|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Back T., Fogel D.B., Michalewicz Z. — Evolutionary computation (Vol. 2. Advanced algorithms and operators) |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Absorption time 145
Adaptation 170 182
Adaptive control 185
Adaptive landscape 102 103
Adaptive parameter control 180 189
Adaptive techniques, recombination operators 160—164
Adaptive value 102
AIC (Akaike information criterion) 15 16
Akaike information criterion (AIC) 15 16
ALECSYS 258
Artificial intelligence (AI) 38
Artificial Neural Networks see "Neural networks"
Asymptotics 247
Baldwin effect 56
Base pair mutations of Eschericia coli 144
Base-level EAs 213 214
Behavioral memory approach 71
Bias 154 155
Biased continuous competition pattern 234
Binary decision diagram (BDD) 261
Binary representation 149
Binary search spaces 206 207
binary strings 4 5
Binary variables, coding 9
Binary vectors see "Binary strings"
Binary-string encodings 45
Bipartite competitive fitness pattern 228
Bit strings see "Binary strings"
Building block hypothesis (BBH) 164
Cauchy density function 197
Chromosomes 111 178
Classification application 231
Classification rules 18
Classifier systems (CFS) 161
Classifier systems (CFS), hardware 257 258
Coarse-grained PGAs 253
Coevolution, definition 224
Coevolutionary algorithms 224—238
Coevolutionary genetic algorithm (CGA) 228—234
Coevolutionary genetic algorithm (CGA), applications 231—234
Coevolutionary genetic algorithm (CGA), future research 236
Coevolutionary model 70 71
Coevolutionary, introduction in EAs 224
Coevolving sorting networks 227 228
Comma-selection 146
Communication topology 105 106
Competition pattern 225
Competitive evolution 220
Competitive fitness 12—14 225—227
Complexity-based fitness evaluation 15—24
Computation time, evolutionary algorithms (EAs) 247—252
Computation time, mutation operators 250
Computation time, recombination operators 251
Computation time, selection operators 247—250
Conceptualization 102
Connection Machine (CM) 257
Constrained optimization problems (COPs) 75 76 77
Constraint satisfaction 232
Constraint-handling methods 69—74
Constraint-handling techniques introduction 38—40 see
Constraint-preserving operators 62—68
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs) 38 75—86
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs), changing the search space 81
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs), solving the transformed problem 82 83
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs), transforming to constrained optimization problem 80
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs), transforming to evolutionary-algorithm-suited problems 77
Constraint-satisfaction problems (CSPs), transforming to free optimization problem 78
Control level parallelism 254
Control problems, coding 9 10
Convergence velocity 143 145
Cooperative coevolutionary genetic algorithms (CCGAs) 235
Correlated mutations 143
Cost assignment strategy 26
Covariances 180
Cross-validation 17
Crossover 178
Crossover operators 111 219
Crossover, one-point 181
Crossover, uniform 181
Crowding techniques 89 90 219
Cultural algorithms 71 72
Cut points 153
Data level parallelism 254
Decision trees 18 19
Decoders 49—55
Decoders, examples 58—61
Decoders, formal description 50—55
Decoders, selection procedure 58 59
Decoding functions 2 4—11
Deme attributes 129—131
Demes 103 104 255
Density classification 233
Derived delta 163
Deterministic crowding 89 90
Deterministic crowding algorithm 89
Deterministic evaluations 244
Deterministic parameter control 179 180
Diffusion models 107 125—133
Diffusion models, formal description 125 126
Diffusion models, implementation techniques 126—131
Diffusion models, theoretical research 131 132
Distribution bias 154 155
Dynamic parameter control 189
Edge recombination crossover 65
Eldredge Gould theory 104
Elitist model 219
Embryology-oriented approach 261
Encoding functions 4—11
Encore 132
Encounter 229
Engineering-oriented approach 260
epochs 106
Evaluation function 178
Evolution 174 178
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs) 174 see
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), 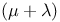 249 249
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), 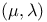 248 248
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), components 179
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), computation time 247—252
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), dedicated hardware implementations 256—258
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), effectiveness 182
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), hardware realizations 253—263
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), implementation 239—246
Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), intelligence 184
Evolutionary programming (EP) 4
Evolutionary robotics see also "Robots"
Evolutionary strategies (ESs) 4 180
Evolutionary strategies (ESs), 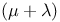 248 249 248 249
Evolvable hardware (EHW) 253 258—261
Exemplars see "Taxon-exemplar scheme"
Exploration power 154
Fast evolutionary programming 197
Feasibility condition 77
Feasibility search space 77
Feedback 172 175
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) 256 257 259
Fine-grained PGAs 256
Finite-state machines 158 205
Fitness assignment strategy 30
Fitness evaluation 1—3 25 26
Fitness evaluation, competitive 12—14
Fitness evaluation, complexity-based 15—24
Fitness evaluation, minimum-description-length-based 17 18
Fitness evaluation, overview 1 2
Fitness evaluation, related problems 2
Fitness landscapes 87
Fitness proportional selection (FPS) 30 89
Fitness sharing 32 87—89 235
Fitness values 152
Fitness variance of formae 160
| Floating-point coding 7 8
Formae 158 165
FORTRAN 248
Free optimization problem (FOP) 76
Free search space 76
Fuzzy rules 163
Gate level evolution 259
Gaussian mutation 174 176
Gaussian mutation operator 174
Generalized Rastrigin function 199
Genetic algorithms (GAs) see also "Specific applications"
Genetic algorithms (GAs) with punctuated equilibria (GAPE) 104
Genetic algorithms (GAs), design 171
Genetic drift 31
GENOCOP III 59 60 73
Genotypes 81 111
Genotypic mating restriction 96 97
Genotypic sharing 88
Genotypic-level combination 153—156
Goal attainment method 27 28
Goal programming 35
Granularity 101
Gray code 198 199
Gray-coded strings 6 7
Hamming cliffs 157
Hamming distance 6 147
Hardware description language (HDL) 259
Hardware realizations, evolutionary algorithms (EAs) 253—263
Heapsort 248
Heuristics 155 156
Identically distributed (IID) random variables 241
Implicit parallelism 134
Inherited delta 163
Integer search spaces 202—204
Interior solutions 41
Intermediary recombination 195
Internet 132
Interval schemata 157
Inverse fitness interaction 224
Island models 101—124 127
Island models, influence of parameters on evolution 113—119
Island models, VLSI circuit design problem 108—113
Isolation-by-distance model 253
Iterated prisoner's dilemma (IPD) 226
Knapsack problem (KP) 49 57 58 147
Ladder neighborhood 130 131
Lamarckian evolution 56
Learning algorithms 94
Learning rates 189
Learning rule adaptation 220
Lexicographic approach 29 30
Lifetime fitness evaluation (LTFE) 230 234 236
Linear congruential method 240
Linkage problem 7
Lisp 4 158 161
Local delta 163
Mask programmable gate arrays (MPGAs) 259
Mating restriction 32 94 96 97
Median-rank approach 31 32
Mesh (or grid) neighborhood 130
Messy coding 7
Meta-algorithm 172
Meta-evolutionary approaches 212—223
Meta-evolutionary approaches, formal description 214 215
Meta-evolutionary approaches, parameter settings 216 217
Meta-evolutionary approaches, pseudocode 215 216
Meta-evolutionary approaches, related work 217—220
Meta-evolutionary approaches, theory 217
Meta-evolutionary approaches, working mechanism 212—214
Meta-GA approach 218 219
Meta-level EAs 213
Meta-optimization 212
Metrics 192
Micro-GA 136
Migrant selection strategies 116—118
MIMD (multiple instruction, multiple data) system 99 127 254 255
Minimax approach 27—29
Minimax problem 235
Minimum Description Length (MDL) Principle 15—23
Minimum description length (MDL)-based fitness evaluation 17 18
Minimum-message-length principle (MML) 15—23
Modem synthesis 102
Monte Carlo (MC) evaluation 244 245
Multimutational self-adaptation 205
Multiobjective function optimization 87
Multiobjective optimization method 25—37 69
Multiobjective optimization, current evolutionary approaches 26
Multiple instruction, multiple data (MIMD) system 99 127 254 255
Mutation 98 178
Mutation function 219
Mutation mechanism 199
Mutation operators 112 178 189—205 242 243
Mutation operators, computation time 250
Mutation parameters 142—151
Mutation parameters for direct schedules 144—149
Mutation parameters for self-adaptation 143 144
Mutation rate 142 144 145 147
Mutation step size parameter 178
Mutation value replacement method 219
Mutational step size 143
n-point recombination 154
Natural evolution, theories 102—104
Near-feasible threshold (NFT) 46
Network weight optimization problem 218
Neural networks 231 260
Neural networks, weight optimization problem 219
Niching methods 87—92
Niching methods, parameters and extensions 88 89
Niching methods, theory 90 91
Noncoevolutionary EAs 228
Nonlinear optimization problems, with linear constraints 64 65
Nonlinear programming 38 59—61
Normalized modification 148
Number of populations 226
Objective fitness 12
Objective fitness functions 12
Objective function 194
Occam's razor 15
Occupancy rate 162
Operations research (OR) 38 see
Operator delta 163
Operator tree 163
Optimal schedules 145
Optimal schema processing 135 136
Optimization problems 174 176
Pallet loading 50
Parallel algorithms 99
Parallel computer architectures 254
Parallel environments for diffusion model implementation 127 128
Parallel evaluation 245 246
Parallel generate-and-test algorithm 245
Parallel genetic algorithms (PGAs) 120 253
Parallel genetic algorithms (PGAs), overview 253—256
Parallel structure 112
Parallelism 255
Parallelization 101 102
Parameter changes 185
Parameter control 170—187
Parameter control, classification schemes 170 171
Parameter control, on-line 185
Parameter control, value of 184
Parameter settings by analogy 173
Parameter settings, optimal 172
Parameter settings, optimizing 183
Parameter tuning 170 173
Parameter values 170 174 181
Pareto optimality 25
Pareto ranking 32 33
Pareto ranking with goal and priority information 33—35
Parthenon 260
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте