|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Easterling K.E. — Introduction to the physical metallurgy of welding |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
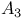 temperature 24 temperature 24
Alexander Kielland disaster 242—257
Aluminium 32 33 62
Aluminium alloy welds 177—179
Aluminium, copper 81
Arc efficiency 18—19
Arc welding 2 3 4 12 see
Austenite 96 97—98 101 103 104 106 109 116
Austenite, formers 108 119 164
Austenite, stabilizers 108 119
Bainite 93 106 107 108 109 110
Base metal 56 127
Basic electrodes 4 5 8
Basic electrodes in arc welding 12
Basic electrodes, effect on properties 121—122 123
Basic electrodes, hydrogen content 13 14
Basicity 5 6
Basicity in MMA welds 6
Basicity, effect on weld properties 8
Borides 140
Carbides 138 139 140
Carbides, coarsening 141
Carbides, dissolution 143—146 149—153 157 158
Carbides, effect on ferrite growth 108 109 110
Carbides, formation 107 138
Carbides, mixed 146
Carbides, niobium 109 110 139 157
Carbides, solubility 139
Carbides, stability 138—140
Carbon equivalent 132—135 262
Case study 152 153 236
Case study, Alexander Kielland disaster 242—257
Casting 56 69 84
Casting, continuous 56
Casting, ingot 56
CCT diagrams see "Continuous cooling diagrams"
Charpy V-notch testing 121 122 123 198 199
Chromium-molybdenum-vanadium steels, effect of preheat 237 242
Chromium-molybdenum-vanadium steels, reheating 236—239
cod see "Crack opening displacement"
Cold cracking 10 133 216—233 252
Cold cracking at grain boundaries 226 227 228 231
Cold cracking in implant test 223 224 226
Cold cracking, 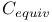 effect 132—135 262 effect 132—135 262
Cold cracking, cracking tests 223 261
Cold cracking, critical factors 216 219 229
Cold cracking, fisheyes 229 232
Cold cracking, incubation time of 216
Cold cracking, mechanism 229—233
Cold cracking, role of hydrogen 219—224
Cold cracking, role of microstructure 226—229
Cold cracking, role of stress 224—226
Cold cracking, types of 216 217 218
Constitutional supercooling 78 83
consumables 4—9
Continuous cooling diagrams 93 109 118—119 176
copper 32
Crack opening displacement 197 198 199
Cracking 191
Cracking in welds 191—242
Cracking, cold 191 216—233
Cracking, dovetail 200—201
Cracking, end 203
Cracking, hydrogen 216—224
Cracking, reheat 233—242
Cracking, solidification 200—207
Cracking, testing formulae 261
creep 233 236 239 242
Crystal growth 69—84
Crystal growth, direction of 63 65—66 80 82
Crystal growth, speed of 65 84
De Long diagram 101
Dendrite 82 83
Dendritic growth 85—87
Diffuse source solution, heat flow equation 27—30
Diffusion 90 100—101
Diffusion in grain growth 146 149
Diffusion in particle coarsening 138 141
Diffusion in steel weld metal 149 222
Diffusion in transformations 90
Diffusion of hydrogen in steel 220 221 230
Diffusion of hydrogen to grain boundaries 231
Diffusion, grain boundary 237 238 239
Diffusion, lattice 141 237 239
Diffusion, profiles at grain boundaries 103
Diffusionless transformations 95—97 see
Dilatometry 35
Dilution 15 56
Duplex stainless steel welds 97—103
Electrode 2 4—5 8
Electrode, basic 4—5 256
Electrode, coating types 4—5 9
Electrode, effect of size 180
Electrode, flux cored 4—5
Electrode, hydrogen content 9
Electrode, hydroscopic properties 5 8 9
Electrode, manipulation 15
Electrode, rutile 4—5
Electron beam welding 151
Electron beam welding, keyholing 85
Electroslag welding 3 4 33 151
Electroslag welding, refining of 87—89
End cracking 48 203
End cracking, avoidance 15 48
Epitaxial solidification 66—69
Equilibrium composition 160
Fatigue 249 250 257
FEM see "Finite element analysis"
Ferrite 98 103 109
Ferrite, acicular 93 107 112—115 119 169 171—172
Ferrite, allotriomorphs 105
Ferrite, formation at grain boundaries 90 91 94 104
Ferrite, formers 108
Ferrite, massive 107
Ferrite, nucleation at inclusions 91 111—118
Ferrite, proeutectoid 93 106 119 122 167
Ferrite, stabilizers 122
Ferrite, Widmanstaetten 105 107 112 119
Finite element analysis 32 48—52
Fisheye fracture 229 232
Flux 2 4 8 14 55
Flux for submerged arc welding 5
Flux, basic 4
Flux, basicity 4
Flux, coating 4 55
Flux, composition 5 55
Flux, hydrogen content 5 8
Flux, hydroscopic properties 5 8 9
Flux, rutile 5
Flux, viscosity 7
Fracture 191—200
Fracture energy release rate 196
Fracture, fisheye 229 232
Fracture, toughness 191—200
Fracture, toughness testing 196—200
Fusion line 80 84 164—167 207
Fusion line, liquation cracking at 165 166 207
Fusion line, melting at 165 166 207
Fusion line, reactions at 164—167 207
Fusion welding 2—18
Fusion welding, solidification theory 49—69
Gas reactions 10—14
Gas reactions, absorption in welds 10
Gas reactions, carburizing 7
Gas reactions, decarburizing 9
Gas reactions, hydrogen absorption 12—14
Gas reactions, hydrogen distribution in weld 12—14 219—224
Gas reactions, nitrogen 10—12
Gas-metal arc welding see "Arc welding"
Gases 10—14
| Gases in welds 10 see
Gases, hydrogen 12 see
Gases, nitrogen 10—12 see
GMA welding see "Arc welding" "Gas-metal
Grain boundary 90 91 94 113 116
Grain boundary, diffusion 102 237 238 239
Grain boundary, energy 90
Grain boundary, enrichment of 102 103 104 231 238
Grain boundary, fracture 192 226 227 231 234 235 239 240
Grain boundary, ledges 240
Grain boundary, nucleation at 90 91 94 117
Grain boundary, sink 231
Grain boundary, sliding 233 241
Grain growth 126 146—155
Grain growth diagrams 151 152 154 157 158 181 237 255
Grain growth, control of 87—88 157 160 164 183 185
Grain growth, diagrams 151 152 154 157 158 181 237 256
Grain growth, during welding 102 103 126 183 185
Grain growth, effect of particle coarsening 153—155
Grain growth, effect of particle pinning 147 148 149 164
Grain growth, kinetics 146 159
Grain growth, zone 126 159
Grain refined zone 126 167—169
Hardness 174—175 253
Hardness changes, aluminium alloy welds 177—179
Hardness contour diagram 177
HAZ see "Heat-affected zone"
Heat flow 18—34
Heat flow in solidification 56 see
Heat flow, three-dimensional 20
Heat flow, two-dimensional 20
Heat input 18—19
Heat-affected zone 126—188
Heat-affected zone in multi-run welds 183
Heat-affected zone, hardnesses in 179
Heat-affected zone, microstructure 126 156 167 168 169—172 176 180 181
Heat-affected zone, properties 169
Heat-affected zone, Rosenthal equation limitations 27 29
Heat-affected zone, sub-zones 126 156 167 168
Heat-affected zone, thermal cycles 184
Heat-affected zone, toughness 172 186
Heat-flow equations 18—34
Heat-flow equations for electroslag welding 32
Heat-flow equations, general heat flow 18
Heat-flow equations, refinements 27—34
Heat-flow equations, simplified equations 24—27
Heat-flow equations, thick and thin plate cases 20 24—27
Hole drilling technique 44—45 48
Hot cracking see "Solidification cracking"
Hydrogen 219—224
Hydrogen cracking see "Cold cracking"
Hydrogen, absorption in welds 8 12—14
Hydrogen, apparent diffusivity of 222
Hydrogen, cracking 133 222 227 228
Hydrogen, cracking tests 223 261
Hydrogen, diffusion characteristics 220 221
Hydrogen, diffusion coefficients 220
Hydrogen, diffusivity in iron 220
Hydrogen, distribution ahead of crack tip 225 230
Hydrogen, effect of  transformation on solubility 12 transformation on solubility 12
Hydrogen, effect of charging 219 224
Hydrogen, effect of fracture of steel 224
Hydrogen, effect on lattice strength 230 231
Hydrogen, embrittlement in lamellar tearing 216
Hydrogen, grain boundary sinks of 226 227 231
Hydrogen, in fisheye fracture 232
Hydrogen, levels in weld deposit 8 14
Hydrogen, measured levels in weld 9 13—14
Hydrogen, reaction 12
Hydrogen, reaction with cementite 227
Hydrogen, role in cold cracking 216—233
Hydrogen, role of stress 224—226
Hydrogen, sinks 216 231
Hydrogen, solubility in binary alloys 13—14
Hydrogen, solubility in iron 13—14
Hydrogen, sources of 13—14
IIW see "International Institute of Welding"
Implant tests 223 224 226
Inclusions 111
Inclusions, cavitation at 209 211 213 214
Inclusions, cold cracking at 229 231
Inclusions, composition in duplex stainless steel 100
Inclusions, effect of basicity 8 121
Inclusions, ferrite forming at 112
Inclusions, fisheye nucleation at 232
Inclusions, nucleation at 113
Inclusions, reheat cracking at 242
Inclusions, site of ferrite nucleation 91 111 116 119
Inclusions, thermal contraction at 117
Interfacial energy 67 89 96 207
International Institute of Welding 133
Iron, carbon phase diagram 75 97
Iron, cementite phase diagram 104
Iron, chromium-nickel alloys 98
Iron, sulphur phase diagram 76 see
J integral stress-strain condition 195—196
Keyholing, electron beam welds 85
Lamellar tearing 209—216 257
Lamellar tearing in Alexander Kielland weld 250 251 252 256
Lamellar tearing, fracture characteristics 212 213 214
Lamellar tearing, main features 213
Lamellar tearing, mechanism 212—216
Lamellar tearing, microstructure 210
Lamellar tearing, susceptibility to 257
Lamellar tearing, testing for 215 261
Laser beams, heat flow equations 27—30
Lehigh test 223
Liquation cracking 165 166 207—209
Liquation cracking, effect of alloying on 166
Manganese sulphides 165 209 212
Manual Metal Arc welding 2 3
Manual metal arc welding in Alexander Kielland construction 248 254 256
Manual metal arc welding, aluminium alloy 178
Manual metal arc welding, effect of slag basicity in 6—7
Manual metal arc welding, example of multi-run 17
Manual metal arc welding, hydrogen content 13—14
Marangoni convection 57
Martensite 95—97 106 107 257
Martensite, morphology 95
Melting point 22
Metal-inert gas welding 2 3
Metal-inert gas welding of stainless steel 67
Metal-inert gas welding, aluminium alloy 179
Metal-inert gas welding, arc efficiency 18—19
Metal-inert gas welding, hydrogen content 13—14
Microanalysis measurements 163
Microstructure diagram 180 181
MIG welding see "Metal-inert gas welding"
MMA see "Manual metal arc welding"
Monel 22 83
Multi-run welds 183—187
Multi-run welds, effect of electrode size 186
Multi-run welds, effect on toughness 186
Multi-run welds, HAZs 185—187
Multi-run welds, influence on transition temperature 186
Multi-run welds, microstructure 17 184 185
Multi-run welds, reheating effects 184
Multi-run welds, thermal cycle of 187
Niobium 109
Niobium, carbide 109 110 139 157 158 237
Niobium, effect of 109 111
Niobium, role in weld metal 109 110
Niobium, steel 25 110 129 131 156 157 158
Nitrides 138 139 140 145
Nitrides, aluminium 139
Nitrides, mixed 160
Nitrides, titanium 139
Nitrides, vanadium 139
Nitrogen 10—12
Nitrogen, solubility in binary alloys 10—12
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



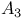 temperature
temperature 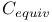 effect
effect  transformation on solubility
transformation on solubility