137 289
digit 109
Directed Hamilton-circuit problem 453—459 462
Distinguishable states 154 157
Distributive law 14 115—116
Document Type Definition see “DTD”
Dominating-set problem 465
Dot 108 (see also “Concatenation”)
DPDA see “Deterministic pushdown automaton”
DTD 169 192 199—204
Dynamic programming 298
Edge-cover problem 465
Electronic money 38
Emptiness test 151—152 296—298
Empty language 31 86 95 102 115 117 384—387
Empty stack see “Acceptance by empty stack”
Empty string 29 86 102 115 117
Endmarker 352 354—355
Equivalence, of boolean expressions 437
Equivalence, of languages 157—159 302 407—408
Equivalence, of regular expressions 117—120
Equivalence, of sets 14 16
Equivalence, of states 154—157
Even, S. 510
Every, J. 253
Exact-cover problem 465
Exponential time 415
exponentiation 503—504
Expression see “Arithmetic expression” “Regular
Extended transition function 49—52 54 58—59 76—77
Extensible Markup Language see “XML”
Factor 209
Factorization 499 505
False positive/negative 495
Fermat's last theorem 309
Final state see “Acceptance by final state” “Accepting
Finite automaton 2—4 37—45 90 228 315
Finite control see “State”
Finite set 8—9 339
Firehouse problem 465
Fischer, P.C. 253 366
Floyd, R.W. 217 411
For all see “Quantifier”
Garey, M.R. 468
Generating symbol 256 258
Ginsburg, S. 166 304 411
Gischer, J.L. 123
givens see “Hypothesis”
Godel, K. 317 366
| Grammar see “Ambiguous grammar” “Context-free “LR(k) “Right-linear
Graph, of a function 328
Grcibach normal form 271—273
Greibach, S.A. 304
grep 110 123
Gross, M. 217
Half, of a language see “Partial-removal operation”
Halting, of a Turing machine 327—328 380
Hamilton-circuit problem 419—420 453 460—462
Hamilton-path problem 466
Hartmanis, J. 167 366 468 510
HC see “Hamilton-circuit problem”
head 171
Hilbert, D. 317
Hochbaum, D.S. 468
Homomorphism 139—140 285 382
Hopcroft, J.E. 166 510
HTML 196—198
Huffman, D.A. 81 166
Hypothesis 6
id see “Instantaneous description”
Idempotent law 116—117
Identity 95 115
If-and-only-if proof 11—13 179
If-else structure 193—194
Incompleteness theorem 317—318
Independent-set problem 448—452 462
Induction principle 20
Inductive proof 19—28
Inductive step 19 22—23
Infinite set 9
Inherently ambiguous language 212—214 302
Init, of a language 147 291
Initial state see “Start state”
Input symbol 46 57 222 227 318—319 327
Instantaneous description 224—227 320—321
Instruction cycle 359—360
INTEGER 22
Interior node 181—182
Intersection 14 121 134—137 285—288 302 382 407—408
Intractable problem 1—2 5 361 413—414
Inverse homomorphism 140—143 289—291 382 425—426
IS see “Independent-set problem”
Johnson, D.S. 468
Karp, R.M. 424 452 468 510
Kasami, T. 298 304
Kernighan, B. 308
Kleene closure see “Closure”
Kleene, S.C. 123 166 366
Knapsack problem 465
Knuth, D.E. 253 488 510
Kruskal's algorithm 416
Kruskal, J.B.Jr. 416
Language 14 30—31 33 52 59 149 177 229—231 326—327 490—492 “Empty “Inherently “Recursive “Recursively “Regular “Universal
Las-Vegas Turing machine 495
Leaf 181—182
Left-sentential form 184 187—189 237—238
Leftmost derivation 175—177 184 187—189 211—212
Length, of a string 29
Lesk, M. 123
Levin, L.A. 468
Lewis, P.M. 11 510
Lex 110—111 123
Lexical analyzer 2 84 109—111
Linear integer programming problem 465
Literal 436
LR(k) grammar 253
markup language see “HTML” “XML”
Max, of a language 147 292
McCarthy, J. 81
McCulloch, W.S. 81
McNaughton, R. 123 167
Mealy, G.H. 81
Membership test 153 298—301
Miller, G.L. 510
Min, of a language 147 292
Minimization, of DFA's 159—164
Minimum-weight spanning tree 415—416
Minsky, M.L. 366 411
Modified Post's correspondence problem 394—402
Modular arithmetic 501—503
modus ponens 7
Monte-carlo Turing machine 493
Moore's law 1
Moore, E.F. 81 167
Motwani, R. 510
Move see “Transition function”
Multihead Turing machine 344
Multiple tracks see “Track”
Multiplication 362 501—503
Multistack machine see “Stack machine”
Multitape Turing machine 336—340
Mutual induction 26—28
Natural language 191
Naur, P. 217
NC see “Node-cover problem”
NFA see “Nondeterministic finite automaton”
Node-cover problem 452—453 462
Nondeterministic finite automaton 55—70 96 150—151 163
Nondeterministic polynomial space see “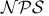 ” ”
Nondeterministic polynomial time see “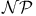 ” ”
Nondeterministic Turing machine 340—342 473 476—478 493 “
Nonrecursive language see “Undecidable problem”
Nonrecursively enumerable language see “Recursively enumerable language”
Nonterminal see “Variable”
Normal form 255—273
NP-complete problem 422 424 447 450 470—472 “Coloring “CSAT” “Dominating-set “Edge-cover “Exact-cover “Firehouse “Hamilton-circuit “Hamilton-path “Independent-set “Knapsack “Linear “Node-cover “Satisfiability “Subgraph “3SAT” “Traveling “Unit-execution-time-scheduling
NP-hard problem 423 (see also “Intractable problem”)
Nullable symbol 259—260 298
Observation 17
Oettinger, A.G. 253
Ogden's lemma 281
Ogden, W. 304
Palindrome 170 177—178
Papadimitriou, C.H. 510
Parent 182
Parse tree 181—189 207 274—275
Parser 169 192—195
Partial function 329
Partial solution, to PCP 395
Partial-removal operation 147 292
Partition 161
Paull, M.C. 304
PCP see “Post's correspondence problem”
PDA see “Pushdown automaton”
Perles, M. 166 304 411
Permutation, of a language 293
Pigeonhole Principle 66
Pitts, W. 81
Polynomial space 469 473—478
Polynomial time 5 (see also 
Polynomial-time reduction 413—414 421—423 478—479
pop 220
Post's correspondence problem 392—402
Post, E. 366 411
Pratt, V.R. 510
Precedence, of operators 88—89 208
prefix property 248—249
Prime number 470 498—508
Problem 31—33 417
Product construction 134
Production 171 (see also “ -production” “Unit -production” “Unit
proof 5—6 12 proof “Deductive “If-and-only-if “Inductive
Property, of languages 387—388
Protocol 2 39—45
PS-complete problem 478—479 (see also “Quantified boolean formula” “Shannon
Public-key signature 500—501
Pumping lemma 126—130 274—281
push 220
Pushdown automaton 219—246 294—295 “Stack
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå