|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katayama T., Sugimoto S. — Statistical Methods in Control and Signal Processing |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
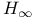 filter 239 filter 239
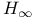 filter, stochastic property of 243 filter, stochastic property of 243
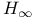 filtering problem 239 filtering problem 239
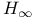 filtering problem, finite horizon 240 filtering problem, finite horizon 240
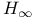 Riccati difference equation (RDE) 241 248 Riccati difference equation (RDE) 241 248
 statistic 113 statistic 113
a priori information 446—447 526 536
Abrupt discontinuities 59
Acceptance probability 527—529
Adaptation 448
Adaptive fuzzy system 468
AIC (Akaike information criterion) 38—39 46—47 60 87 98—99 114 162 166—167 179
AIC of composite model 114
AIC, small sample correction 99
Algebraic Riccati inequality 3
Algorithm, alternating conditional expectation (ACE) 108
Algorithm, Amplitude modulation, quadrature 377
Algorithm, parallel 483
Algorithm, relaxation-type 525
Algorithm, sequential 482
Algorithm, subspace 99 403
Algorithm, supervised learning 490—491
Amplitude process 331
Antenna array 400
AR model or process 43—47 337 335 404 443
AR model or process, time-varying (TVAR) 49 66
ARM AX model 482 466
ARM AX parametrization 86 97
ARMA model or process 125 128 179 180—182 190 464
ARMA model or process, multivariable 182 194 360
ARMA order estimation or test 179—180 186—187
Array error parametrizations 406
Array response 402—404
Array signal processing, robust 399
Array signal processing, simulation results 421
Array steering vectors 404
Asymptotically normal 128 187 203 205—206
Attractor 502 507 515
Attractor in discrete random dynamics 284
Aumann-like integral 308 324
Backward shift operator 122
Bandwidth expansion 442
Bayesian approach 399
Bayesian approach to time series analysis 41
Beamformer, MAP 413
Beamformer, MVDR 412
Beamforming 404 412 425
Beamforming, adaptive 409
Bessel function 440
beta function 281
Bias errors 161
BIC (Bayes information criteria) 86
Binary random variable 488—489
Binary tree, biased-search 488
Binary tree, fair-search 488
Binary tree, structure 487
Birkhoff theorem 385
Birth-and-death process 290
Bispectrum 360
Bispectrum, integrated 362
Blind deconvolution 375 378 379
Bose — Einstein statistics 276 293
Boundary preserving mapping 511
Boundary value problem 503
Brodaz’s texture data 535
Brownian motion process 217
Calibration 433
Calibration, array 402
Canonical variable 92 112
Canonical variate analysis (CVA) 83 89 91
Canonical variate analysis (CVA) of past and future 93
Canonical variate analysis (CVA), applications 108—116
Canonical variate analysis (CVA), computational aspects 99
Canonical variate analysis (CVA), extension to nonlinear system 107
Canonical variate analysis (CVA), model identification 113
Canonical variate analysis (CVA), theorem 91—92
Cayley — Hamilton theorem 184 202
Central limit theorem 187 193 205
Change detection 454 471 482
Change detection with model uncertainty 457
Change detection, robust 453
Change detection, robust, KDI-based 462
Change detection, scheme 454 471
Change detection, system 453—455
Chi-square random variable 63
Conditional expectation 11 107
Conditional likelihood 91
Conditional probability 484—485 504
Consistency 369
Consistent estimate 187
Contraction mappings or process 506—507 509
Contraction mappings or process, boundary preserving 508
Controllability 184
Controllability, matrix, extended 185
Controller form 136
Covariance matrix 7 29 90—91 182 184 187 201 205
Covariance matrix, Hankel 180 185
Cramer — Rao lower bound 86 418
Cross validation 86
Cross-spectrum 360—362
Cross-spectrum, estimators 364
Cumulant (function or statistics) 357 376 379
Cumulant (function or statistics), fourth-order 361 378
Cumulant (function or statistics), higher-order 357
Cumulant (function or statistics), nth-order 376
Cumulant (function or statistics), second-order 389
Cumulant (function or statistics), third-order 357 360
Cyclostationary process 327—328
Cyclostationary process, discrete-time (DTCS) 327 334
Cyclostationary process, spectral theory of 328
de Finetti’s theorem 288
Decimator 343
Detailed balance equation 531
Difference constraints 40 43
Direction finding (DF) 399 402
Direction of arrival (DOA) 400—401 403 405 413
Direction of arrival (DOA), estimation 411 421
Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) 334 363 364 400
Discrete random dynamics 284
Discrete robust mapping 482 484
Distributed parameter system 503 511
Distribution, binomial 69
Distribution, chi-square 187 198 207
Distribution, conditional 54 74 75 502 517
Distribution, Dirichlet 275 276 280—281 297
Distribution, Gibbs 526—527
Distribution, logarithmic series 290
Distribution, multinomial 275 277
Distribution, Poisson — Dirichlet 275 277 282 286 296—297
Distribution, Rician 440
Distribution, stationary 275 530
Distribution, Zipf’s 290
Dynamic programming 224
Eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) 188 191 195 203 207 410
Elevation angle 435
Emergent market, shares in 273
Emitter localization 399
Emitter waveforms 405
Energy function 527
Equalization 375 378
Equalizer 377
Equation error (EE) 126
Equation error (EE), criterion 127
Equation error (EE), formulation 368 369
Ergodic 7 483 490
ESPRIT algorithm 401 402 423
Estimation 434
Estimation of abruptly changing spectrum 66
Estimation of integrated polyspectrum 363
Estimation of MA models 132 137
| Estimation of smoothly changing spectrum 47
Estimation, function 439
Estimation, nonstationary trend 61
Estimation, order 179 182
Estimation, parameter 434
Estimation, state or state vector 41 74 75 85 435
Estimator inconsistency 400
Euler constant 63 296
Evolutionary spectrum 51
Ewens sampling formula 276 278 282—283 292
Exchange algorithm 526
Explorative expansion 501
Exponential quadratic error criterion 243
F-test 213 215
False alarm 187 492
False alarm, curve 494
False alarm, rate 457
Fault detection 112 453
Feature pattern 506 517
Feature pattern, detector 508
Feature points 502
Feature points, invariant subsets of 502
Feedback-free processes 12
Filter see also Kalman filter
Filter banks 343—344
Filter banks, alias-free 328 346—347
Filter banks, analysis 345
Filter banks, conjugate quadrature 351
Filter banks, optimization of 349
Filter banks, perfect reconstruction (PR) 349 351
Filter banks, synthesis 346
Filter divergence 438
Filter, analysis 343
Filter, Butterworth 168
Filter, Kautz 131 144
Filter, Laguerre 131
Filter, Monte Carlo 61 75
Filter, Poisson 133 138
Filter, prediction 443
Filter, state variable 140
Filter, synthesis 343
Filter, Wiener 20 412
Filtering 41 54 56 57
Filtering, minimax 243
Filtering, reduced-order 257 266—270
Final prediction error (FPE) 179
Finite impulse response (FIR) filter 351 443
Fisher information matrix 101 371 445
Fractal dimension 507
Fractal patterns 499 516
Frequency spectrum 283—285
Fuchs test 189
Fuchs test, multivariable 194
Fuzzy random vector (FRV) 299 303—305
Fuzzy random vector (FRV), expectation of 307
Fuzzy random vector (FRV), second moments of 310—313
Fuzzy random vector (FRV), set representation 305
Fuzzy random vector (FRV), statistical properties of 307
Fuzzy, perception 304
Fuzzy, random data (FRD) 299
Fuzzy, random matrix 306
Fuzzy, set 300—302 468
Fuzzy, vector or matrix 300—303
GA (genetic algorithm) 163 460
Gain and phase errors 407 421
Gaussian random process, complex 405
Gaussian sum approximation 37 55 61
General state space modeling 37
General state space modeling, applications of 59
Generation probability 527—528
Gibbs random field (GRF) 525—527 529 533 535 536
Gibbs random image model 526
Gibbs sampler 525 528
Girsanov’s transformation 220
Gladyshev’s formula 327—328 334
Goodness of fit 39
Gram — Schmidt method 165
Gray levels 526
Hamilton — Jacobi equation 223
Hamilton — Jacobi equation, numerical procedure 227—229
Hamiltonian 262
Hammersley and Clifford theorem 526
Hankel matrix 134—135 188
Hankel matrix, block 31 183
Hard bound 454
Hausdorff metric 304
Higher-order statistics 355 357
Hilbert space 9
Hilbert space of nonlinear functions 107
Hilbert space of the observed data 6
Hilbert space, relative 15
Homotopy 511
Homotopy, maximality of 512
Hypergeometric function, confluent 442
Hyperparameters 41 51
Identifiability 368
Identifiability, parameter 358
Identification 153 see
Identification of (system) impulse response 149
Identification of continuous-time systems 121
Identification of parametric model 123
Identification, automated and objective 87
Identification, robust 454
Identification, under feedback 103—107
Ill-conditioned problem 150
Imaging processes 501
Impulse response 377 392
Impulse response of ideal low-pass filter 330
Impulse response, continuous-time (CTIR) 152—153
Inhomogeneous discrete process 67
Innovation representation 13 182
Instantaneous spectrum 51—52
Interpolator 343
Intersymbol interference, multichannel 392
Invariant feature 499 507—508 515 519
Invariant feature, existence of 508
Invariant measure 507
Invariant measure, support of 507
Invariant probability 529
Invariant set 507
Ito’s formula 220
K-distribution 439—440
K-means methods 535
Kallianpur — Striebel formula 219
Kalman filter 41 245 247 257 260 433 438 see
Kalman filter, extended 75 436 440
Kalman filter, fading memory 448
Kalman filter, full-order 264
Kolmogorov — Gabor polynomial 465
Kronecker product 198 366 416
Kullback discrimination information (KDI) 98 453—454 456—457 460 469 471
Kullback — Leibler matching criterion 489
Kullback(— Leibler) information or number 38 98 101—103 482—483 492 see
Kullback(— Leibler) information or number, expected 101—102
Lagragian multiplier 262
Laplace operator 503
Large deviation probabilities 483
LDU-decomposition 196—197
Least-squares (LS) estimate or estimation 126 128 134
Least-squares (LS) method 86 152 442
Least-squares (LS) orthogonal 152 163—164
Least-squares (LS) problem, Bayesian interpretation of 50
Least-squares (LS) problem, constrained 50
Least-squares (LS) recursive (RLS) 86 126
Least-squares (LS) solution 367
Level set 300
Likelihood function 456 460
Likelihood functional 229
Linear matrix inequality (LMI) 3
Linear process 357—358
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 filter
filter  statistic
statistic